Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: RA – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose:
Rituximab targets CD20-positive B cells and is used to treat rheumatoid arthritis (RA). B cell depletion may result in hypogammaglobulinemia. Hypogammaglobulinemia is a risk factor for infections. We sought to evaluate the safety of long-term exposure to Rituximab in patients with RA.
Methods: Serum levels of IgG (g/l) and clinical information were evaluated retrospectively from the database of adult patients with RA receiving Rituximab at King’s College Hospital NHS Trust, London for the time period between May 2013 to April 2023 and were analysed over time and number of Rituximab infusions. Data were analysed using Cox regression analysis and Kaplan-Meier survival curves.
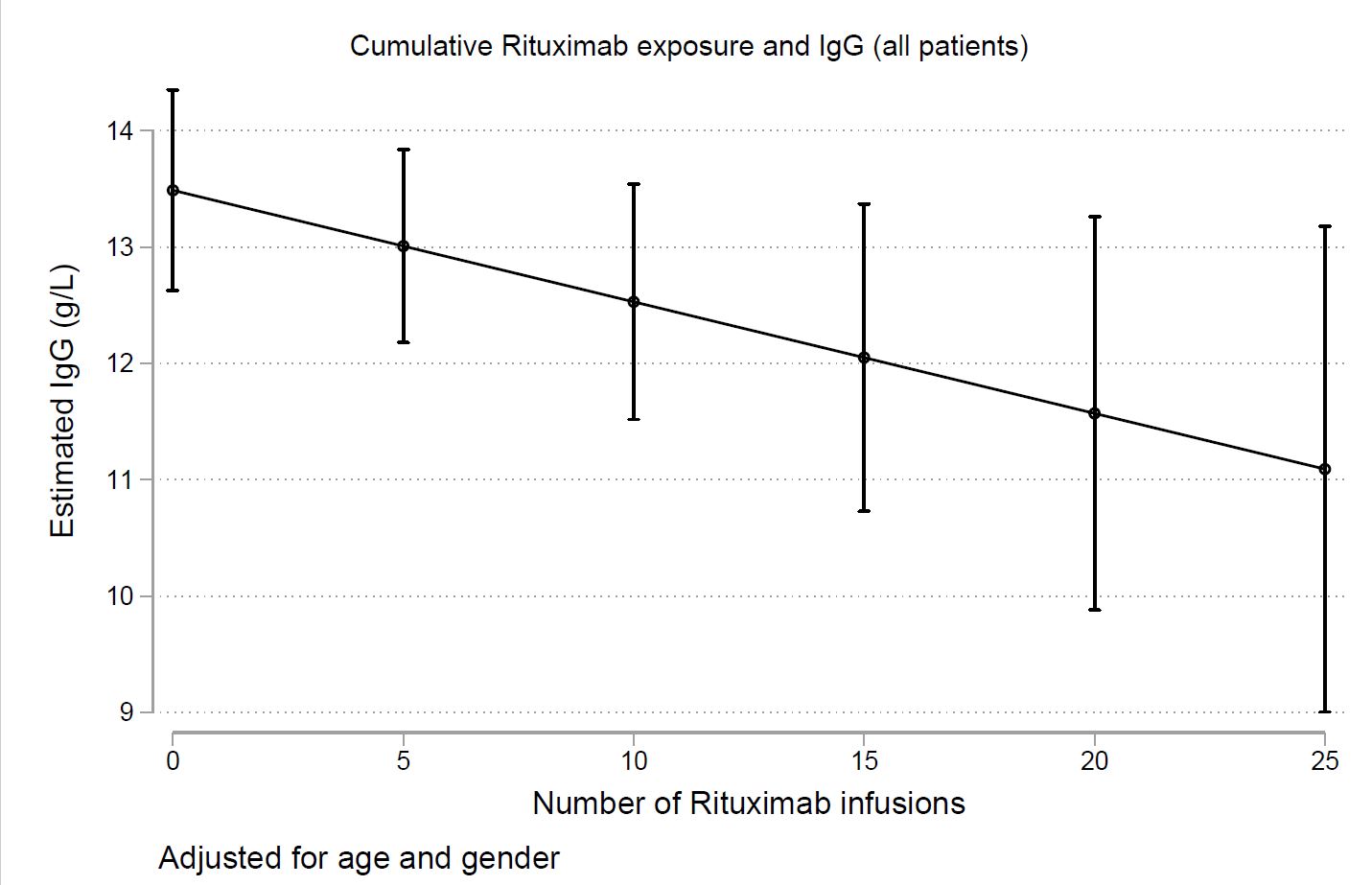
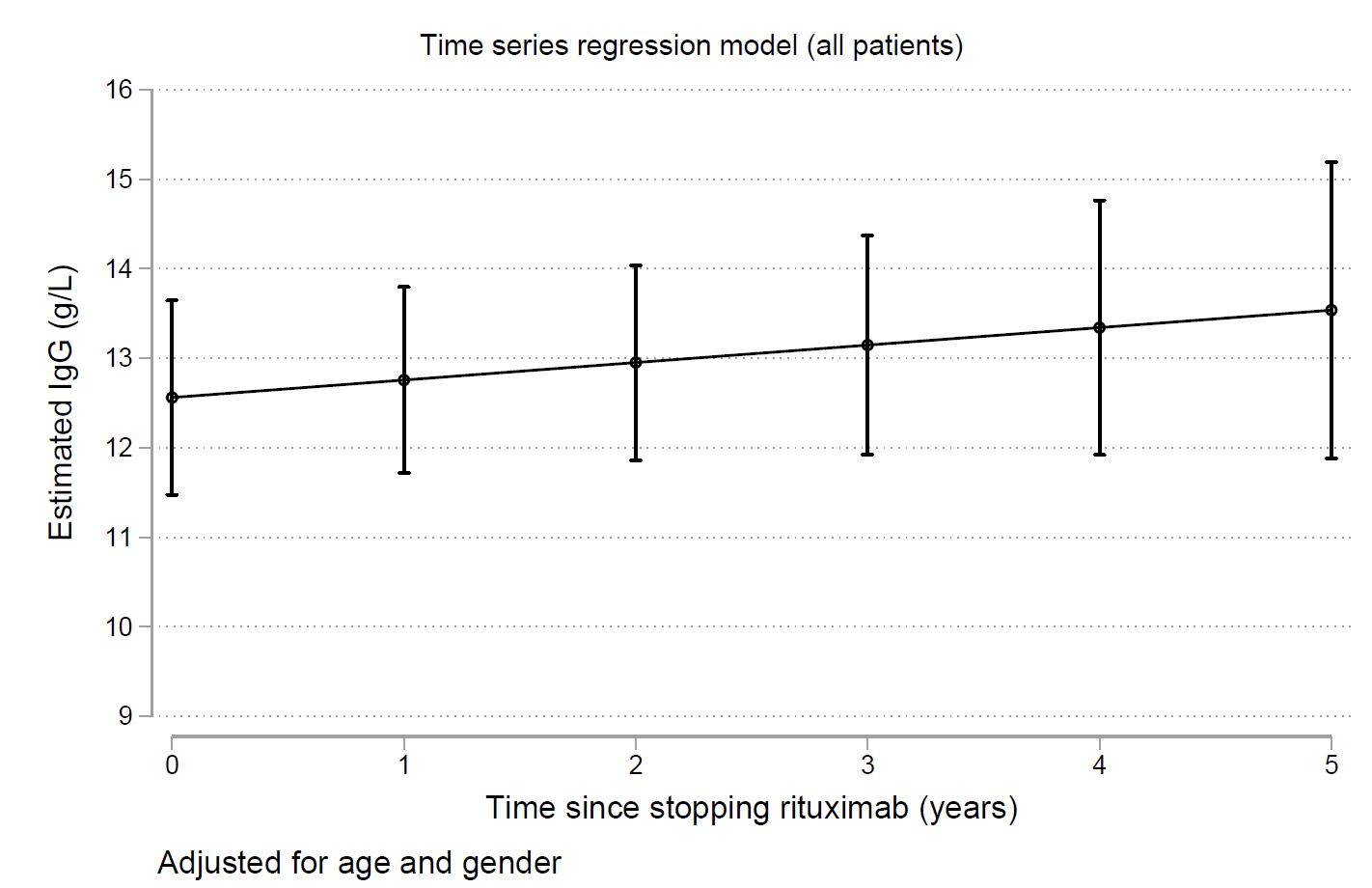
Results: Data from 164 patients with RA registered in the database were extracted. The disease duration as mean (Standard Deviation, SD) was 13.2 (11.7) years, mean age 59 years (range: 20-90 years) and the baseline serum IgG levels [mean (SD)] were 14 (5) g/l. For up to 6 years of observation or 25 Rituximab infusions, the mean serum levels of IgG for all patients decreased over time but this was not significant with increasing Rituximab dose (p=0.09) and remained within the normal reference range. By discontinuing Rituximab, a trend towards gradual non-significant (p=0.5) increase of serum IgG levels was observed for up till 5 years. The risk for infection-related hospitalisation increased during the 1st year of Rituximab administration [20 admissions out of a total of 44 recorded; mean admission rate: 14 admissions/100 patient years (PY), 95% C.I.: 9-22/100PY] and was higher in patients receiving simultaneously prednisolone [Hazard Ratio, HR 2.1 (95% CI 1.3 to 3.4), p=0.002].
Conclusion: Cumulative exposure to Rituximab seems to influence the levels of serum IgG. Nevertheless, the risk for infection-related hospital admissions peaks during the first year of administration and is higher with concurrent prednisolone.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Karafotias I, Adas M, Bechman K, Williamson N, Hughes M, Mehta D, Roy R, Norton S, Galloway J. Effects of Cumulative Rituximab Exposure in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results from Cohort at a Tertiary Academic Health Care Setting [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-cumulative-rituximab-exposure-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-results-from-cohort-at-a-tertiary-academic-health-care-setting/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-cumulative-rituximab-exposure-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-results-from-cohort-at-a-tertiary-academic-health-care-setting/