Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (0955–0977) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Basic Science Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: S100 proteins are involved in the inflammatory responses of autoimmune diseases. We previously showed that S100 proteins regulate macrophage function via CD68. Based on this, we developed a novel human hybrid protein, human MIKO-1 (hMIKO-1), derived from the primary structure of human S100. This study aimed to investigate its effects on macrophage polarization and its therapeutic potential in a systemic sclerosis (SSc) mouse model with interstitial lung disease (ILD).
Methods: Murine macrophages were co-cultured with hMIKO-1 to evaluate its effect on macrophage polarization. In vivo, female C57BL/6 mice were injected subcutaneously with bleomycin (200 μg/mouse, every other day) to induce skin and lung lesions resembling SSc-associated ILD (SSc-ILD). Mice were divided into three groups: sham control, disease control (BLM + vehicle), and treatment (BLM + hMIKO-1). After four weeks, skin and lung tissues were collected and assessed histologically.
Results: hMIKO-1 significantly inhibited M2 polarization of murine macrophages in vitro. In vivo, lung fibrosis scores were significantly lower in the hMIKO-1-treated group compared to the disease control group, while no significant difference was found in skin fibrosis. F4/80-positive macrophages in both skin and lung tissues were significantly reduced in the hMIKO-1 group. Notably, hMIKO-1 accumulation differed between lungs and skin.
Conclusion: hMIKO-1 attenuated inflammation and fibrosis in the lungs of SSc-ILD model mice. Its limited effect in the skin may be due to differences in tissue accumulation. hMIKO-1 may serve as a potential targeted therapy for SSc-associated ILD.
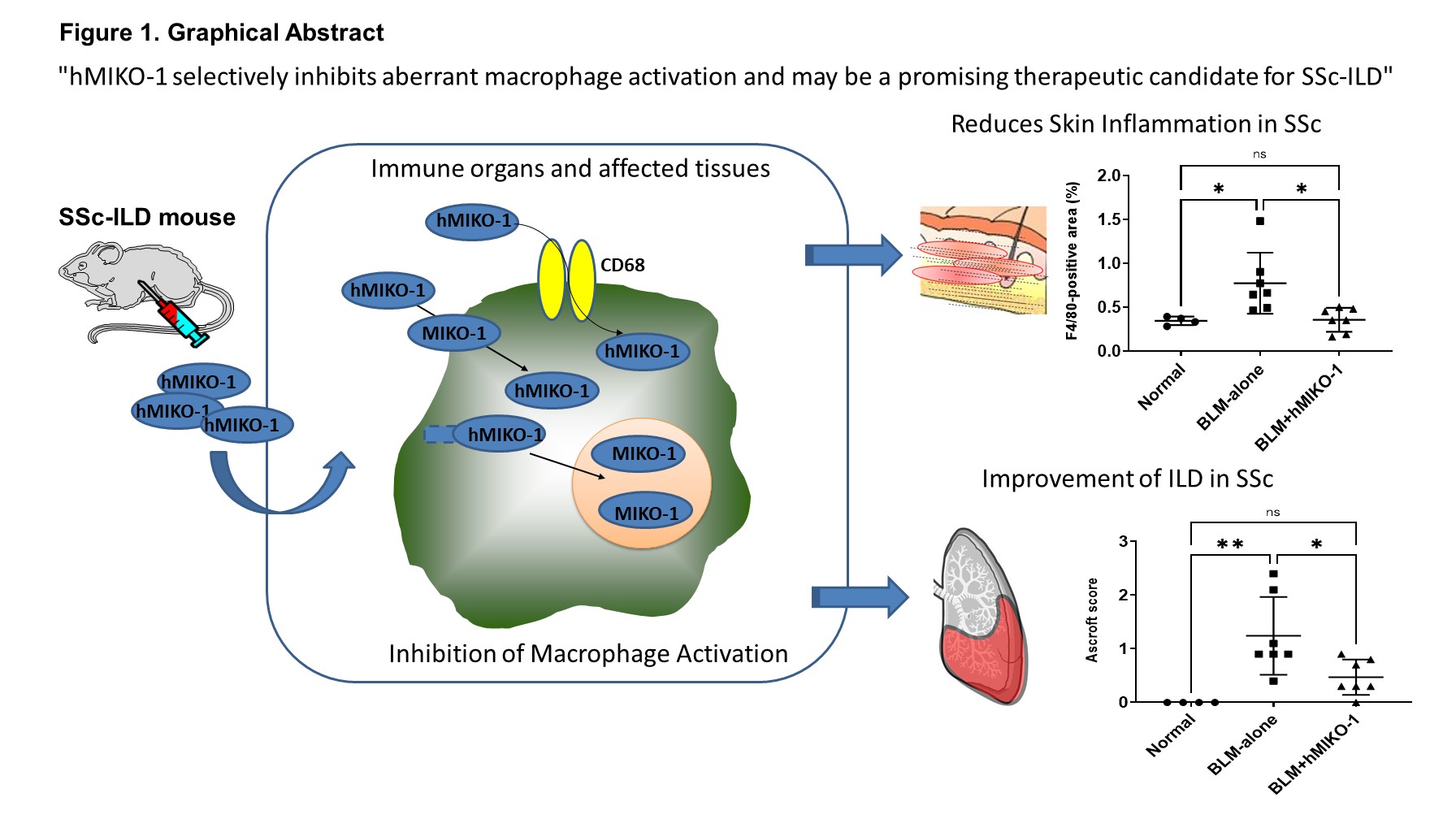 Figure 1. Graphical Abstract: Mechanism of Action and Therapeutic Effects of hMIKO-1
Figure 1. Graphical Abstract: Mechanism of Action and Therapeutic Effects of hMIKO-1
hMIKO-1 enters the macrophage cytoplasm via CD68-mediated uptake and endocytosis, forming complexes with β-actin and NF-κB. It subsequently binds to nuclear transport proteins and translocates into the nucleus. In THP-1 cells, hMIKO-1 significantly suppresses the mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and TGF-β. In systemic sclerosis (SSc) mouse models, hMIKO-1 reduces skin inflammation and improves interstitial lung disease (ILD). These findings suggest that hMIKO-1 selectively inhibits aberrant macrophage activation and may represent a promising therapeutic candidate for SSc-ILD.
.jpg) Figure 2. Inhibitory Effect of hMIKO-1 on M2 Polarization of Murine Macrophages
Figure 2. Inhibitory Effect of hMIKO-1 on M2 Polarization of Murine Macrophages
(A) hMIKO-1 was designed based on the amino acid sequences of S100A8 and S100A9.
(B–D) Co-culture with hMIKO-1 was conducted using murine peritoneal macrophages polarized toward the M2 phenotype.
(B) Flow cytometry showed a significant reduction in the CD163/CD64 ratio compared to control, indicating suppression of M2 polarization.
(C) The IL-10/IL-12 ratio in the culture supernatant also decreased significantly.
(D) qPCR confirmed reduced CD163/CD64 expression, supporting the inhibitory effect of hMIKO-1.
Ctrl: without hMIKO-1. Data are mean ± SD (n = 6). **p < 0.01; NS: not significant.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kotani T, Suzuka T, Matsuda S, Takeuchi T. Effects of a Novel Hybrid Protein Based on S100 on Macrophage Polarization and Its Therapeutic Efficacy in a Bleomycin-Induced Systemic Sclerosis Mouse Model. [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-a-novel-hybrid-protein-based-on-s100-on-macrophage-polarization-and-its-therapeutic-efficacy-in-a-bleomycin-induced-systemic-sclerosis-mouse-model/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-a-novel-hybrid-protein-based-on-s100-on-macrophage-polarization-and-its-therapeutic-efficacy-in-a-bleomycin-induced-systemic-sclerosis-mouse-model/
