Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Title: Osteoarthritis – Clinical Aspects I: Pain and Functional Outcomes
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Inflammation is a key contributor to osteoarthritis (OA).1 OA pain is mediated by interactions between inflammatory cytokines and other features including local tissue damage, synovitis and cellular response mechanisms.1 Synovitis is integral to OA, and is associated with symptom severity, joint dysfunction and cartilage loss.2 FX006, an extended-release formulation of triamcinolone acetonide (TA) for intra-articular (IA) injection, provided statistically and clinically significant, sustained improvements in pain/stiffness/function of knee OA vs placebo in clinical trials.3 We compared FX006 efficacy in patients with and without baseline inflammation determined by clinical assessment.
Methods: A pooled subgroup analysis of 3 double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trials (NCT01487161/NCT02116972/NCT02357459) was conducted. Patients with Kellgren-Lawrence grade 2/3 knee OA and Average Daily Pain (ADP)-intensity score ≥5–≤9 (0–10 Numerical Rating Scale) received a single IA injection of FX006 40 mg or saline-placebo. Investigators assessed index knees for clinical indicators of inflammation (effusion, Baker’s cyst, tenderness, swelling, and/or redness/heat). ADP-intensity was assessed daily for 24 weeks. Western Ontario and McMaster University Arthritis Index for OA (WOMAC; 0–4 Likert scale) pain (A), stiffness (B), and physical function (C) were assessed at baseline and Weeks 4/8/12.
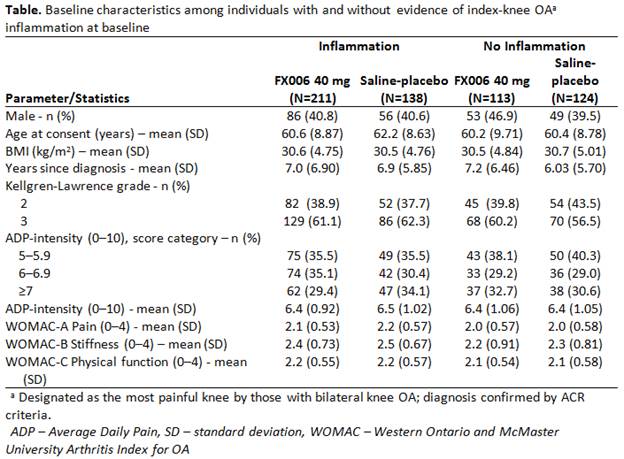
Results: 349/586 patients (60%) had baseline clinical inflammation (Table). Changes from baseline in weekly mean ADP-intensity and WOMAC-A, B, C consistently favored FX006 vs saline-placebo (Figure). FX006 effect was enhanced, generally >2-fold, in patients with vs without baseline clinical inflammation: least squares mean differences for ADP and WOMAC-A, B, C, respectively, was –1.84 vs –0.74, –0.71 vs –0.27, -0.82 vs -0.41, and -0.69 vs -0.26 at Week 8, and –1.35 vs –0.37, –0.44 vs –0.16, -0.50 vs -0.27, and -0.44 vs -0.16 at Week 12.
Conclusion: FX006 provided sustained clinical improvement in knee OA vs saline-placebo irrespective of baseline clinical inflammation. Enhanced FX006 effect in patients with baseline clinical inflammation is consistent with the role of inflammation in OA pathogenesis and known anti-inflammatory action of TA. A drawback of this study is the lack of standardized measures of inflammation. Longer-term evaluations with objective inflammation measures (e.g., ultrasound, biomarkers) are needed.
1Robinson WH, et al. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12:580-92.
2Sellam J. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010;6(11):625-35.
3Conaghan P, et al. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2017;25:S432-S433.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Baraf HSB, Lattermann C, Jones DG, Conaghan PG, Lufkin J, Johnson J, Kelley S, Bodick N. Effectiveness of FX006 Intra-Articular Injection in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis Who Present with and without Clinical Inflammation at Baseline: A Pooled Analysis of Data from 3 Double-Blind, Randomized, Parallel-Group Clinical Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effectiveness-of-fx006-intra-articular-injection-in-patients-with-knee-osteoarthritis-who-present-with-and-without-clinical-inflammation-at-baseline-a-pooled-analysis-of-data-from-3-double-blind-ran/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effectiveness-of-fx006-intra-articular-injection-in-patients-with-knee-osteoarthritis-who-present-with-and-without-clinical-inflammation-at-baseline-a-pooled-analysis-of-data-from-3-double-blind-ran/