Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: Abstracts: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment III: AxSpA
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-5:30PM
Background/Purpose: The effect of Ixekizumab (IXE) on structural lesions in the sacroiliac joints (SIJ) of patients (pts) with radiographic Axial Spondylarthritis (r-axSpA) assessed by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has not been analyzed. This analysis evaluated the effect of IXE versus placebo and active control, adalimumab (ADA), on structural lesions in SIJ assessed by MRI at week 16 in bio-naïve pts with r-axSpA.
Methods: COAST V (NCT02696785) is a phase 3, multicenter, randomized, double blind, placebo and active controlled study in bio-naïve adult pts (≥18 years) with active r-axSpA (1). Pts were randomly assigned 1:1:1:1 to placebo (PBO), 80 mg subcutaneous IXE, every 2 weeks (IXE Q2W) or 4 weeks (IXE Q4W), or 40 mg ADA Q2W (active reference group). Post-hoc analyses of pts with MRI available at baseline (BL) and week 16 for PBO, IXE Q2W, IXE Q4W and ADA groups are reported. Changes in MRI structural lesions were scored using the Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada (SPARCC) sacroiliac joint structural scores (SSS) for erosion, backfill, fat lesion and ankylosis. For each of the 4 lesion types, analysis of covariance was utilized for treatment comparisons in observed cases after adjusting for BL values, BL SPARCC bone marrow edema (BME), and stratification factors (treatment, geographic region, BL CRP) and for backfill the analysis was also adjusted for BL erosion. Sensitivity analyses included adjustment of different factors and subsets of pts with less severe ankylosis scores. Subgroup analyses were conducted for changes in structural lesions by sex, HLA-B27 status, and SPARCC BME BL cutoffs ≥4, < 4.
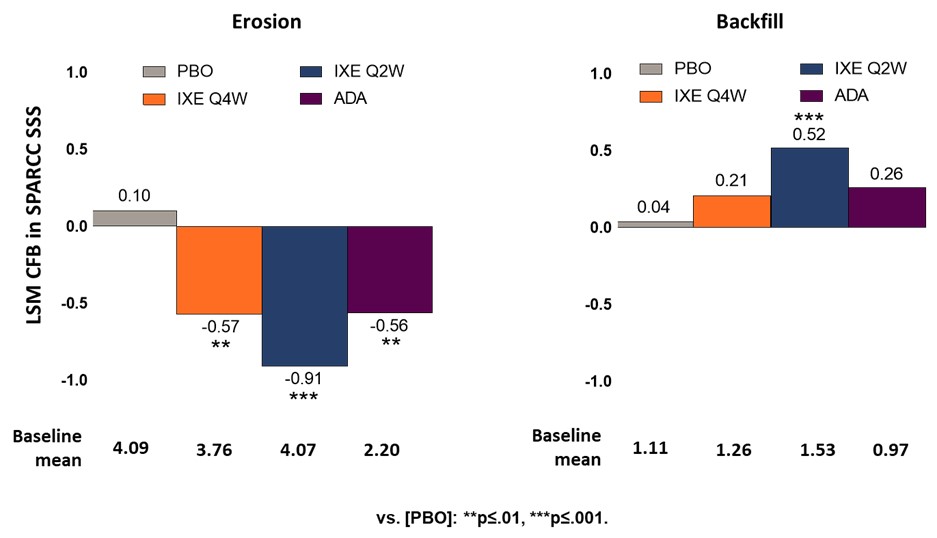
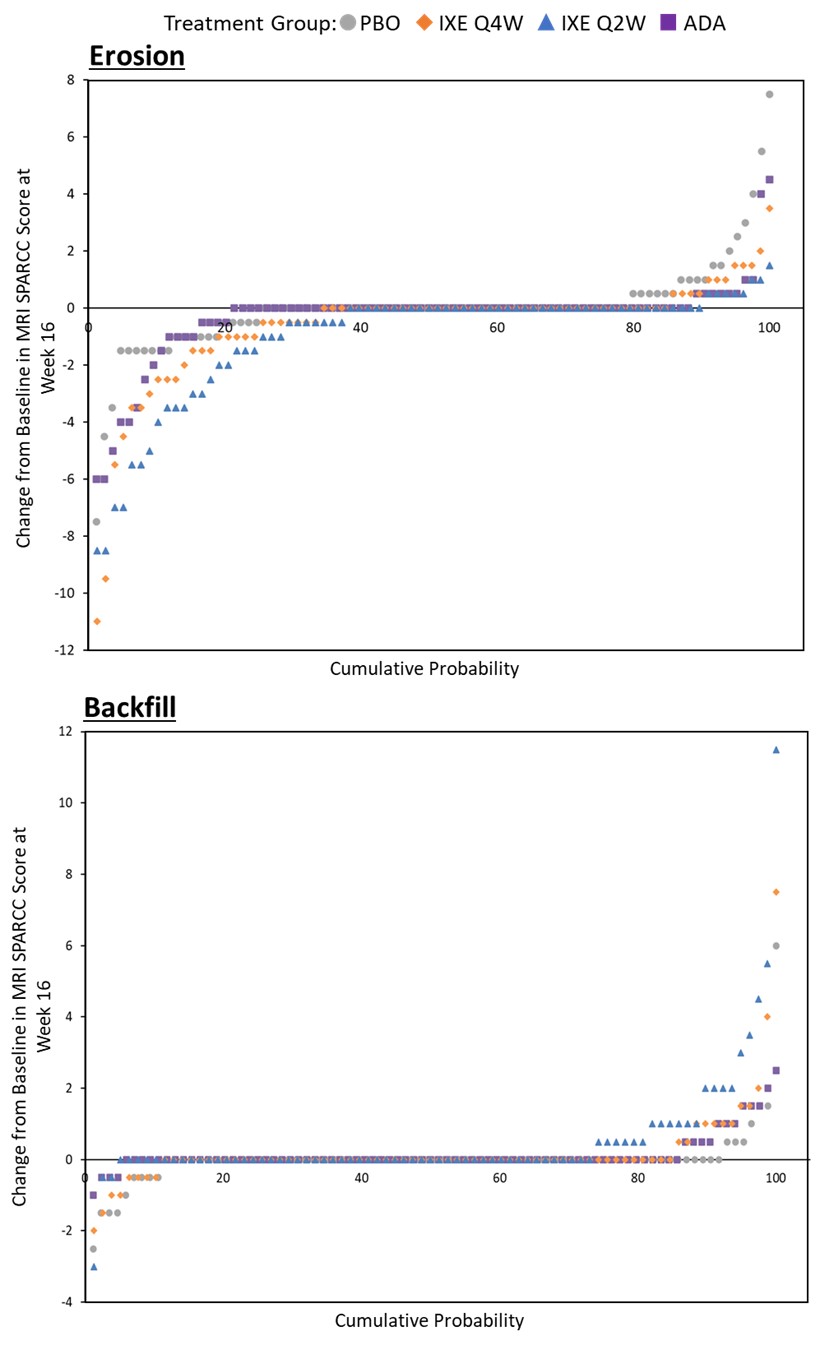
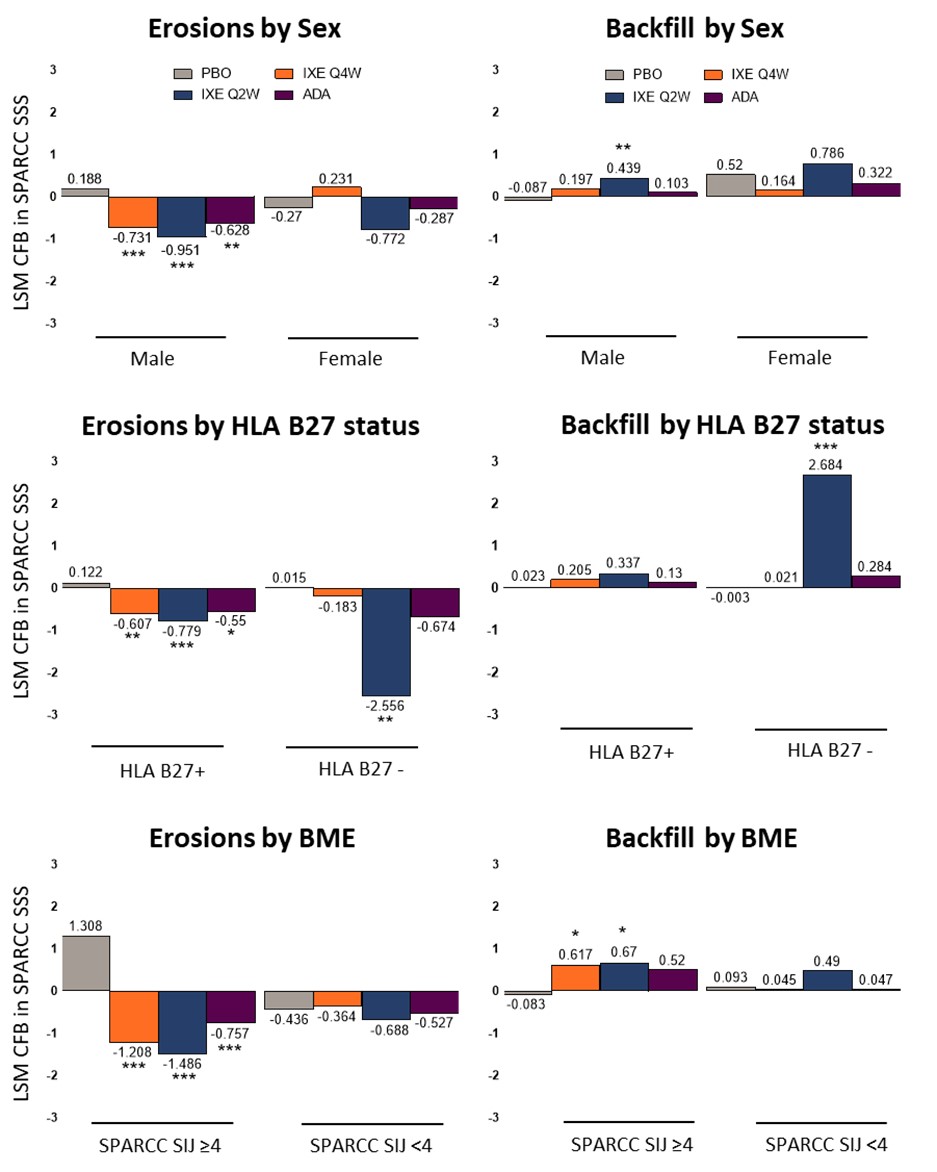
Results: Of the 341 pts in the COAST V study, MRI scans were available for 325 pts at BL and week 16. At BL, the mean (std) scores for SPARCC SSS erosions for PBO, IXE Q4W, IXE Q2W and ADA were comparable. A significant decrease in SPARCC SSS erosion score, LSM (SEM), was observed in both IXE doses with the greatest decrease in IXE Q2W -0.91 (0.19). An increase in SPARCC SSS backfill score, LSM (SEM), was evident in both IXE doses, but a significant mean change was observed only in IXE Q2W 0.52 (0.12) (Figure 1). Cumulative probability of change from BL to week 16 in SPARCC SSS and sensitivity analyses confirmed the findings (Figure 2). SPARCC SSS erosions score, LSM (SEM), were significantly decreased in males for IXE Q4W -0.731 (0.199) and IXE Q2W -0.951 (0.207), in HLA B27 positive pts for IXE Q4W -0.607 (0.189) and IXE Q2W -0.779 (0.189), in HLA B27 negative pts for IXE Q2W -2.556 (0.656), and in pts with SPARCC SIJ BME ≥4 for IXE Q4W -1.208 (0.359) and IXE Q2W -1.486 (0.344) (Figure 3). SPARCC SSS backfill score, LSM (SEM), was significantly increased in males for IXE Q2W 0.439 (0.141), in HLA B27 negative pts for IXE Q2W 2.684 (0.434), and in pts with SPARCC SIJ BME ≥4 for IXE Q4W 0.617 (0.249) and IXE Q2W 0.67 (0.239).
Conclusion: In pts with bio-naïve r-axSpA, IXE treatment for 16 weeks decreased erosion scores and increased backfill scores, particularly in the IXE Q2W group, consistent with rapid tissue repair. Cumulative probability of change from BL to week 16 in SPARCC SSS and sensitivity analyses confirmed this. This documents that IXE may have an impact in structural damage progression and healing in pts with r-axSpA.
1. van der Heijde D et al. Lancet, 2018.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Maksymowych W, Lambert R, Krishnan E, Zhu B, Bolce R, Østergaard M. Effect of Ixekizumab Treatment on MRI Structural Lesions in the Sacroiliac Joints of Patients with Radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis; A Post-hoc Analysis of a Placebo and Active Controlled RCT [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-ixekizumab-treatment-on-mri-structural-lesions-in-the-sacroiliac-joints-of-patients-with-radiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-a-placebo-and-active-controlled-rct/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-ixekizumab-treatment-on-mri-structural-lesions-in-the-sacroiliac-joints-of-patients-with-radiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-a-placebo-and-active-controlled-rct/