Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Early diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is essential to establish treatment to improve long-term disease outcomes. Musculoskeletal ultrasound (US) is able to detect subclinical synovitis and erosions earlier than simple radiological study. In recent years, several reduced joint US assessment models have been developed to allow global evaluation of synovitis and joint erosions. The main objective is to evaluate the diagnostic ability of a reduced joint US assessment model in patients with clinically suspected RA.
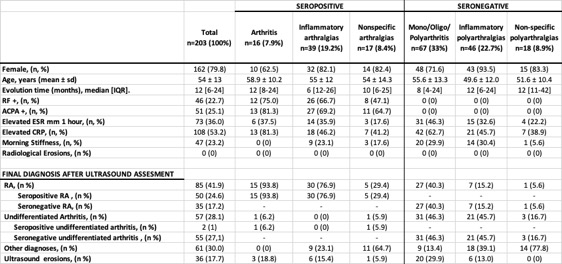
Methods: Descriptive cross-sectional study including 203 consecutive patients referred to a US care unit for suspected RA, yet not meeting the EULAR/ACR 2010 RA Classification Criteria. Patients were classified into six groups: a) Seropositive (SP) (RF and/or ACPA positive) mono-oligoarthritis, b) SP inflammatory arthralgias c) Nonspecific SP arthralgias, d) Seronegative (SN) (RF and ACPA negative) arthralgias, e) SN Inflammatory Arthralgia, f) SN nonspecific arthralgias. Each patient underwent a reduced standardized US count to evaluate synovitis in 20 joints (bilateral wrists, 1st-5th metacarpophalangeal (MCPs), and 2nd-5th metatarsophalangeal (MTPs)) and a simplified US count of erosions in 10 joints (bilateral wrists, 2nd and 5th MCPs, 2nd hands proximal interphalangeal (PIP), and 5th MTP). B-mode synovial hypertrophy (SH) and synovial Power Doppler (PD) signal were scored from 0-3 at each joint of the hands, while only the synovial PD signal was scored in metatarsophalangeal joints. Scores ≥ 1 in both B-mode or PD were considered synovitis. The definitive diagnosis was based on the number of inflamed joints detected by physical examination and new joints where synovitis was identified on US.
Results: The study included 203 patients, with 80% women and an average age of 54 ± 13 years. Demographic, clinical features, and laboratory tests are summarized in Table 1. RA was diagnosed in 85 patients (42%). The subgroups with the highest RA diagnosis rates were SP arthritis (93.8%), SP inflammatory arthralgias (76.9%), SN arthritis (40.3%), and SP nonspecific arthralgias (29.4%). Only 15.2% and 5.6% of patients were diagnosed with RA in the SN inflammatory arthralgias and SN nonspecific arthralgias groups, respectively.Undifferentiated arthritis was diagnosed in 57 patients (28.1%), primarily from SN groups: SN arthritis (n=31) and SN inflammatory arthralgias (n=21). Other diagnoses included nonspecific arthralgias and osteoarthritis. No patients had erosions on simple radiological study, but US detected erosions in 36 patients (18%), aiding early diagnosis and indicating a poor long-term functional prognosis. In the SP arthritis group (mainly 1 or 2 joint arthritis), 94% were finally diagnosed with RA, with only one remaining undifferentiated. In contrast, the SN arthritis group (1-9 joints) saw only 40% RA diagnosis, with 46% remaining undifferentiated, highlighting the difficulty in diagnosing RA in SN patients.
Conclusion: Reduced US joint assessment effectively aids in early RA diagnosis and treatment, improving prognosis. The efficacy depends on the clinical scenario prior to the US study.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Corrales Selaya C, Secada Gómez C, Fernandez-Aguado S, Morante-bolado I, Santos-gomez M, Alonso-Castro S, Portilla-González V, Blanco-Alonso R, Rueda Gotor J, Corrales-Martínez a. Early Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Role of Joint Ultrasound Assessment [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/early-diagnosis-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-role-of-joint-ultrasound-assessment/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/early-diagnosis-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-role-of-joint-ultrasound-assessment/