Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is the most prevalent autoimmune disease, where various immune cells are associated such as monocytes, natural killer (NK) cells, B cells, and T cells. Additionally, soluble mediators aid in the interaction between immune and non-immune cells. Cytokines are soluble mediators that play a crucial role in the inflammatory processes that could lead to joint destruction associated with RA, while chemokines play a major role in the migration of various cell types into inflammatory sites in RA (Brennan and McInnes 2008, Szekanecz, Vegvari, et al. 2010, Elemam, Hannawi, et al. 2020). In this study, we aimed at exploring chemokines and cytokines that could possibly be used to aid in evaluating the differences between healthy controls and RA patients.
Methods: Publicly available transcriptome dataset (GSE64708) of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of RA patients and healthy controls were analyzed using the GEO2R tool. Then, the cytokines and chemokines were selected from the top 250 significant genes. Whole blood samples were collected from the recruited 17 RA patients (satisfying the 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria for RA) and 16 healthy controls (with no diagnosis of autoimmune diseases). Then, blood was separated to obtain PBMCs using the Ficoll density gradient method. RNA was extracted and gene expression was assessed using qRT-PCR. Statistical analysis was done using the unpaired t-test or Mann-Whitney test, after the assessment of data distribution. P-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results: In silico analysis showed that several chemokines, cytokines, and innate receptors such as toll-like receptors were differentially expressed between RA patients and healthy controls. Hence, some of these cytokine and chemokine ligands and receptors were validated and assessed in PBMCs of RA patients and healthy controls. Regarding the chemokines, CCR4, CCL2, CKLF, and CXCL10 were found to be upregulated in RA patients (Figure 1). Similarly, the proinflammatory chemokine IL-1β, IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL1RN) as well as the cytokine receptor component IL12RB2 exhibited an upregulation in the PBMCs of RA patients while the T helper 1 cytokine IFN-γ did not display any differential expression in PBMCs of RA patients. Furthermore, the innate toll-like receptors TLR3 and TLR10 were upregulated in PBMCs of RA patients.
Conclusion: In conclusion, certain chemokines and cytokines seem to play a major role in the pathogenesis of RA disease. Gene expression of these molecules; CCR4, CCL2, CKLF, CXCL10, IL-1β, IL-1RN, IL12RB2, TLR3, and TLR10 in PBMCs could be used as promising biomarkers for RA disease.
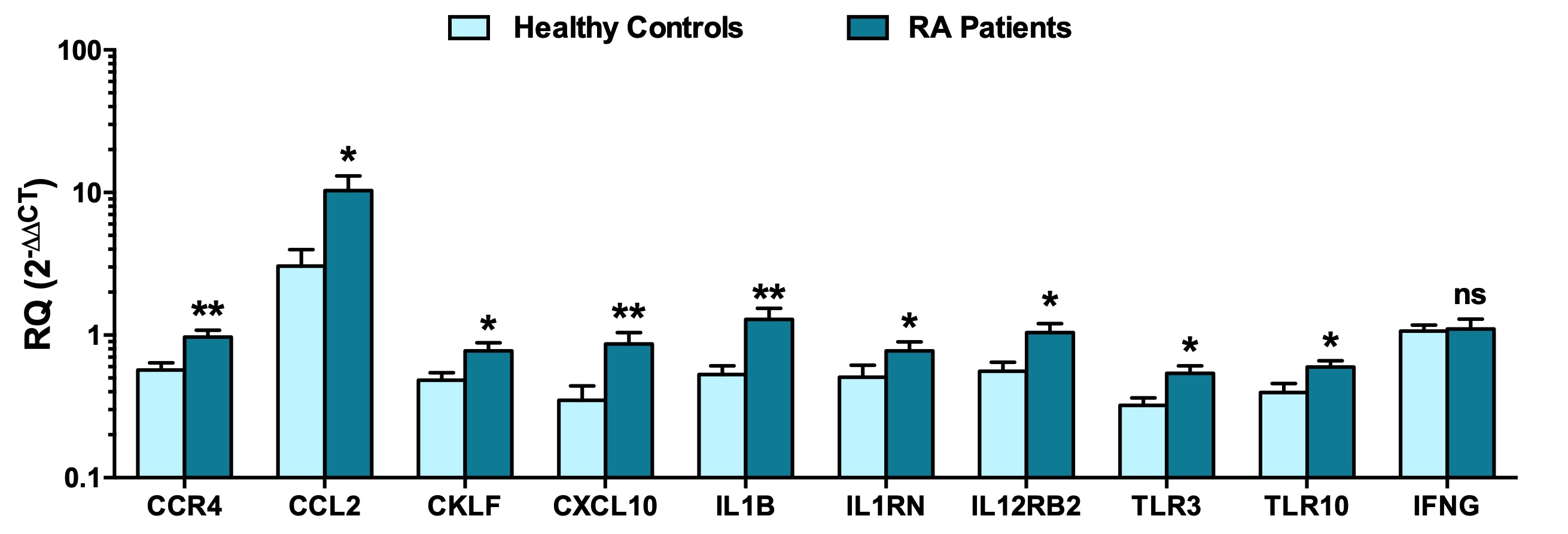 Figure 1. Assessment of gene expression of chemokines, cytokines, and toll-like receptors in the PBMCs of RA patients and healthy controls.
Figure 1. Assessment of gene expression of chemokines, cytokines, and toll-like receptors in the PBMCs of RA patients and healthy controls.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Elemam N, Hachim M, Hannawi S, Maghazachi A. Differentially Expressed Chemokines and Cytokines in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMCs) of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/differentially-expressed-chemokines-and-cytokines-in-peripheral-blood-mononuclear-cells-pbmcs-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/differentially-expressed-chemokines-and-cytokines-in-peripheral-blood-mononuclear-cells-pbmcs-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-patients/
