Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Circulating bioactive lipids can provide information about the pathogenesis of specific diseases and potentially help predict therapeutic response. Choosing the right biological therapy earlier in the course of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) could help reach the goal of remission. We hypothesized that circulating bioactive lipids at baseline would identify specific metabolic profiles that predict patient response to therapy and would define elements of metabolic pathobiology in arthritis.
Methods: Bioactive lipids were measured in plasma from two cohorts of RA patients from the CorEvitas (formerly known as Corrona) CERTAIN registry at baseline prior to treatment with TNF inhibitors (all biologic naïve, N=102) or anti-IL6 (all previously exposed to biologics, N=114). Response to treatment was categorized by minimal clinically important difference (MCID) in Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) at 6 months after treatment initiation. Patients had to have a 6 month follow up visit. Liquid chromatography (LC) system coupled with high resolution QExactive orbitrap mass spectrometer (LC/MS) was used for bioactive lipids profiling. Around 300 spectral features were identified as potential oxylipins by searching against an in-house MS/MS library. Logistic regression analyses adjusted for gender, age and BMI was perfomed using R software.
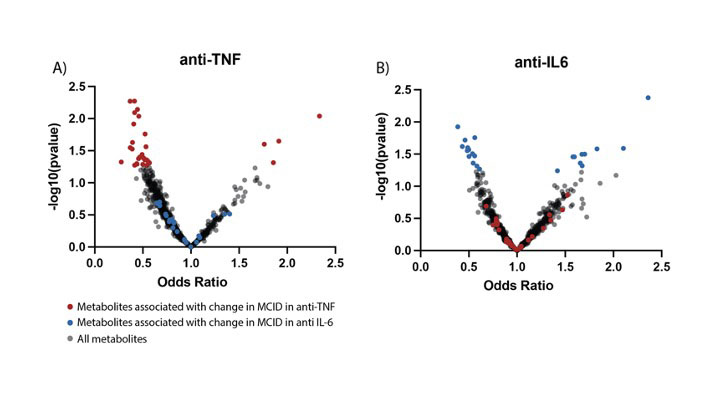
Results: 102 patients (average age 54, standard deviation [SD] 12.6, 82% female [83], average BMI 29.7, SD 6.7, average CDAI 27.1, SD 13.7) starting anti-TNF therapy and 114 patients (average age 57, SD 13, 90% female [102], average BMI 30.5, SD 7.4, average CDAI 28.7, SD 13.8) starting tocilizumab were analyzed. Twenty-five oxylipins discriminated between RA patients classified as anti-TNF responders (R, n = 74) and non-responders (NR, n = 28). The anti-inflammatory SPM maresin 2 was increased in R (OR 1.7; 95%CI 1.07–2.9), and oxylipins 15d PGJ2 (OR 0.4; 95%CI 0.2–0.8), and 5,6-diHETE (OR 0.5; 95%CI 0.3–0.9) were decreased in R, among other metabolites Figure 1 and 2. Twenty different metabolites discriminated anti-IL6 R (n=73) and NR (n=41) as shown in Figure 1 and 2. The anti-inflammatory oxylipin 14-15EET (OR 1.7; 95%CI 1.05–2.7) and 8-iso-PGF1a (OR 1.8; 95%CI 1.07–3.1) were increased in R, whereas the pro-inflammatory oxylipins 16-HETE (OR 0.4; 95%CI 0.2–0.9) and 5S-HpETE (OR 0.5; 95%CI 0.26–0.95) were decreased in R.
Conclusion: Circulating bioactive lipid analysis using LC/MS provided a rapid analysis of a wide range of metabolites and can be used to describe metabolic signatures that predict response to therapies. These results lay the groundwork for more deliberate investigations of novel metabolic-based interventions to predict response to therapy and reduce arthritis morbidity.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Alotaibi M, Coras R, Pappas D, Mikuls T, Kremer J, Thiele G, jain m, Guma M. Different Bioactive Lipid Profile Predicts Response to TNF or IL6 Inhibitors in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Result of the CorEvitas CERTAIN Comparative Effectiveness Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/different-bioactive-lipid-profile-predicts-response-to-tnf-or-il6-inhibitors-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-result-of-the-corevitas-certain-comparative-effectiveness-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/different-bioactive-lipid-profile-predicts-response-to-tnf-or-il6-inhibitors-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-result-of-the-corevitas-certain-comparative-effectiveness-study/