Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: B Cell Biology & Targets in Autoimmune & Inflammatory Disease Poster
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
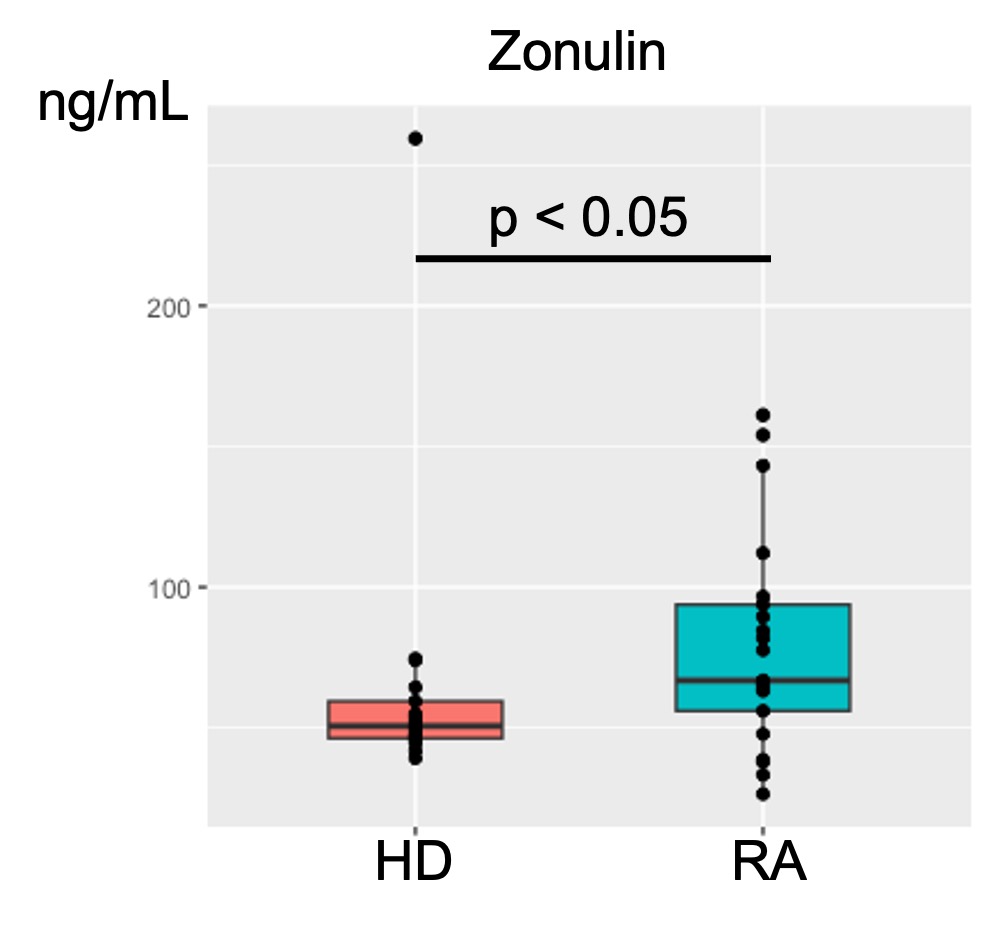
Background/Purpose: The gut is a key mucosal tissue that can impact the immune system and contribute to systemic inflammation in the setting of increased intestinal permeability. The levels of serum zonulin, a surrogate marker of intestinal permeability, have been reported to be increased in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and pre-onset RA. In a model mice of RA increased zonulin was associated with immune cell migration from the gut to the synovium. We postulated that gut permeability may be a driver of pathogenic B cells involved in the pathogenesis of human RA.
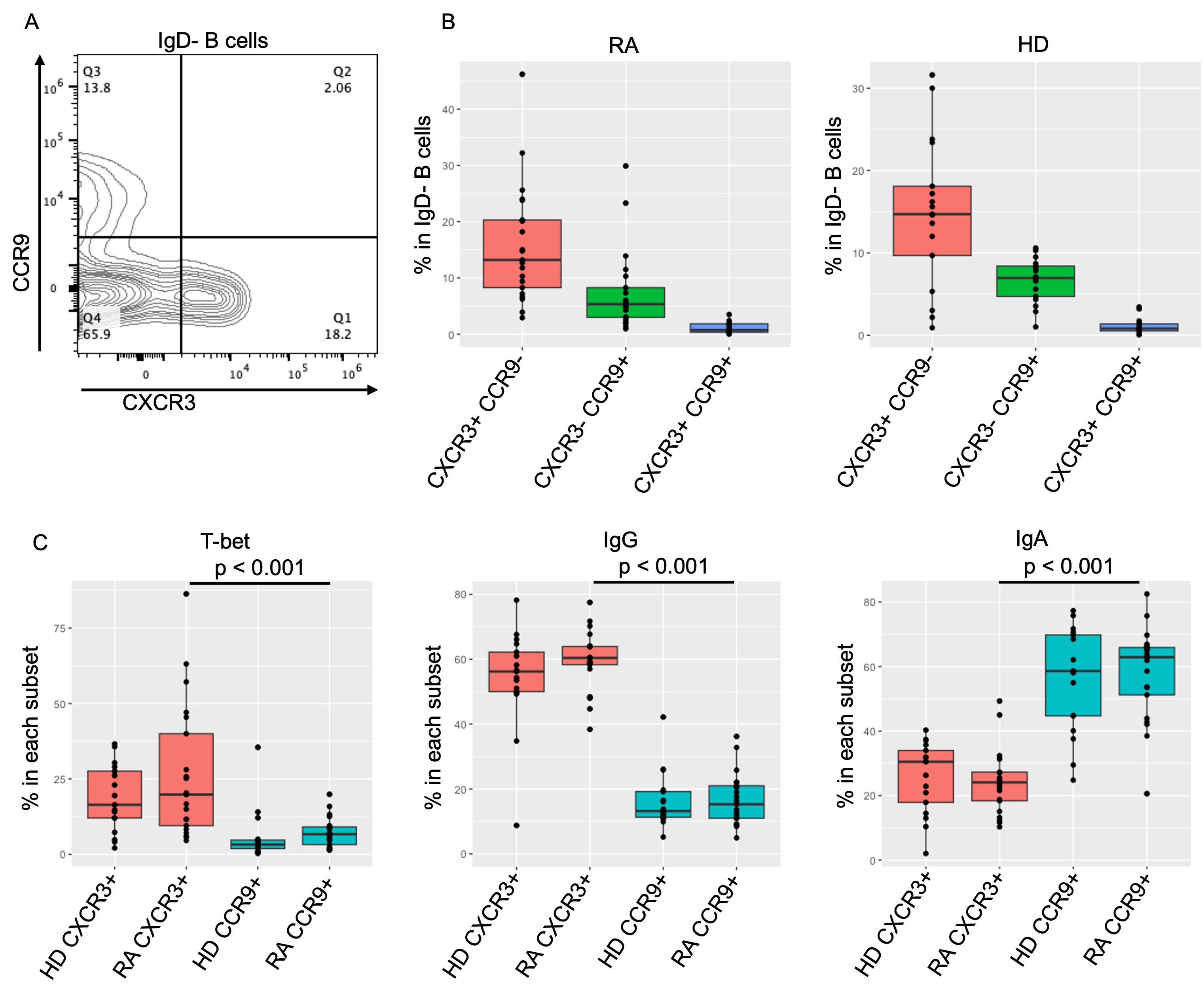
Methods: Zonulin levels were measured by ELISA in sera from 17 healthy donors (HD) and 21 patients with RA. Paired PBMCs were analyzed by flow cytometry. Naïve B cells (IgD+ and CD27-) were classified into resting (rNAV, CD11c- and CD21+) and activated (acNAV, CD11c+ and CD21-). Among IgD- antigen-experienced B cells, autoimmunity/age-associated B cells (ABC) were defined as CD27-, CD11c+ and CD21-. Antibody-secreting cells (ASC) were defined as CD27++ and CD38++. Chemokine receptor expression was examined as a read-out of cell migration potential, CCR9 for gut-homing and CXCR3 for migration to inflammatory tissues. We also looked at the expression of those chemokine receptors in single cell analysis data from the Accelerating Medicines Partnership Program: Rheumatoid Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (AMP RA/SLE) Network.
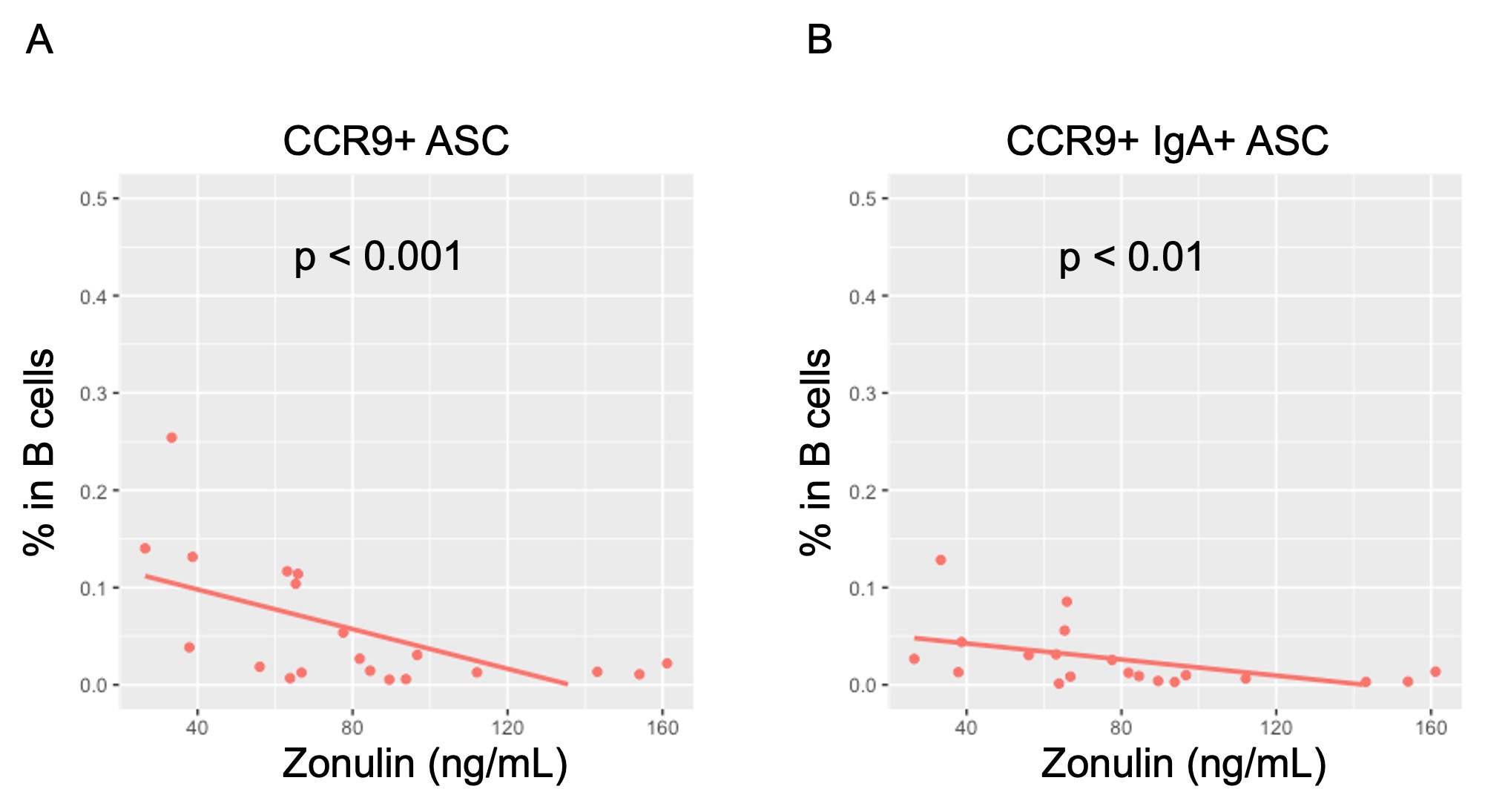
Results: Our RA cohort was characterized by long-standing seropositive disease (70% duration > 5 years; 82 % positive for anti-CCP antibodies). RA had significantly higher levels of serum zonulin than HD, and this was inversely correlated with CCR9+ and CCR9+ IgA+ ASC. ABC and acNAV were significantly more abundant in RA than HD (ABC, 0.9% vs 0.35%, p < 0.05; acNAV, 0.78% vs 0.56%, p < 0.05), but their frequencies were not correlated with zonulin.
CXCR3 and CCR9 were exclusively expressed on IgD- subsets (CXCR3% on IgD- 15% vs rNAV 0.78%, CCR9% 7.0% vs 0.69%). Notably, CXCR3 and CCR9 expression was mutually exclusive, and their frequencies were inversely correlated in RA (p = 0.066, Spearman’s correlation test). Compared to CCR9+ B cells, both T-bet+ and IgG+ B cells were significantly enriched in CXCR3+ B cells, while IgA+ B cells were more enriched in CCR9+ B cells. Despite the low frequencies (0.73%), CCR9+ CXCR3+ B cells primarily comprise IgA+ CD11c+ T-bet+ B cells. When synovial B cells from AMP RA/SLE Network were analyzed, CCR9 expression was notably absent in most of the B cell subsets, but CXCR3 expression was enriched in ABCs. 0.05
Conclusion: Our study implicates increased gut permeability and ABC expansion in long-standing RA. Dichotomous phenotypes of CXCR3+ and CCR9+ in antigen-experienced B cells may reflect different developmental pathways and migration propensity. Given there is little evidence on the role of IgA+ B cells in RA, the ongoing studies are underway to assess the functional difference between IgG+ and IgA+ B cells in the synovium. We will also examine clonal relationships between B cell populations in the blood and synovium to capture the dynamics of their migration.
Spearman’s correlation test was done.
B. The boxplot figures showing the frequencies of each subset delineated in IgD- B cells in RA and HD.
C. The boxplot figures showing the positivity of T-bet, IgG and IgA in CXCR3+ and CCR9+ IgD- B cells. The Mann-Whitney U test was done.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yasaka K, Wang R, Pellett N, Krenitsky D, Thakar J, Anolik J. Dichotomous Expression of CXCR3 and CCR9 and Relationship to Intestinal Permeability in B Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dichotomous-expression-of-cxcr3-and-ccr9-and-relationship-to-intestinal-permeability-in-b-cells-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dichotomous-expression-of-cxcr3-and-ccr9-and-relationship-to-intestinal-permeability-in-b-cells-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/