Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: Pediatric Rheumatology – Clinical Poster III: SLE, Vasculitis, & JDM
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
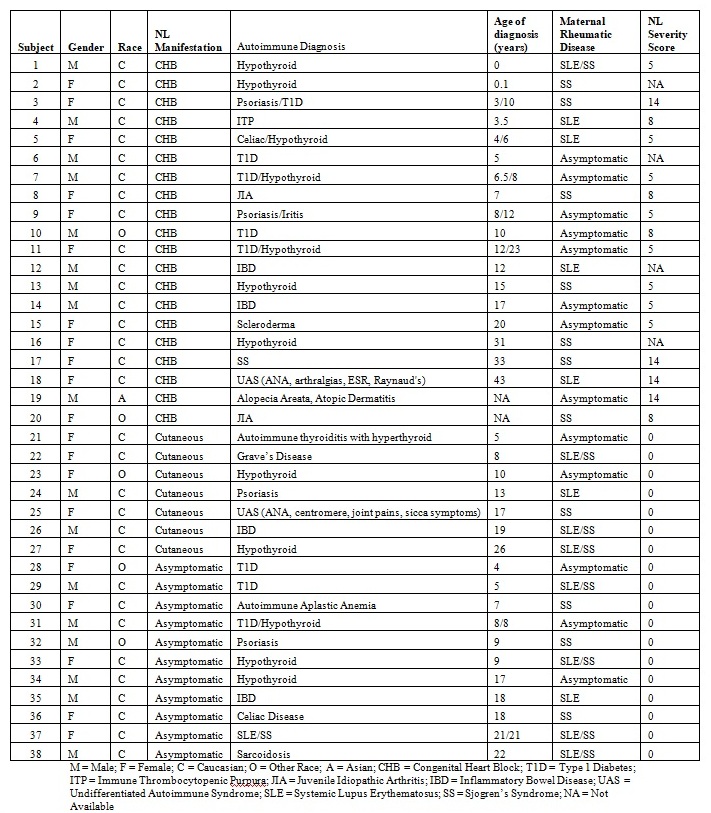
Background/Purpose: Neonatal Lupus (NL) is a model of passively acquired autoimmunity conferred by exposure to maternal anti-Ro antibodies with major manifestations being congenital heart block (CHB) and/or cutaneous disease. This study was initiated to address the development of de novo autoimmunity in these children and identify associated clinical and genetic risk factors.
Methods: In a retrospective cohort study of enrollees in the Research Registry for Neonatal Lupus (RRNL), 511 children exposed to anti-Ro in utero responded to a follow up questionnaire focused on symptoms of autoimmunity. Self-reported diseases were confirmed via medical record review. Bivariate analyses were performed with potential risk factors for the development of autoimmune disease (AD) and included the NL status per se, a disease severity score based on mortality risk factors, and maternal AD (inclusive of lupus, Sjogren’s syndrome, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, or thyroid disease). A subset of 99 CHB, 9 cutaneous, and 55 unaffected anti-Ro exposed RRNL individuals were genotyped at Class II HLA DRB1 and DQB1 four-digit alleles, which were assigned by imputation (HIBAG) or sequencing. Generalized estimating equations (logit link, exchangeable correlation) were used to test for associations between HLA alleles and the development of AD.
Results: Of the respondents, 182 offspring had CHB, 95 had cutaneous only NL and 234 were siblings without NL. Females comprised 53% and 80% were Caucasian. The mean age was 14.2±9.7; 4% age 0-2 years, 48% 2-13 years, and 47% > 13 years. An AD developed in 38 offspring (20 CHB, 7 cutaneous NL, 11 non-NL siblings; Table 1). The most prevalent AD was thyroid disease. The development of an AD was significantly associated with presence of CHB vs. cutaneous only or non-NL siblings (11% vs. 5%, p=0.033). The maternal health status did not influence the development of an AD in the child (7% mothers with AD vs. 6% asymptomatic mothers, p=0.67). Mean NL severity score was higher in offspring with AD (3.8±4.8 vs. 2.2±4.0, p= 0.031). Other markers of fetal CHB disease severity were associated with subsequent AD development, including in-utero exposure to fluorinated steroids (15% vs. 6%, p=0.088) and beta agonists such as terbutaline (23% vs. 9%, p=0.043). In the study of 163 RRNL cases with HLA data (20 with AD, 143 without), HLA DRB1*03:01 (OR 3.4, CI 1.46-7.90, p=0.0045), DQA1*05:01 (OR 3.39, CI 1.16-9.92, p=0.0262), and DQB1*02:01 (OR 4.28, CI 1.73-10.62, p=0.0017) were associated with increased risk of AD (of note, these loci are in high linkage disequilibrium). In contrast, these alleles were not significantly associated with development of CHB (99 CHB vs. 64 without).
Conclusion: The development of an autoimmune disease was more common in anti-Ro exposed children with CHB, greater NL severity, and MHC Class II haplotypes. These factors may relate to an inherent susceptibility to inflammation and fibrosis, occuring in utero and later in life.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Saxena A, Garza Romero A, Gratch D, Izmirly P, Ainsworth H, Marion M, Langefeld C, Clancy R, Buyon J. Development of Autoimmune Diseases and HLA Associations in Children with Neonatal Lupus and Their Unaffected Siblings [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-of-autoimmune-diseases-and-hla-associations-in-children-with-neonatal-lupus-and-their-unaffected-siblings/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-of-autoimmune-diseases-and-hla-associations-in-children-with-neonatal-lupus-and-their-unaffected-siblings/