Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster IV: Lifespan of a Disease
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients is usually measured by an index like DAS28,1 a composite measure consisting of 28 swollen and/or tender joint counts (SJC28/TJC28), an acute phase reactant (APR, e.g. ESR/CRP) and patient’s general health, typically using a visual analogue scale (VAS). Particularly assessment of joint counts is time consuming, requires a trained health professional and its inter-observer variety is high. The HandScan is developed to measure inflammation in hand joints using optical spectral transmission (OST, score 0-66) within 5 minutes, without taking time of a health professional.2 The correlation between DAS28 and a single measurement of OST is moderate.3 We hypothesised that a composite measure consisting of OST (representing joint inflammation), VAS and APR would lead to an appropriate disease activity index.
Objective:
To develop and validate a composite disease activity index for assessing RA patients using OST values obtained by the HandScan.
Methods: At a single Rheumatology centre routinely using the Handscan, RA patients with at least one concurrent OST-score and DAS28 measurement were included. Data was extracted from medical records. A random sample of 2/3 of the patients was used as development cohort, the remaining 1/3 was used as validation cohort. In the development cohort, linear regression analyses with DAS28 as outcome were performed to create a disease activity index (DAS-OST). In these analyses, OST-score, ESR and VAS, as well as gender, age, disease duration and RF-status, were evaluated as predictor variables. A final model was derived, based on statistical significance and model fit. Patients were classified as being in DAS28 based remission, low and high disease activity by DAS-OST using the established DAS28 cut-offs. In the validation cohort, agreement of DAS28 and DAS-OST was estimated with a two-way mixed effect intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC) and the measurement error was estimated using the Bland and Altman method. Diagnostic accuracy were determined for DAS-OST using the cut-offs as defined above for all disease activity states.
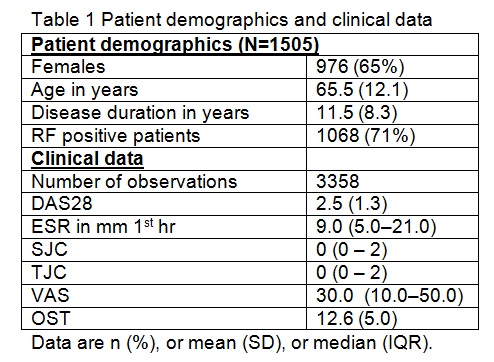
Results: Data of 3358 observations within 1505 unique RA patients were extracted. Patients’ demographic and clinical data are shown in Table 1.
The formula for DAS-OST derived in the development cohort was: -0.44 + OST*0.03 + male*-0.11 + LN(ESR)*0.77 + VAS*0.03.
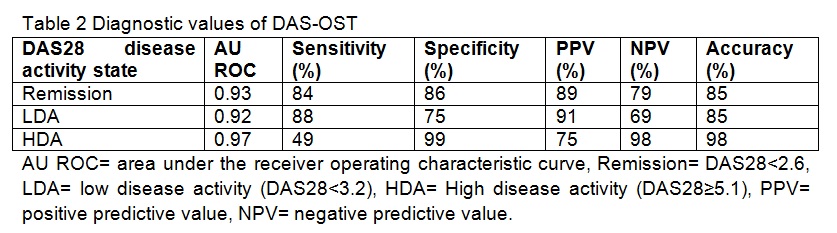
In the validation cohort, the explained variance of DAS-OST was 78%. For agreement, the ICC was 0.88 (95%CI 0.87-0.90) and the measurement error was 0.58. Diagnostic accuracy of DAS-OST for DAS28 based remission, LDA and HDA remission is shown in Table 2.
Conclusion: Using the HandScan, disease activity can be accurately estimated in RA patients, when its score is combined with ESR, VAS and gender into an objective disease activity index (DAS-OST).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Verhoeven M, Welsing P, Tekstra J, van Laar J, Lafeber F, Jacobs J, Westgeest A. Development of a Disease Activity Index for Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Using the HandScan [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-of-a-disease-activity-index-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-using-the-handscan/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-of-a-disease-activity-index-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-using-the-handscan/