Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Shared decision making is a key component of a treat-to-target approach for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). We created an EHR tool that displays patient-reported outcomes (PROs) on a dashboard for use during RA clinical visits to support shared decision making. We evaluated patient and clinician perspectives regarding incorporation of the dashboard into a clinical visit.
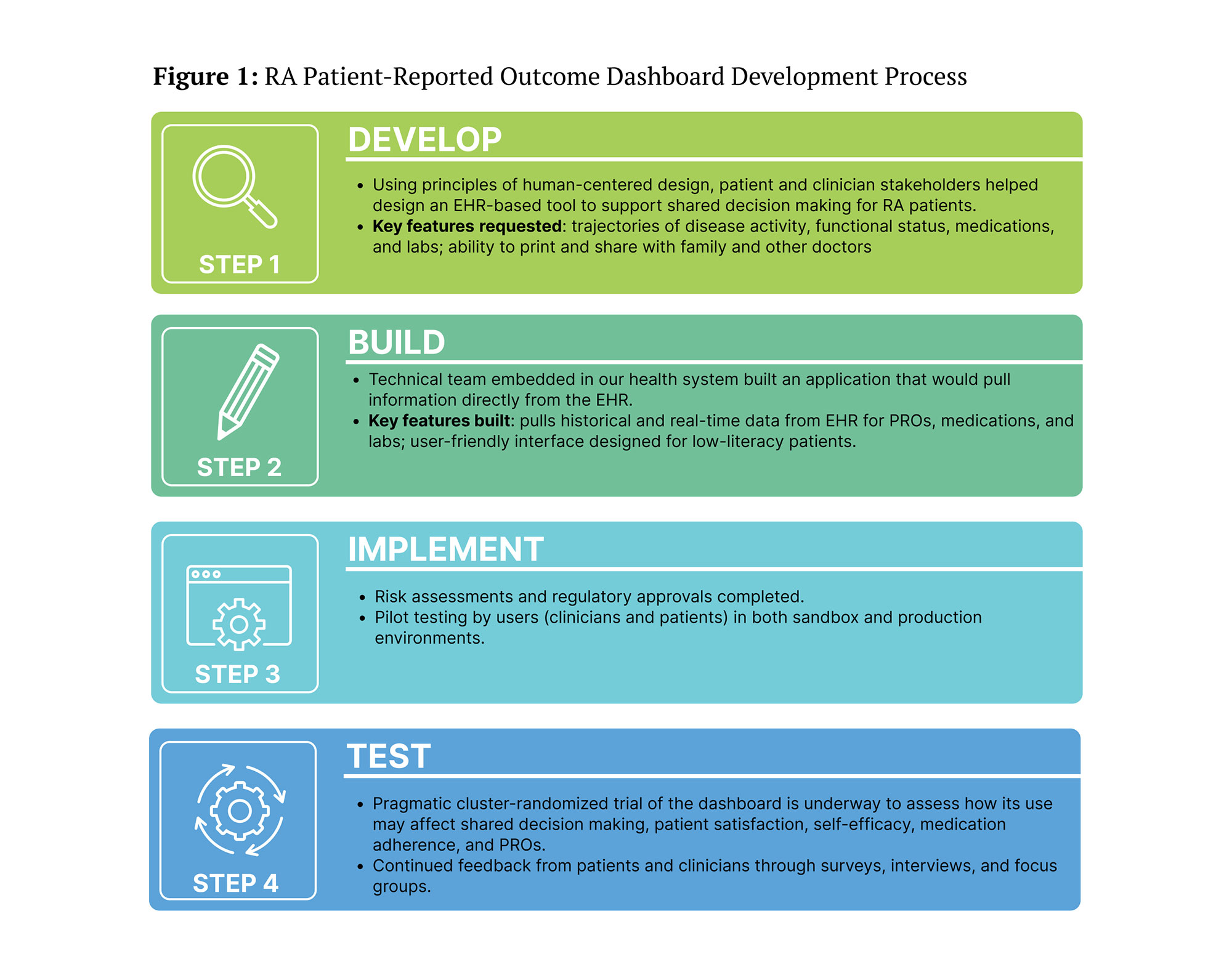
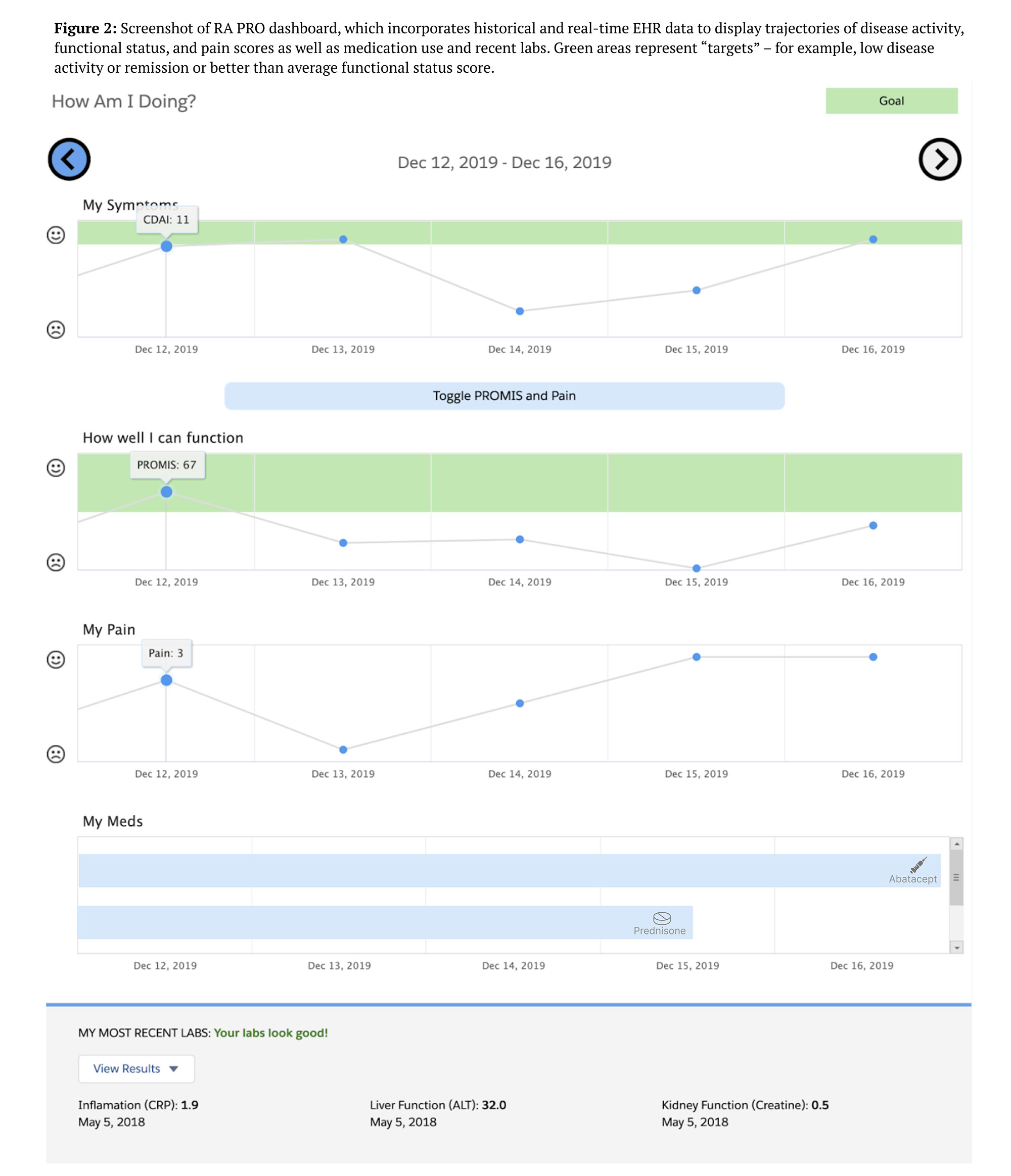
Methods: The dashboard was developed using a human-centered design approach with input from patients and clinicians (Figure 1). It incorporates historical and real-time EHR data to display trajectories of disease activity, functional status, pain scores, and medication use and recent labs (Figure 2). The dashboard was implemented at a university rheumatology clinic (Epic EHR), launching via Salesforce automatically when a patient’s chart is opened at the start of a visit. As a part of an ongoing pragmatic trial, patient and clinicians who used the dashboard between August 2021 and May 2022 were invited to complete a survey regarding its features, usability, and suggestions for improvement. For a subset of participants, patient and clinician responses from the same encounter were directly compared. A focus group of clinicians was also conducted to assess perceptions of the dashboard. Open-ended survey questions and focus group transcripts were analyzed thematically using grounded theory.
Results: 50 unique patient surveys and 47 surveys from 4 clinicians were completed. Most patients were female (88%), mean age was 61, 46% were self-reported non-Hispanic white, and mean (SD) CDAI score was 19.7 (10.7). 3 of 4 clinicians were physicians; one was a nurse practitioner (NP). Nearly all (92.0%) patients were interested in seeing the dashboard at a future visit, reporting that it helped to visualize their disease activity and facilitated communication with their clinician on disease progression and treatment plans. Several patients requested that the dashboard be accessible via the health portals for sharing with family and other clinicians.
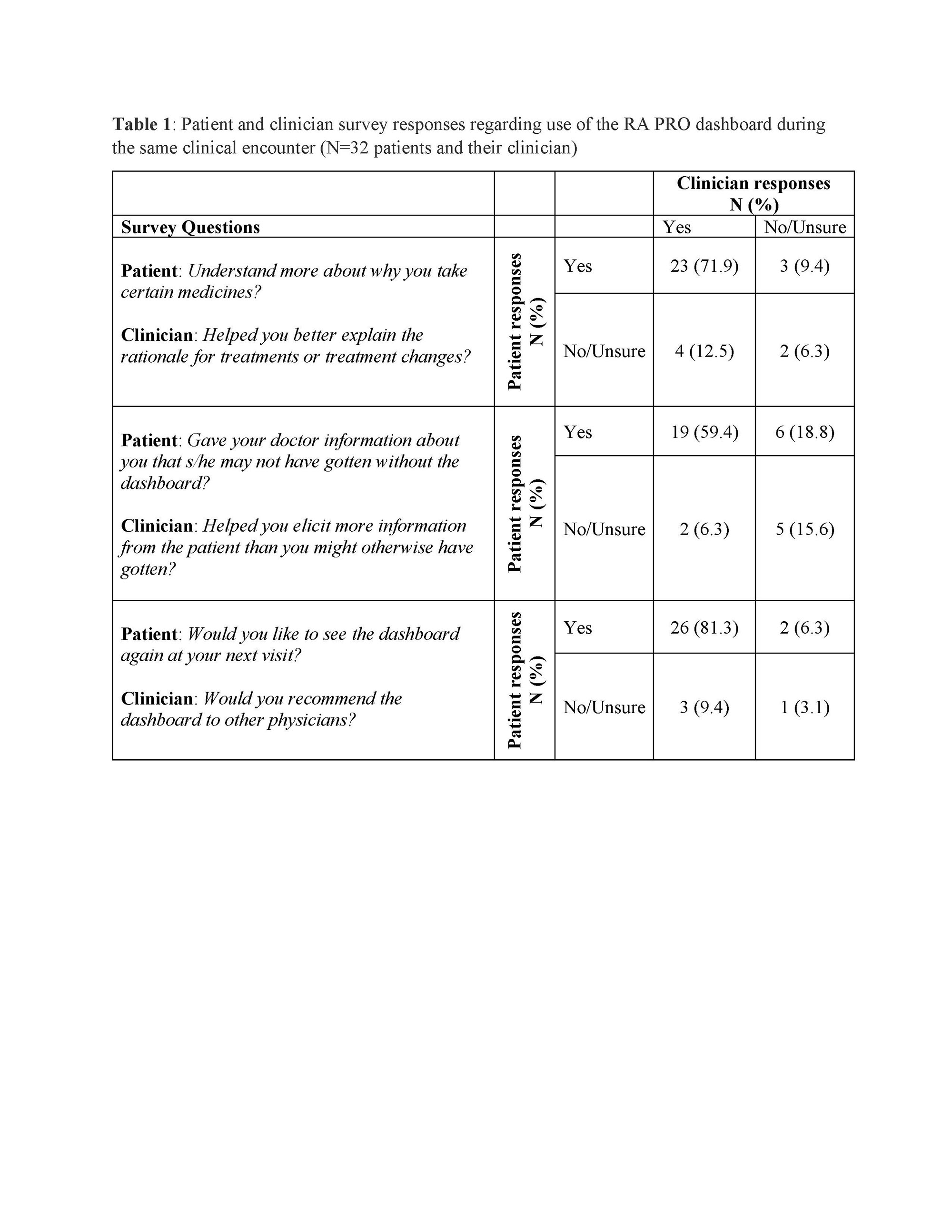
32 patients and their treating clinician completed surveys related to the same visit: 72% of patient-clinician dyads agreed that the dashboard increased patient understanding of their medications, 59% agreed that the dashboard improved communication, and 81% of dyads recommended the dashboard for use in future visits (Table 1). During a focus group (N=5, including attendings, fellows, and an NP), 2 main challenges emerged: 1) missing historical data from incomplete PRO collection in-person or during virtual visits, resulting in a less helpful visualization, and 2) time constraints to discuss PROs during visits. Interestingly, more experienced clinicians were more comfortable incorporating PRO collection and discussion using the dashboard.
Conclusion: A patient-facing, EHR-based dashboard that displays PROs during RA clinical visits was well-accepted by both patients and clinicians. An ongoing pragmatic trial will assess whether use of the dashboard systematically improves patient satisfaction, self-efficacy, and patient-reported outcomes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Young C, Montgomery A, Nasrallah C, Jacobsohn L, Barton J, Murray S, Yazdany J, Schmajuk G. Development, Implementation, and Usability Testing of a New Rheumatoid Arthritis Patient-Reported Outcomes EHR-based Dashboard: A Mixed-Method Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-implementation-and-usability-testing-of-a-new-rheumatoid-arthritis-patient-reported-outcomes-ehr-based-dashboard-a-mixed-method-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-implementation-and-usability-testing-of-a-new-rheumatoid-arthritis-patient-reported-outcomes-ehr-based-dashboard-a-mixed-method-study/