Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In rheumatoid arthritis [RA], synovial biopsies were shown to guide therapy selection1. However, biopsies require special training for clinicians and are semi-invasive for patients. Blood-based tests are a common procedure in clinical practice. Prior research failed to capture synovial signals in RA patients via blood because of the limited circulation of synovial-specific biomarkers and the dilution of molecular signals within the bloodstream. The study aims to investigate synovium-specific transcriptomic signal in blood plasma by employing a novel DNA capture platform to comprehensively analyze and characterize the molecular signatures in RA.
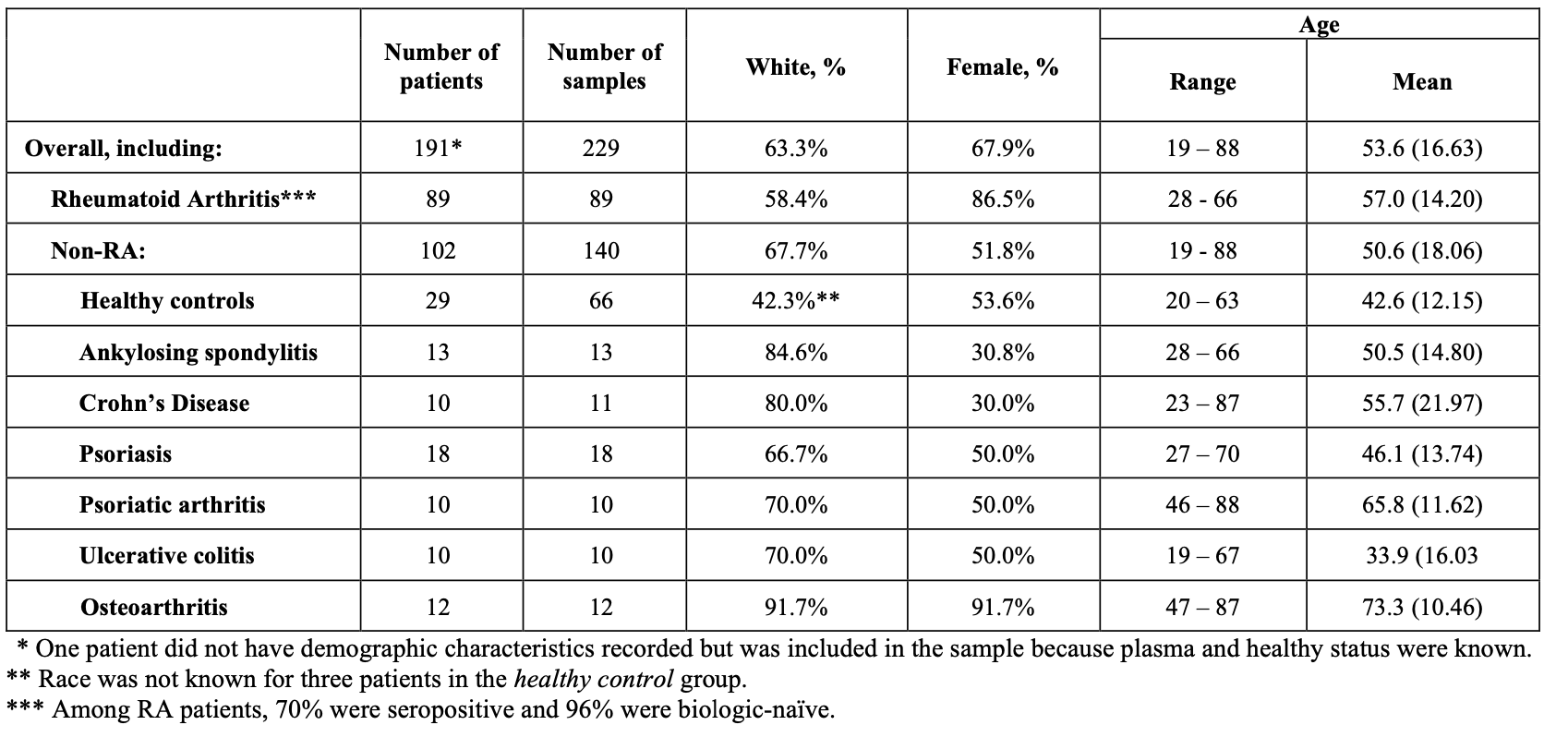
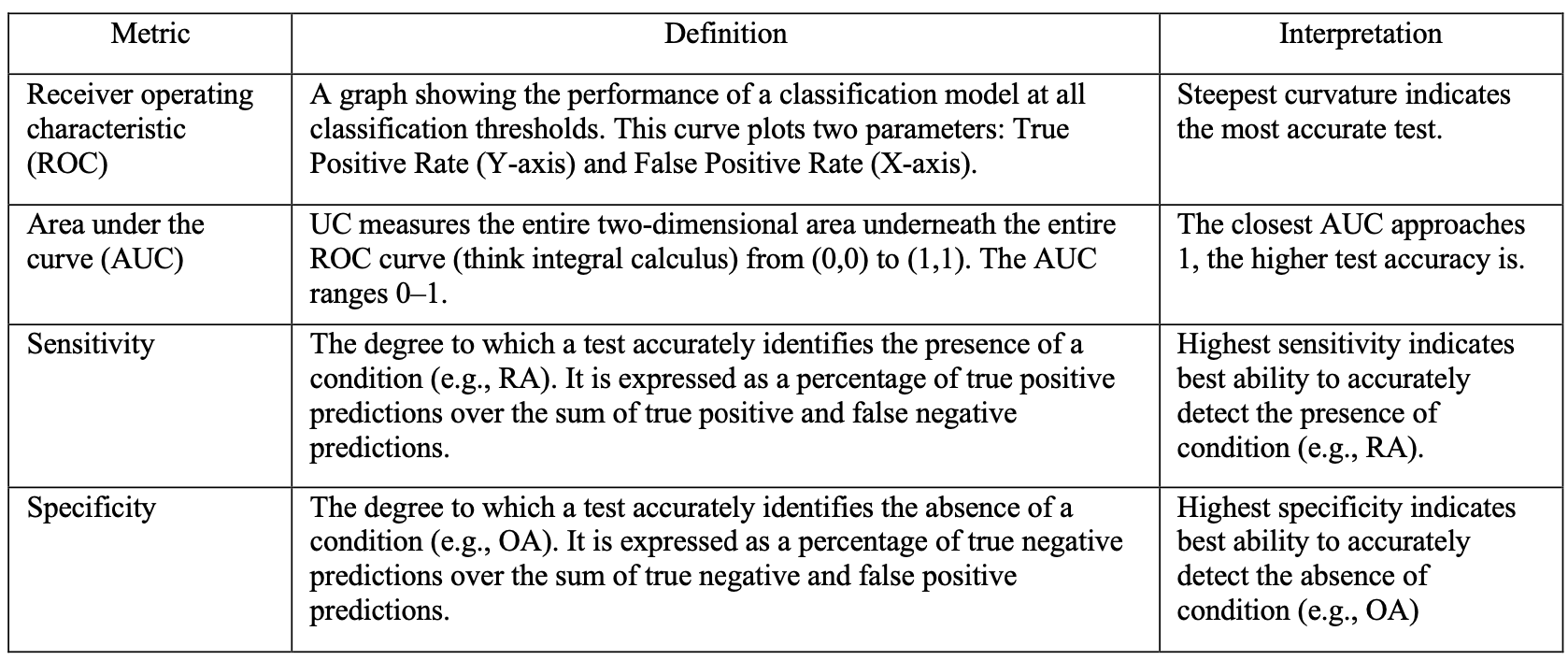
Methods: Plasma samples (n=229) from 89 individuals meeting 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria for RA, 62 with inflammatory conditions, 12 with OA, and 29 healthy controls (Table 1) were processed using a blood-based assay that enriches for non-hematopoietic signals. The epigenome atlas, comprised of 600,000 features, was evaluated using bootstrap methods to select features that robustly differentiate RA from non-RA samples to generate a candidate list of genomic feature locations. These were mapped to genes and compared to the reported pathways2 identified in whole blood and synovial tissue of patients with RA. A machine-learning training used 5-repeat 10-fold cross validation of the candidate features that have overlapping genes with synovial pathways. The training generated the average area under the curve (AUC) and performance metrics (sensitivity and specificity; Table 2)
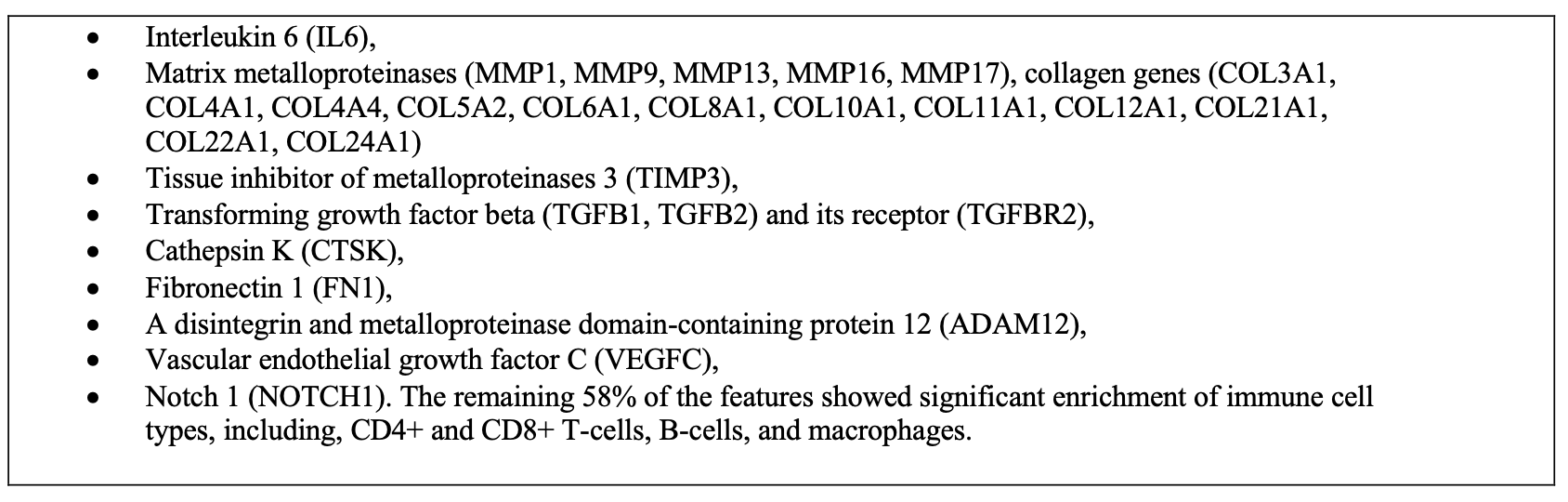
Results: Participants had a mean (standard deviation, SD) age of 53.6 (16.63) years and were mostly female (67.9%) and white (63.3%; Table 2). The RA patients were mostly seropositive (70%) and biologic-naïve (93%). In the list of identified genomic features, 88% overlapped with synovium pathway genes and 30% with blood pathway genes. Within identified synovial signatures, 42% represent synovial fibroblast genes (Table 3); the remaining 58% of the features showed significant enrichment of immune cell types, including, CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells, B-cells, and macrophages.
Conclusion: The developed non-invasive DNA capture assay identified synovium-specific gene expression signatures in blood plasma of RA patients. Further clinical research is needed to validate these synovial signatures and confirm the clinical utility of the developed classification system.
1. Humby F, et al. (2019); PMID: 30878974
2. Rychkov D, et al. (2021); PMID: 34177888
Note: both Dr. Shadick and Dr. Weinblatt are last authors.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Taylor P, Antonova J, Geis J, Dilger K, Chernoff D, Abdueva D, Shadick N, Weinblatt M. Detection of Synovial Signatures in Peripheral Blood of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis via a Novel Blood-Based DNA Capture Assay [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/detection-of-synovial-signatures-in-peripheral-blood-of-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-via-a-novel-blood-based-dna-capture-assay/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/detection-of-synovial-signatures-in-peripheral-blood-of-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-via-a-novel-blood-based-dna-capture-assay/