Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 6, 2021
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I: Cardiovascular Pulmonary Disease (0268–0295)
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Bronchiectasis is a known extra-articular manifestation of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) characterized by bronchial damage and excessive mucus production that predispose patients to risk of serious infection and increased mortality. Traction bronchiectasis is a consequence of architectural distortion from RA-associated interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD), but little is known about risk factors for isolated RA-associated bronchiectasis (RA-BR) that occurs independently of RA-ILD. We investigated factors associated with isolated RA-BR among RA patients.
Methods: We performed a case-control study using a large institutional biobank and research data repository that recruited patients from clinical sites throughout a multi-hospital healthcare system in New England. Patients with RA were identified using a previously described algorithm and confirmed by medical record review. All patients with RA who had chest computed tomography (CT) imaging, lung biopsy, or autopsy data were reviewed for RA-related lung disease. For each patient, the CT chest imaging performed closest to enrollment was independently reviewed by two expert radiologists and scored for the presence of RA-ILD and interstitial lung abnormalities. Cases of RA-BR were confirmed by review of clinical records and CT scan report, and isolated RA-BR was defined as clinical evidence of bronchiectasis with no evidence of RA-ILD or interstitial lung abnormalities on expert radiology review. Controls had RA but no RA-related lung disease on expert review of CT chest imaging. Covariate data were obtained through survey enrollment and medical record review. The associations between demographic, lifestyle, and clinical factors and RA-BR were examined using multivariable logistic regression.
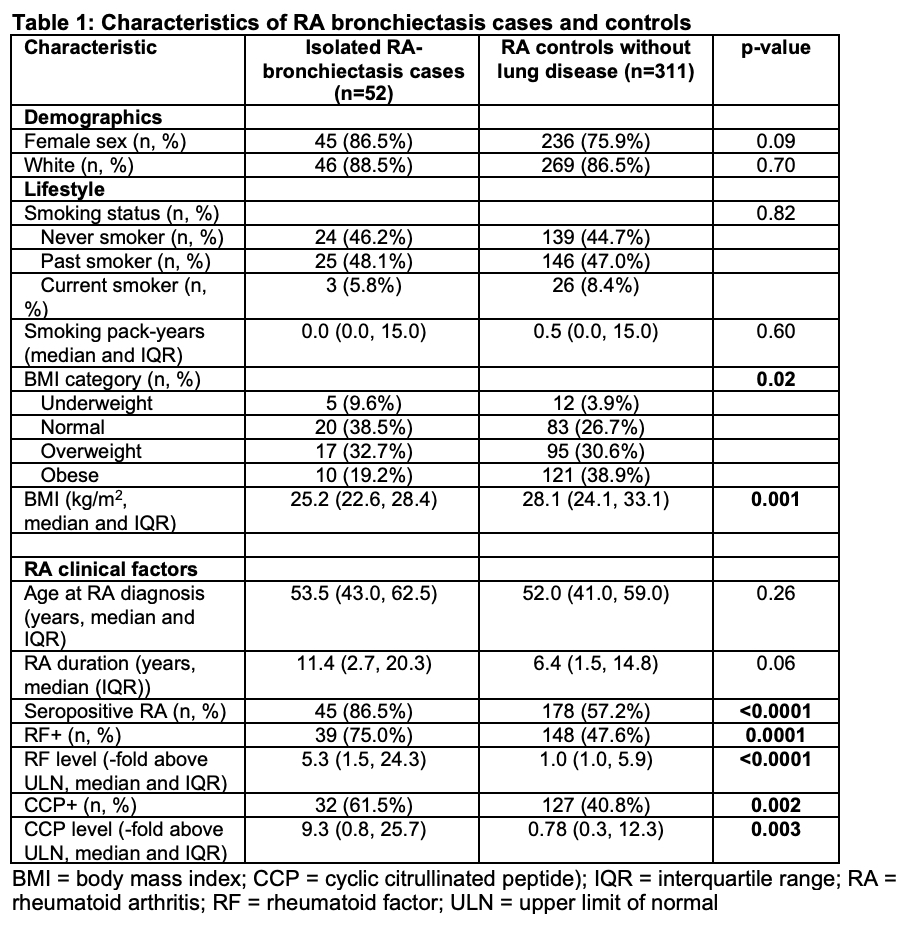
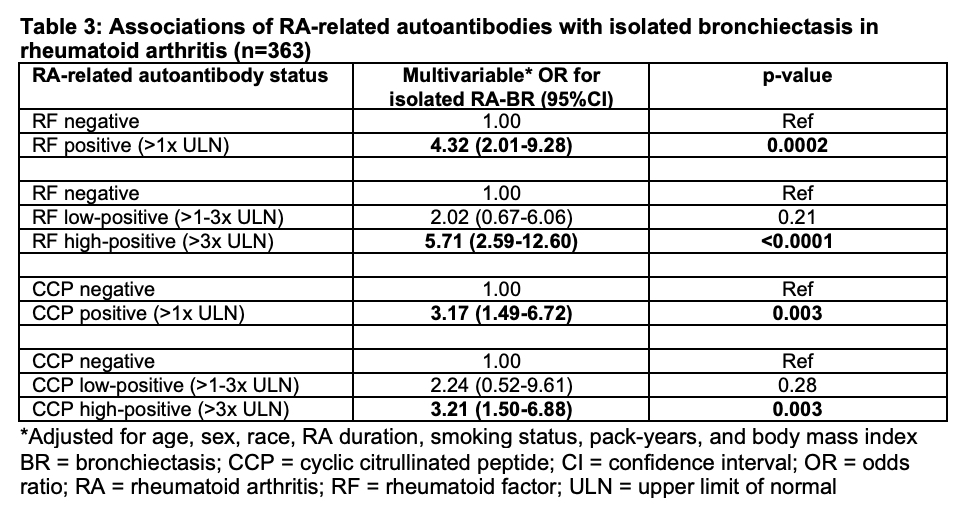
Results: We identified 52 isolated RA-BR cases and 311 RA controls without RA-related lung disease. There was no significant difference in age between RA-BR cases and controls (median 53.5 vs. 52.0 years, p=0.26); 86.5% of RA-BR cases and 75.9% of controls were female (p=0.09). The median body mass index (BMI) was lower (25.2 kg/m2, IQR 22.6, 28.4) in RA-BR cases than controls (28.1 kg/m2, IQR 24.1-33.1; p=0.001). There was a greater proportion of seropositive patients among RA-BR cases (86.5%) than in the control group (57.2%) (p< 0.0001). Seropositive RA had multivariable OR for RA-BR of 4.40 (95%CI 1.87-10.35) compared to seronegative RA. Older age and longer RA duration were each associated with RA-BR (OR 1.46 per decade [95%CI 1.07-1.98], and OR 1.04 per year [95%CI 1.00-1.08], respectively). There was no association of smoking with RA-BR. Patients with high-positive RF had OR for RA-BR of 5.71 (95%CI 2.59-12.60). High-positive CCP was also associated with RA-BR (OR 3.21, 95%CI 1.50-6.88).
Conclusion: We identified seropositivity, older age at RA onset, longer RA duration, and lower BMI as potential novel risk factors for isolated bronchiectasis in RA not due to RA-ILD. High-positive RF and CCP were each strongly associated with RA-BR, suggesting a pathogenic link between RA-related autoantibodies and airway damage in bronchiectasis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
McDermott G, Gill R, Gagne S, Byrne S, Huang W, Prisco L, Zaccardelli A, Martin L, Shadick N, Dellaripa P, Doyle T, Sparks J. Demographic, Lifestyle, and Clinical Risk Factors for Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Bronchiectasis: Role of RA-related Autoantibodies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/demographic-lifestyle-and-clinical-risk-factors-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-associated-bronchiectasis-role-of-ra-related-autoantibodies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/demographic-lifestyle-and-clinical-risk-factors-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-associated-bronchiectasis-role-of-ra-related-autoantibodies/