Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: RA – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Abatacept, a CTLA-4-Ig fusion protein, is widely used as a treatment for rheumatoid arthritis (RA). We conducted this study to identify novel predictive and pharmacodynamic biomarkers for abatacept treatment in RA patients.
Methods: A total of 23 RA patients were enrolled in this study. All participants fulfilled the 1987 ACR criteria or 2010 ACR/EULAR criteria. At baseline, week 6, week 14, and week 24, serum levels of CXCL13, IL-21, and soluble PD-1 (sPD-1) were measured with ProcartaPlex by Luminex, while serum levels of rheumatoid factor (RF) IgM and anti-CCP antibody were determined by ELISA. Plasma samples were collected and measured for levels of calprotectin and NE-DNA complexes by ELISA at the time points mentioned above. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated and analyzed for changes in percentages of CD19+ CD11c+ B cell and CD19+ CD11c+ IgD–CD27– B cell by flow cytometry at baseline, week 14, and week 24. Responders to abatacept were defined as subjects who achieved ACR20 response at week 24. Baseline levels and longitudinal changes in these biomarkers were compared between responders (R) and non-responders (NR).
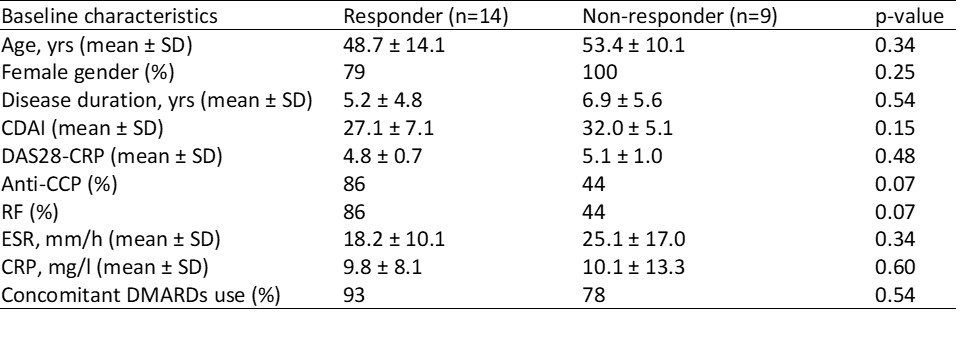
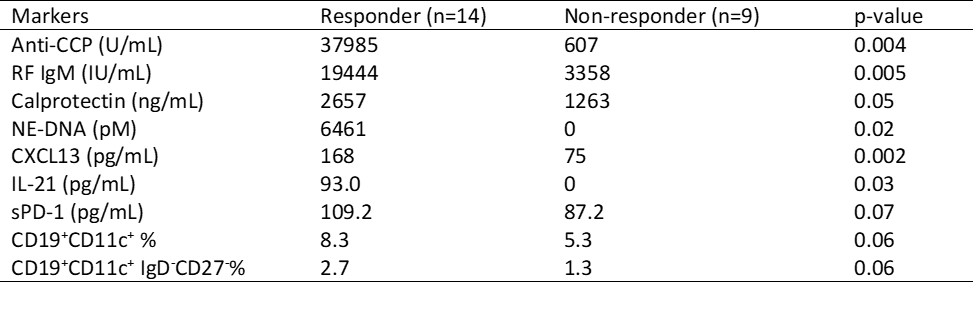
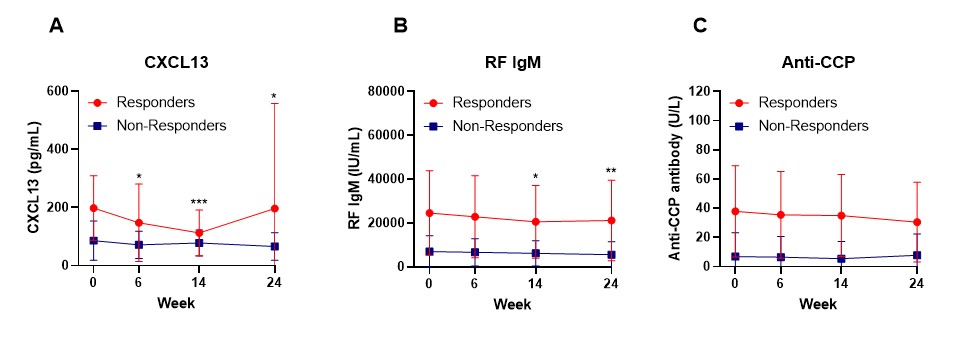
Results: After 24 weeks of treatment, 14 patients (61%) achieved an ACR20 response, 10 patients (43%) achieved an ACR50 response, and 3 patients (13%) achieved an ACR70 response. Although there were no significant differences in baseline characteristics between responders and non-responders, the percentages of anti-CCP (86% vs 44%, p= 0.07) and RF (86% vs 44%, p= 0.07) tended to be higher among responders (Table 1). Patients achieving ACR20 response at 24 weeks had elevated serum levels of anti-CCP, RF IgM, CXCL13, and IL-21 as well as plasma levels of calprotectin and NE-DNA at baseline (Table 2). For longitudinal changes (Figure 1), serum RF IgM and CXCL13 levels decreased only in responders who achieved ACR20 response, while serum anti-CCP levels did not decrease significantly in either responders or non-responders.
Conclusion: In patients with RA, ongoing immune complex-driven immune activation, as defined by heightened levels of anti-CCP, IgM RF, NE-DNA complexes, calprotectin, CXCL13, and IL-21, predicted the treatment response to abatacept. Further, IgM RF and CXCL13 levels were superior to anti-CCP in assessing and monitoring the response to abatacept.
Differences between groups were assessed by the Mann-Whitney test. P values < 0.05 were considered significant.
Differences between groups were assessed by the Mann-Whitney test. P values < 0.05 were considered significant.
Data are displayed as a mean of serum levels of CXCL13 (A), RF IgM (B), and anti-CCP(C) before and after treatment of abatacept in responders (n=14) and non-responders (n=9), error bars display the 95% confidence. Differences between baseline and post-treatment (week 6, week 14, and week 24) were determined by the Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test. P values < 0.05 were considered significant. ***p<0.001, **p<0.01and *p<0.05.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wang T, Stultz R, Giltiay N, Lood C, Han B. CXC Chemokine Ligand 13 and Rheumatoid Factor as Pharmacodynamic Biomarkers for Abatacept Treatment in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cxc-chemokine-ligand-13-and-rheumatoid-factor-as-pharmacodynamic-biomarkers-for-abatacept-treatment-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cxc-chemokine-ligand-13-and-rheumatoid-factor-as-pharmacodynamic-biomarkers-for-abatacept-treatment-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/