Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 6, 2021
Title: Abstracts: Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies (0441–0444)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:45AM-10:00AM
Background/Purpose: Numerous Covid-19 vaccines have demonstrated efficacy and safety against SARS-CoV-2 in general population. Despite favorable adverse effect (ADRs) profile of vaccines, there have been concerns regarding activation of aberrant immune responses. Moreover, vaccine safety data in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) and other systemic autoimmune diseases (AID) is rather limited. We aimed to evaluate safety of Covid-19 vaccines in IIMs patients in comparison with other AIDs and non-autoimmune disease controls using a patient reported world-wide electronic survey by an international CoVAD study group.
Methods: We developed an extensive self-report e-survey to assess safety of the COVID-19 vaccine in IIMs and other AIDs and non-autoimmune controls. The questionnaire was pilot tested, validated and translated into 15 languages on surveymonkey.com, and vetted by international experts. The survey questions were designed to evaluate previous COVID infection, current vaccination status, as well as short term (within one week) as well as long term (1-12 months) adverse drug reactions (ADRs) following vaccine administration. Rheumatologists from >50 centers conducted the e-survey to their patients as well as their non-autoimmune family members. In addition, the survey was floated on social media platforms and online patient support group members across the world. We analyzed the data from baseline survey (Feb – May 2021, 7-day ADRs) for descriptive statistics as well as inter-group comparison using chi-square or t-test.
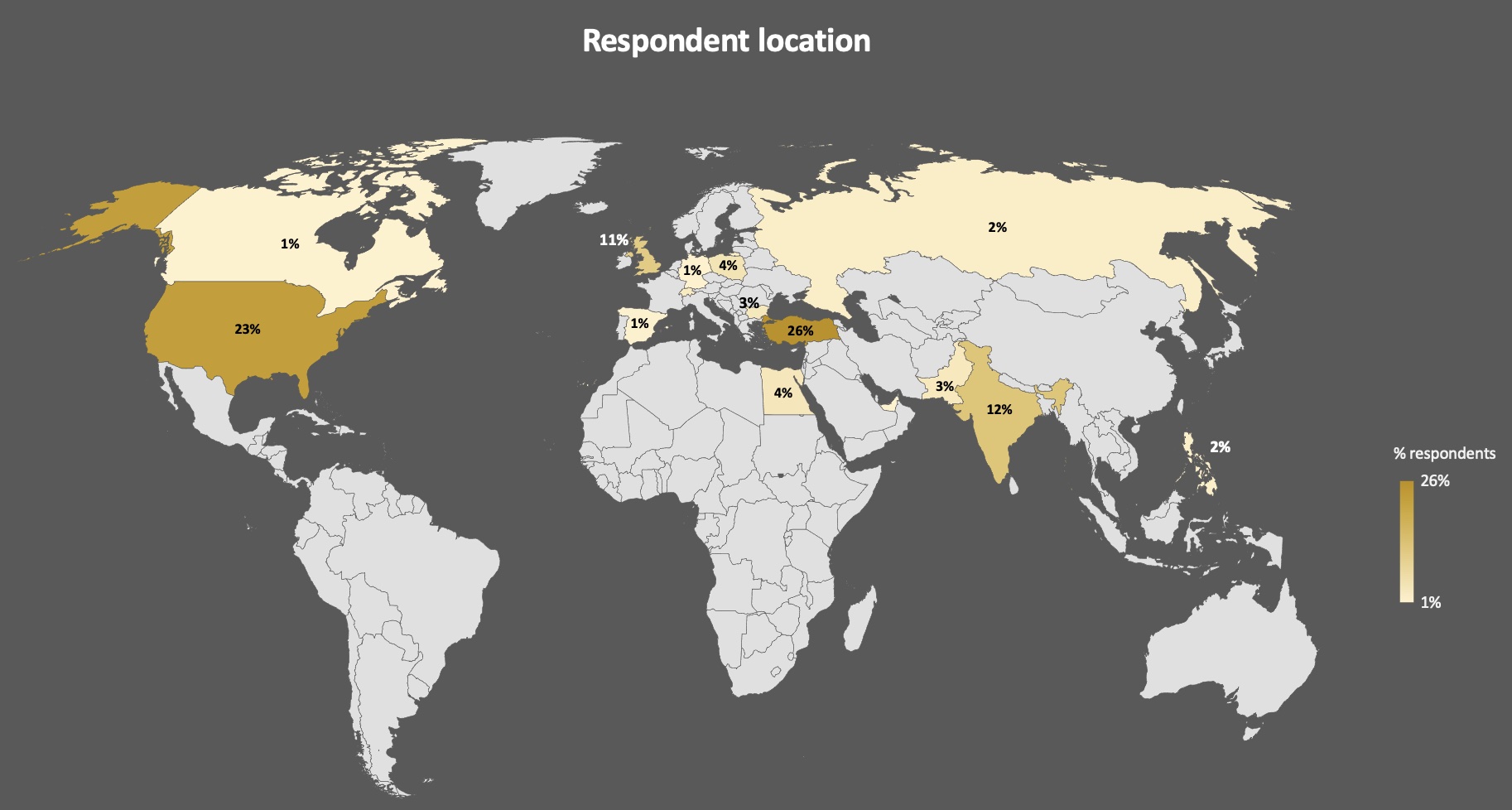
Results: A total of 7467 subjects attempted the survey with mean age of 42.6 years, 71.4% female, 60.9% Caucasians with most patients from US, European Union and India (table 1, figure 1). Among these 5219 (69.9% of respondents) were fully vaccinated and 1540 (20.2%) were not vaccinated with vaccine hesitancy (657,42.7%) and non-availability (534, 34.7%) being the most common reasons. Among 5927 vaccinated respondents, 979 (16.5%) had IIM, 2566 (43.3%) other AIDs, and 2382 (40.1%) were controls.
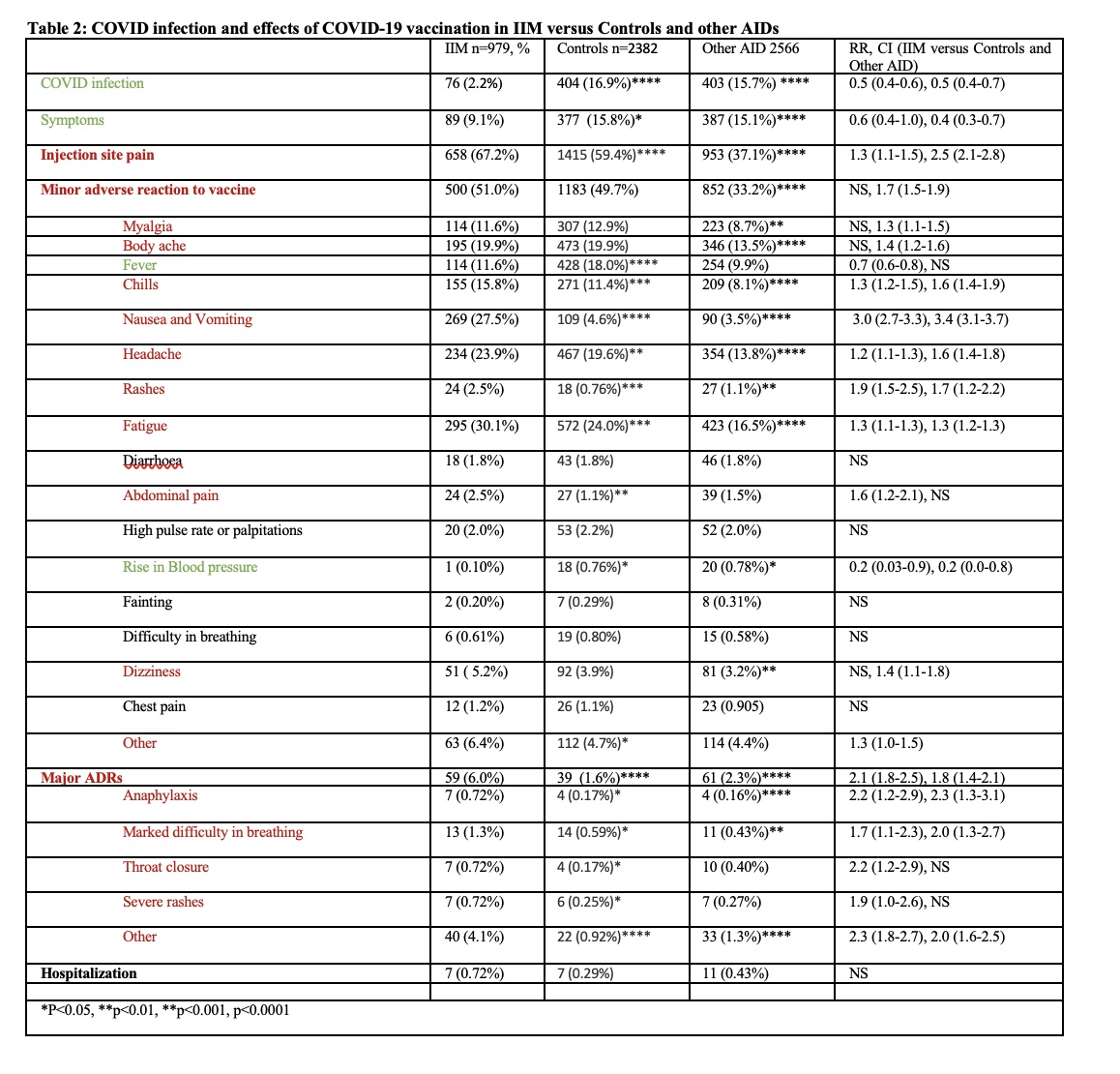
Respondents with IIM were elder (60 years) than other AIDs and controls (42.6 and 34.7 year respectively) (Table 1, Figure 1). A total of 875 (15.3%) respondents got Covid-19 infection, with significantly lower proportion of IIM patients (76, 2.2%) as compared to AIDs (403, 15.7%) and controls (404, 16.9%), p < 0.0001. Notably IIM patients were also less likely to be symptomatic than AIDs and controls when they got infected [RR 0.6 (0.4-1.0), 0.4 (0.3-0.7)].
Overall, 51.0% IIM had some symptoms (minor ADRs) after vaccination with only 6.0% being severe ADRs. IIM patients were equally prone to minor reactions as compared to controls (Table 2). However, they were more prone to anaphylaxis, marked dyspnea, and severe rashes. Overall, IIM exhibited higher prevalence of severe ADRs as compared with other AIDs. However, there was no difference in hospitalization among the groups.
Conclusion: IIMs patients had a modest increase in severe ADRs 7-day post vaccination as compared to controls as well as other autoimmune diseases, although not contributing to increased hospitalization. The survey in ongoing and will have much larger patient population and longitudinal results in future.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gupta L, Lilleker J, Agarwal V, Kardes S, Milchert M, Gheita T, Salim B, Velikova T, Distler O, Chinoy H, Aggarwal V, Aggarwal R. COVID-19 Vaccination in Autoimmune Disease (CoVAD) Study: Interim Analysis of Safety in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies from a Large Multicentre Global Survey [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/covid-19-vaccination-in-autoimmune-disease-covad-study-interim-analysis-of-safety-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies-from-a-large-multicentre-global-survey/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/covid-19-vaccination-in-autoimmune-disease-covad-study-interim-analysis-of-safety-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies-from-a-large-multicentre-global-survey/