Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative disease characterized by altered homeostasis of joint cartilage and bone, the functionality of which relies on chondrocytes and osteoblasts, that leads to the formation of a defective extracellular matrix (ECM). The ECM plays an essential role in bone biology as it provides the structure of cartilage which serves as a template for bone formation. Collagen X, main component of the ECM, has been described by our group as down-regulated in OA. Our data also points to an important role of the Wnt pathway in OA. Furthermore, Wnt proteins have been reported to inhibit chondrogenesis, and the Wnt pathway and its modulators have gained attention. Glypicans (GPC1 to GPC6) and NOTUM have been identified as modulators of this pathway. Notably, due to its highly specific inhibition of the Wnt pathway, NOTUM has been proposed as a therapeutic target in conditions with a high activity of the Wnt pathway is involved, such as OA.
We hypothesize that modulators of the Wnt pathway are involved in the development of OA. The aim of this study is to evaluate the presence of Glypicans and NOTUM in the serum, and their gene expression on BM-MSCs of OA patients and healthy individuals in order to determine whether significant differences exist and could clarify their likely involvement in OA.
Methods: Peripheral blood samples were obtained from OA patients, according to the ACR criteria, during routine rheumatologist visits. Samples from healthy individuals were obtained from the local Blood Bank. In both cases, serum was obtained. BM-MSCs form OA patients and healthy donors were isolated and expanded.
Quantitative ELISA assays for GPC1-6 and NOTUM were carried out using commercial kits (GPC1, #E-EL-H1710, Elabscience; GPC2, #E-EL-H1711, Elabscience;GPC3, #E-EL-H1712, Elabscience;GPC4, #E-EL-H1713, Elabscience;GPC5, #ELH-GPC5, RayBiotech;GPC6, #CSB-EL009708HU, Cusabio;NOTUM, #EK3787, Sab Biotech).
Expression of GPC1-6 was evaluated by RT-qPCR using gene-specific probes (Applied Biosystems; Assay ID: GPC1 Hs00892476_m1; GPC2 Hs00242584_m1; GPC3 Hs01018936_m1; GPC4 Hs00155059_m1; GPC5 Hs00270114_m1; GPC6 Hs00170677_m1).
Protein concentration in serum and ΔCt for each gene was calculated using GraphPad Prism 7 software. Differences between samples were analysed with Mann-Withney U and multiple t-test. Significance level set was p< 0.05.
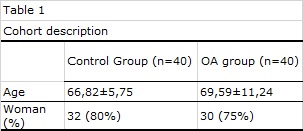
Results: A total of 40 OA patients and 40 healthy donors were included (Table 1).
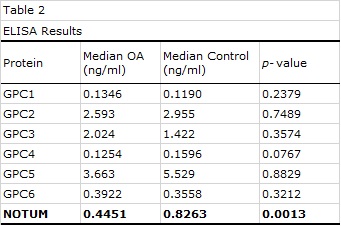
Out of 7 proteins analyzed, only NOTUM showed a significant difference groups (Table 2): MedianOA=0.4451ng/mL, MedianCONTROL=0.8263ng/mL, p=0.0013.
Gene expression analysis showed a significant down-expression of 3 genes (Figure 1): GPC1, MeanOA=5.74, MeanCONTROL=6.48 , p=0.53; GPC2, MeanOA=13.32, MeanCONTROL=14.53 , p=0.34; GPC3, MeanOA=10.07, MeanCONTROL=16.73 , p< 0.0001; GPC4, MeanOA=7.94, MeanCONTROL=7.63 , p=0.79; GPC5, MeanOA=15.31, MeanCONTROL=18.71 , p=0.042; GPC6, MeanOA=6.94, MeanCONTROL=14.17 , p< 0.0001.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that low levels of GPC3, GPC5, GPC6 and NOTUM may contribute to the development of OA. The lack of these inhibitors promotes the activation of the Wnt pathway, high activity of which has been related with OA.
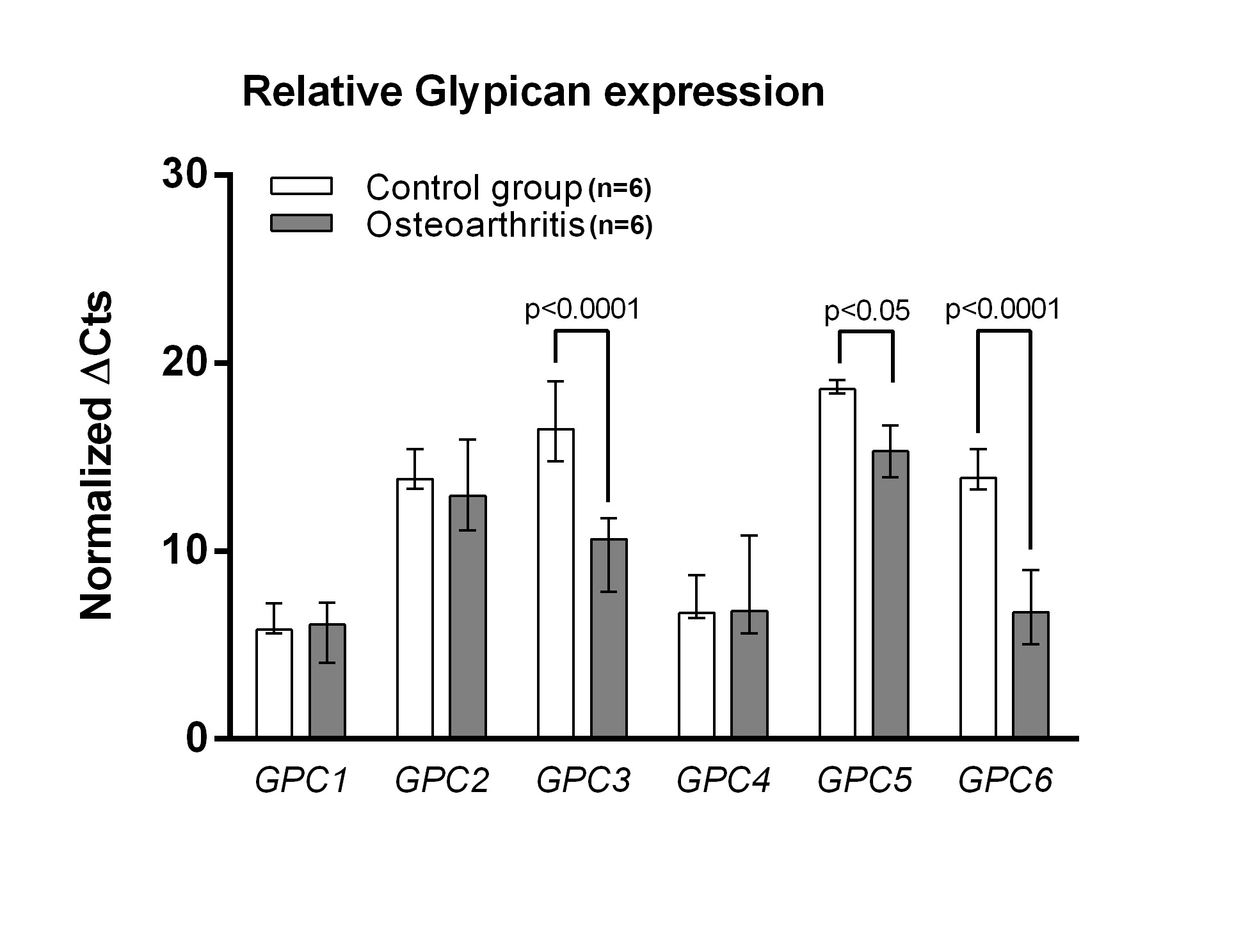 Figure 1. Glypican 1-6 gene expression on BM-MSCs form OA patients and healthy donors (∆Cts normalized to house-keeping genes β-actin and RNA18S5).
Figure 1. Glypican 1-6 gene expression on BM-MSCs form OA patients and healthy donors (∆Cts normalized to house-keeping genes β-actin and RNA18S5).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mucientes A, Herranz E, Lois P, Candelas G, Abasolo L, Rodriguez-Rodriguez L, Lamas J, Fernandez-Gutierrez B. Contribution of NOTUM and Glypicans to the Development of Osteoarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/contribution-of-notum-and-glypicans-to-the-development-of-osteoarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/contribution-of-notum-and-glypicans-to-the-development-of-osteoarthritis/