Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: RA – Treatments Poster II: PROs, Biomarkers, & Systemic Inflammation (1223–1256)
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: In MTX-naïve patients (SELECT-EARLY/M13-545 Phase 3 study) UPA 15 mg QD monotherapy (UPA Mono) demonstrated significant and clinically meaningful improvements in RA signs and symptoms vs MTX.1 In MTX-IR patients (SELECT-MONOTHERAPY/M15-555 Phase 3 study), switching to UPA Mono showed significant improvements in RA signs and symptoms versus continuing MTX.2 These study populations offer excellent opportunities to dissect disease and therapeutic mechanisms using biomarker analysis. The objective of this analysis was to compare the biological activity of MTX and UPA Mono in MTX-naïve and MTX-IR RA patients, via evaluation of circulating protein biomarkers related to inflammation compared with clinical disease activity.
Methods: Patients from the SELECT-EARLY (MTX, n = 96; UPA 15 mg QD, n = 96) and SELECT-MONOTHERAPY (MTX, n = 79; UPA 15 mg QD, n = 99) studies were randomly selected from the subsets of patients with available plasma samples. The levels of 92 inflammation related proteins were analyzed using the Olink platform; change from baseline in protein levels were expressed as Log2 Fold Change; a Repeated Measure Mixed Linear Model identified proteins differentially modulated by MTX and UPA compared to Baseline. Pathway analysis was performed with Ingenuity Pathway Analysis.
Results: In MTX-naïve RA patients, both UPA Mono and MTX modulated a broad range of protein biomarkers associated with key pathways implicated in RA pathogenesis. UPA Mono had a faster onset of effect than MTX (Table 1) determined by impact on protein biomarker levels. Moreover, UPA Mono had a more profound effect on biomarkers that are significantly associated with baseline disease activity measures. In MTX-IR RA patients, only UPA Mono exerted significant effects on a subset of the biomarkers identified above, whereas continued treatment with MTX had no measured effect. Pathway analysis indicated that in MTX-naïve RA Patients, UPA Mono and MTX were predicted to elicit similar effects on adaptive, innate immune cells and on non-immune bone, connective tissue, and angiogenesis related pathways; but UPA Mono did so faster than MTX. In MTX-IR RA patients, only UPA Mono was predicted to affect those pathways, although to a lesser extent than in MTX-naïve RA patients.
Conclusion: UPA Mono exerted significant effects on protein biomarkers in both MTX-naïve and MTX-IR patients, whereas MTX did so only in MTX-naïve patients. The more profound and rapid effects of UPA Mono in MTX-naïve patients provide a possible mechanism for the superior clinical efficacy of UPA Mono over MTX. Overall, treatment with UPA monotherapy resulted in the normalization of key pathways associated with the pathobiology of RA in both MTX-naïve and MTX-IR patients, consistent with our previous observations on the effect of UPA in combination with csDMARDs in csDMARD-IR RA patients.3,4
References:
- Smolen JS et al. Lancet 2019;393:2303-11.
- van Vollenhoven R et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2020;72:1607-20.
- Sornasse T et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2019;78:365-6.
- Sornasse T et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79:581-2.
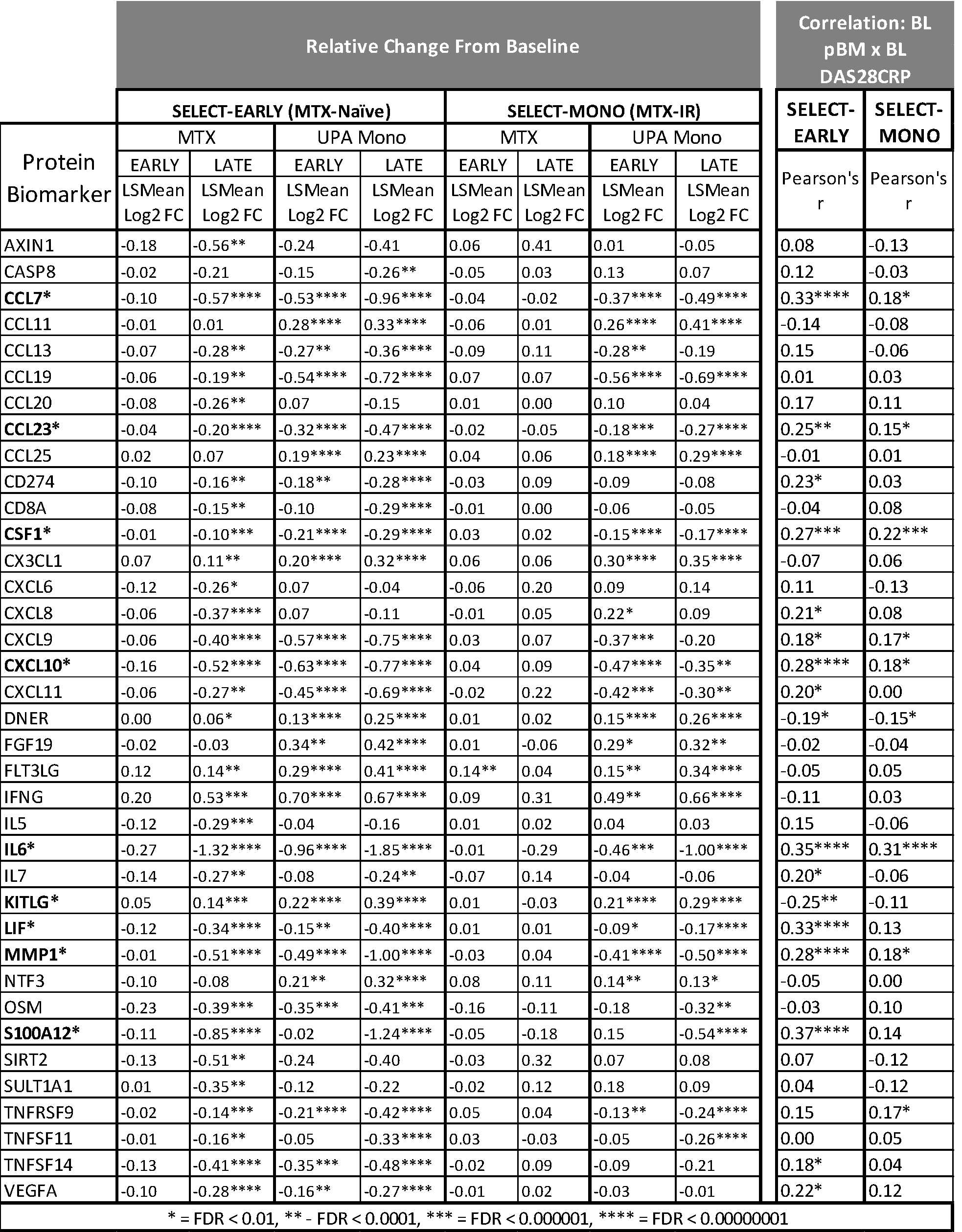 Table 1: Overview of Biomarkers Modulated by UPA or MTX
Table 1: Overview of Biomarkers Modulated by UPA or MTX
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sornasse T, Camp H, Cai F, Klaff J, McInnes I. Comparison of the Effects of Upadacitinib Monotherapy with MTX on Protein Biomarkers in MTX-Naïve and MTX-Inadequate Responders in Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results from the SELECT-EARLY and SELECT‑MONOTHERAPY Phase 3 Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-the-effects-of-upadacitinib-monotherapy-with-mtx-on-protein-biomarkers-in-mtx-naive-and-mtx-inadequate-responders-in-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-results-from-the-select-ea/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-the-effects-of-upadacitinib-monotherapy-with-mtx-on-protein-biomarkers-in-mtx-naive-and-mtx-inadequate-responders-in-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-results-from-the-select-ea/
