Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Oral health impairment is common in patients with immune-mediated rheumatic diseases (IMRDs) due to chronic inflammation and immune dysregulation. These complications can worsen systemic inflammation, potentially influencing disease activity and quality of life. Although previous studies have explored oral health in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and Sjögren’s syndrome (SS), few have compared oral health status and dental care practices between IMRDs and non-immune-mediated rheumatic diseases (NIMRDs). Understanding these differences may help optimize integrated care strategies for rheumatic patients.
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study including 670 patients: 569 with IMRDs and 101 with NIMRDs. Patients were consecutively enrolled from rheumatology outpatient clinics at a tertiary care center between December 2021 and May 2025, based on confirmed diagnoses according to international classification criteria. The IMRD group included patients with RA, SLE, and SS, while the NIMRD group included patients diagnosed with osteoarthritis and osteoporosis. Clinical, demographic, and treatment characteristics were recorded. A structured survey evaluated awareness of dental impact, rheumatologist advice, referral desire, dental visits, and toothbrushing habits. Primary comparisons were made between IMRDs and NIMRDs, with additional subgroup analyses comparing RA, SLE, and SS individually to the NIMRD group. Comparisons were performed using the Student’s t-test and Chi-square test, with p < 0.05 considered statistically significant.
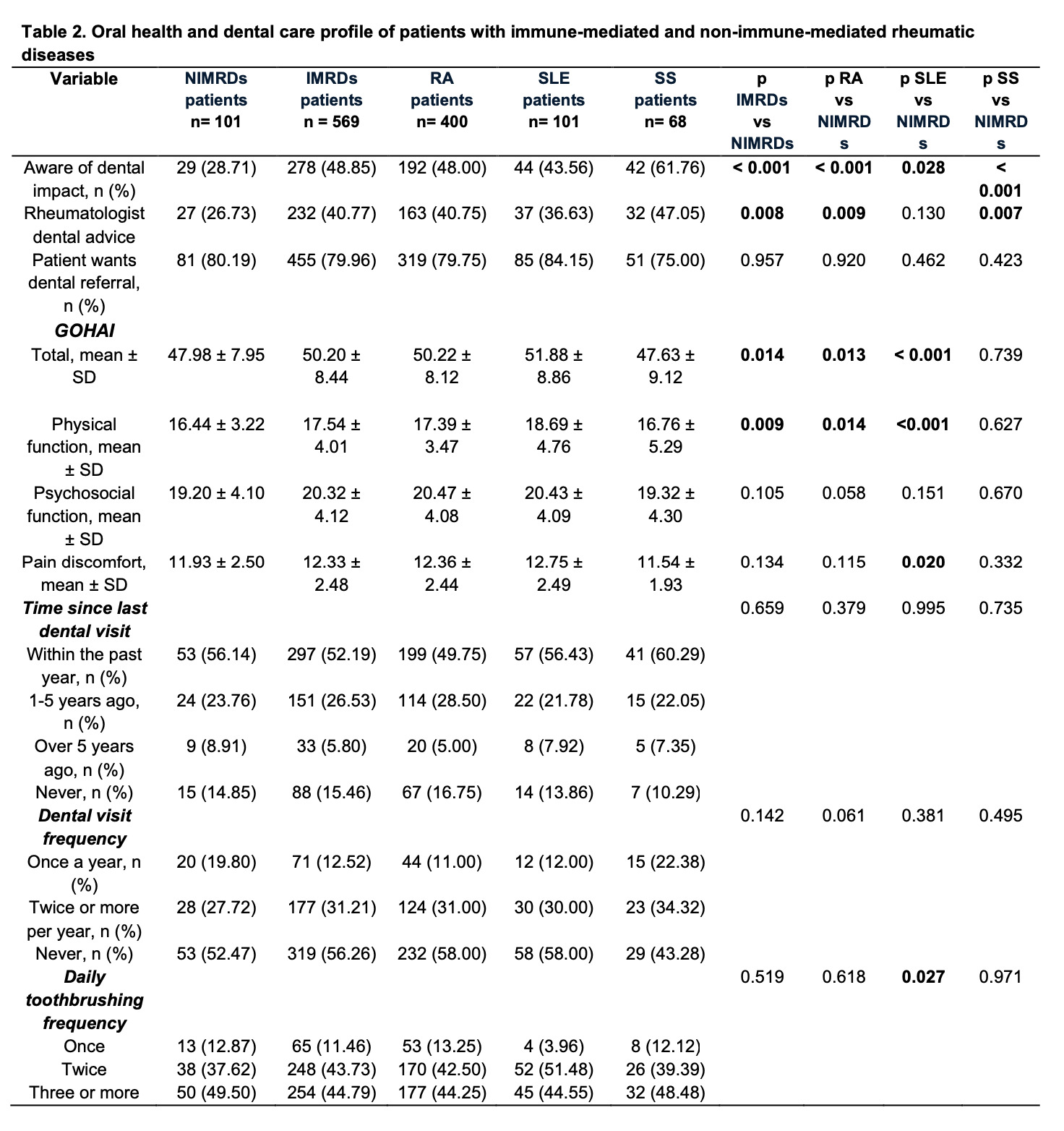
Results: We included 670 patients (569 IMRDs: RA n=400, SLE n=101, SS n=68; 101 NIMRDs). IMRD patients were predominantly female (93.14%) with a mean age of 50.70 ± 14.68 years. Awareness of the oral impact of rheumatic disease was higher in IMRDs vs. NIMRDs (48.85% vs. 28.71%; p < 0.001), as was rheumatologist dental advice (40.77% vs. 26.73%; p=0.008). Referral desire was high across both groups (79.96% vs. 80.19%; p=0.957). GOHAI total scores were 50.20 ± 8.44 in IMRDs and 47.98 ± 7.95 in NIMRDs (p=0.014), with significant differences also observed in the physical function domain (17.54 ± 4.01 vs. 16.44 ± 3.22; p=0.009). No significant differences were found in psychosocial function or pain/discomfort. Subgroup analysis showed that SS patients had the lowest GOHAI total score (47.63 ± 9.12) and the lowest pain/discomfort score (11.54 ± 1.93). Dental visit frequency and toothbrushing habits showed no significant differences between groups.
Conclusion: Patients with IMRDs demonstrated greater awareness of oral health and received more dental advice than those with NIMRDs; however, significant oral health impairment persists, particularly among SS patients. These findings highlight the unmet need for integrated rheumatology-dental care to improve oral health outcomes across all rheumatic disease populations.
Table 1. Clinical and treatment characteristics of patients with immune-mediated and non-immune-mediated rheumatic diseases
.jpg) Table 2. Oral health and dental care profile of patients with immune-mediated and non-immune-mediated rheumatic diseases
Table 2. Oral health and dental care profile of patients with immune-mediated and non-immune-mediated rheumatic diseases
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Alarcon-Jarquin M, Garcia-Garcia F, Lopez-Flores V, Galindo-Bandt A, Arellano-Alvarez M, Gonzalez-Melendez A, Figueroa-Parra G, Galarza-Delgado D, Riega-Torres J. Comparative Analysis of Oral Health and Dental Care in Patients With Immune-Mediated and Non-Immune-Mediated Rheumatic Diseases [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparative-analysis-of-oral-health-and-dental-care-in-patients-with-immune-mediated-and-non-immune-mediated-rheumatic-diseases/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparative-analysis-of-oral-health-and-dental-care-in-patients-with-immune-mediated-and-non-immune-mediated-rheumatic-diseases/