Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Few studies have been reported on the use of metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS) in patients with connective tissue disease (CTD) co-infections, and more relatively large-scale data are still needed to support the value of mNGS in patients with CTD co-infections. We aim to evaluate the clinical value of mNGS in patients with CTD co-infections and the impact on anti-infection regimens.
Methods: A total of 180 patients diagnosed with CTD co-infections who were hospitalized in the Department of Rheumatology and Immunology of the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University between October 2020 and April 2024 were included in this study, and 193 specimens were collected. The results of mNGS were retrospectively analyzed to compare the positivity rates of different samples, testing methods, periods, and various CTDs, and finally to analyze their impact on anti-infection regimens.
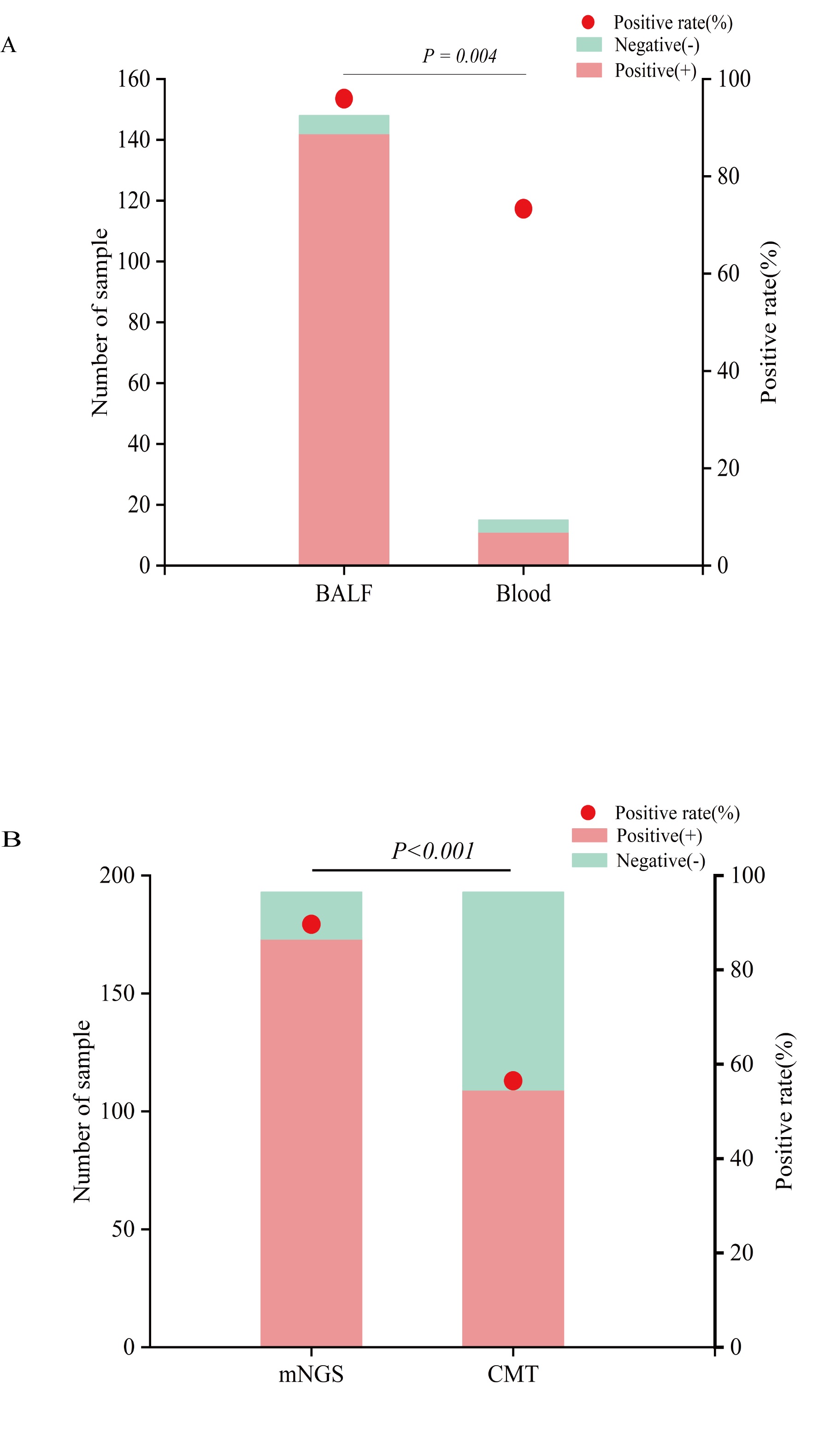
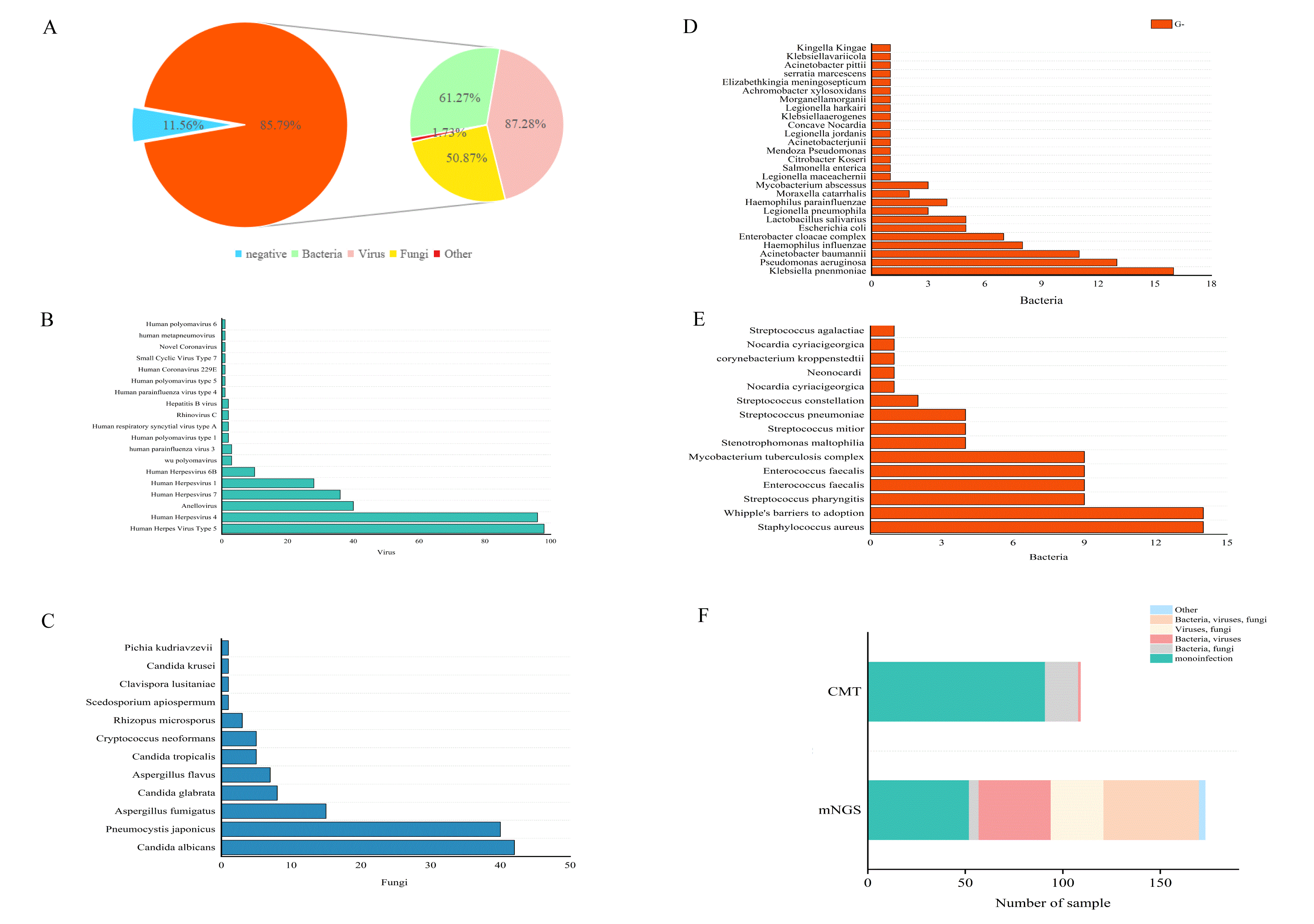
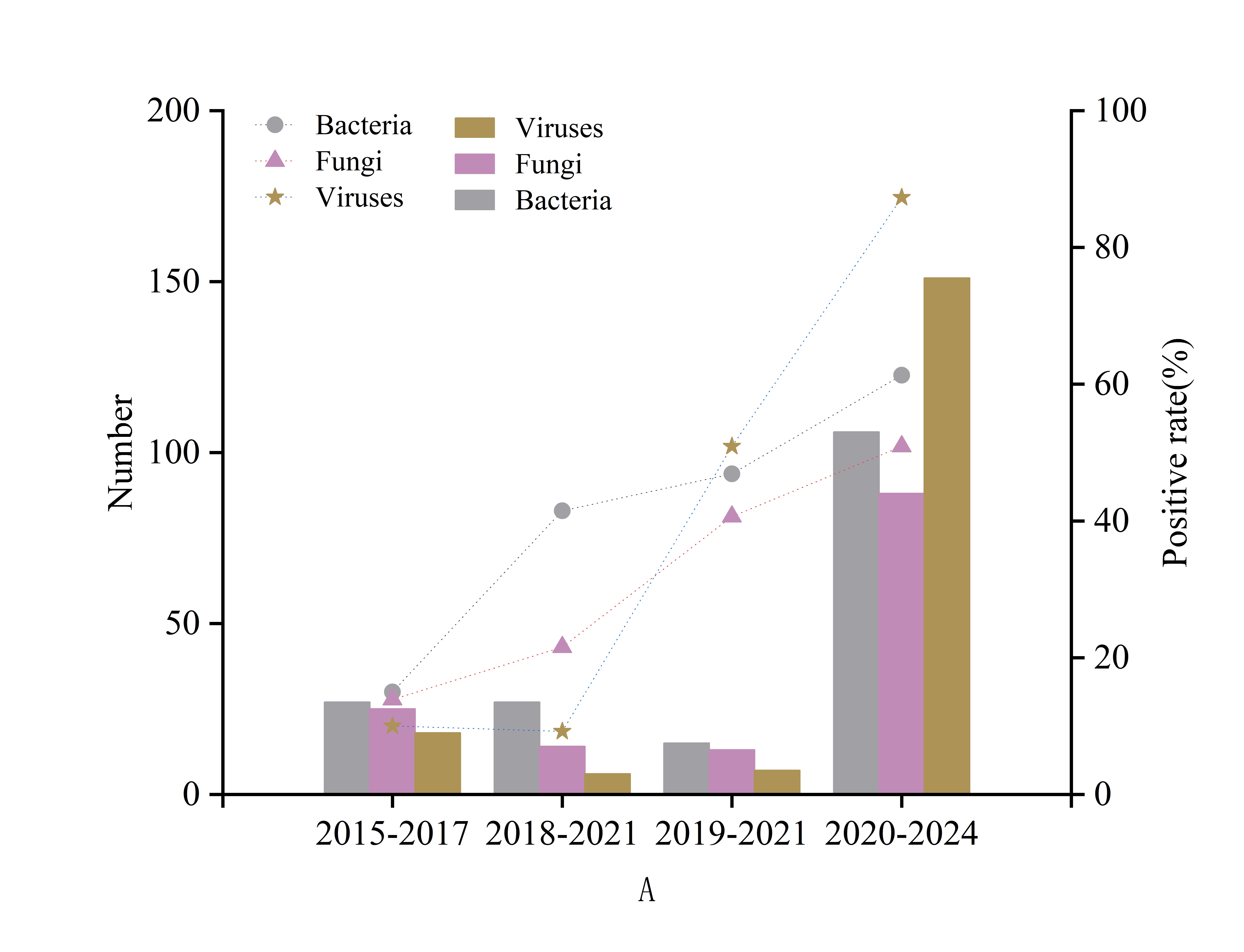
Results: Results: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) was most common in infected CTD. mNGS has a higher pathogen detection rate in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid(BALF) samples compared to blood samples (95.95%VS73.33%, p=0.004) and showed 100% positivity in cerebrospinal fluid samples (Figure 1). In comparison to conventional methods testing (CMT), mNGS has a higher positive rate (89.64%VS55.96%, p< 0.001), as shown in Figure 1. Pathogen positivity rates have increased annually, with variations between periods(Figure2). The most common pathogens detected were viruses (n=151,87.28%), followed by bacteria and fungi (Figure3). There were differences in pathogen susceptibility among different CTD. In particular, there was a statistically difference (p=0.03) in fungi. A total of 160 individuals received antibiotics, 95.63% demonstrated significant improvements in their infections compared to those observed before the initiation of treatment.
Conclusion: mNGS has great potential in diagnosing co-infections in CTD patients and is superior to conventional methods testing. It is effective in helping clinicians identify infections and optimize antibiotic therapy.
Distribution of mNGS results by pathogen type. Type distribution of mNGS(A); Distribution of viruses (B); Distribution of fungi(C); Distribution of G- bacteria(D); Distribution of G+ bacteria(E); Comparison of CMT and mNGS for disease pathogens(F).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Xiao Y, Lu A, Mo H, He Z, Wen J, Yin X. Clinical Value of Metagenomic Next-generation Sequencing in Patients with Connective Tissue Disease Co-infections: A Single-center Study from Southern Hospital in China [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-value-of-metagenomic-next-generation-sequencing-in-patients-with-connective-tissue-disease-co-infections-a-single-center-study-from-southern-hospital-in-china/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-value-of-metagenomic-next-generation-sequencing-in-patients-with-connective-tissue-disease-co-infections-a-single-center-study-from-southern-hospital-in-china/