Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2022
Title: Systemic Sclerosis and Related Disorders – Clinical Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: The clinical importance of nailfold capillaroscopy (NFC) has grown since its inclusion in the 2013 ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria for systemic sclerosis (SSc), yet few centers have expensive video NFC systems, and dermatoscope evaluations have limited sensitivity for abnormality detection. Dinolite™ (AF4515-N2UT) offers a handheld, inexpensive, and convenient method for in-clinic NFC images at 200x magnification (Fig. 1). We piloted the clinical utility of Dinolite NFC in patients with SSc.
Methods: Patients who fulfilled ACR/EULAR 2013 SSc Classification Criteria with Raynaud phenomenon (RP) symptoms (n=15) and healthy controls (HC) (n=14) were recruited to this prospective pilot study. Dinolite NFC was performed for bilateral fingers, excluding the thumb, in the clinic. Two adjacent 1mm images in the middle of the nailfold were captured and analyzed for each finger (Fig. 2). First, a blinded assessor classified NFC as “normal” or “abnormal” based on the presence or absence of the “scleroderma pattern” as previously described. Second, the prevalences of specific NFC morphological abnormalities were recorded (Table 1). Lastly, the distal capillary row was analyzed using Dinolite measurement software to calculate per linear mm, 1) Mean semi-quantitative score (0 = no changes, 1 = ≤ 33%, 2 = 34–66%, 3 = ≥ 67%) for proportion of capillary alterations/reductions consistent with scleroderma pattern, and 2) Mean capillary density. Patients completed the newly developed RP patient-reported outcome, the Assessment of Systemic Sclerosis – Associated Raynaud Phenomenon (ASRAP) questionnaire (range 20-80, with higher scores indicating worse symptoms). Descriptive statistics, Fischer exact tests, Spearman’s Rho coefficient, and Wilcoxon rank-sum tests were performed using Stata, v.17.0, College Station, TX.
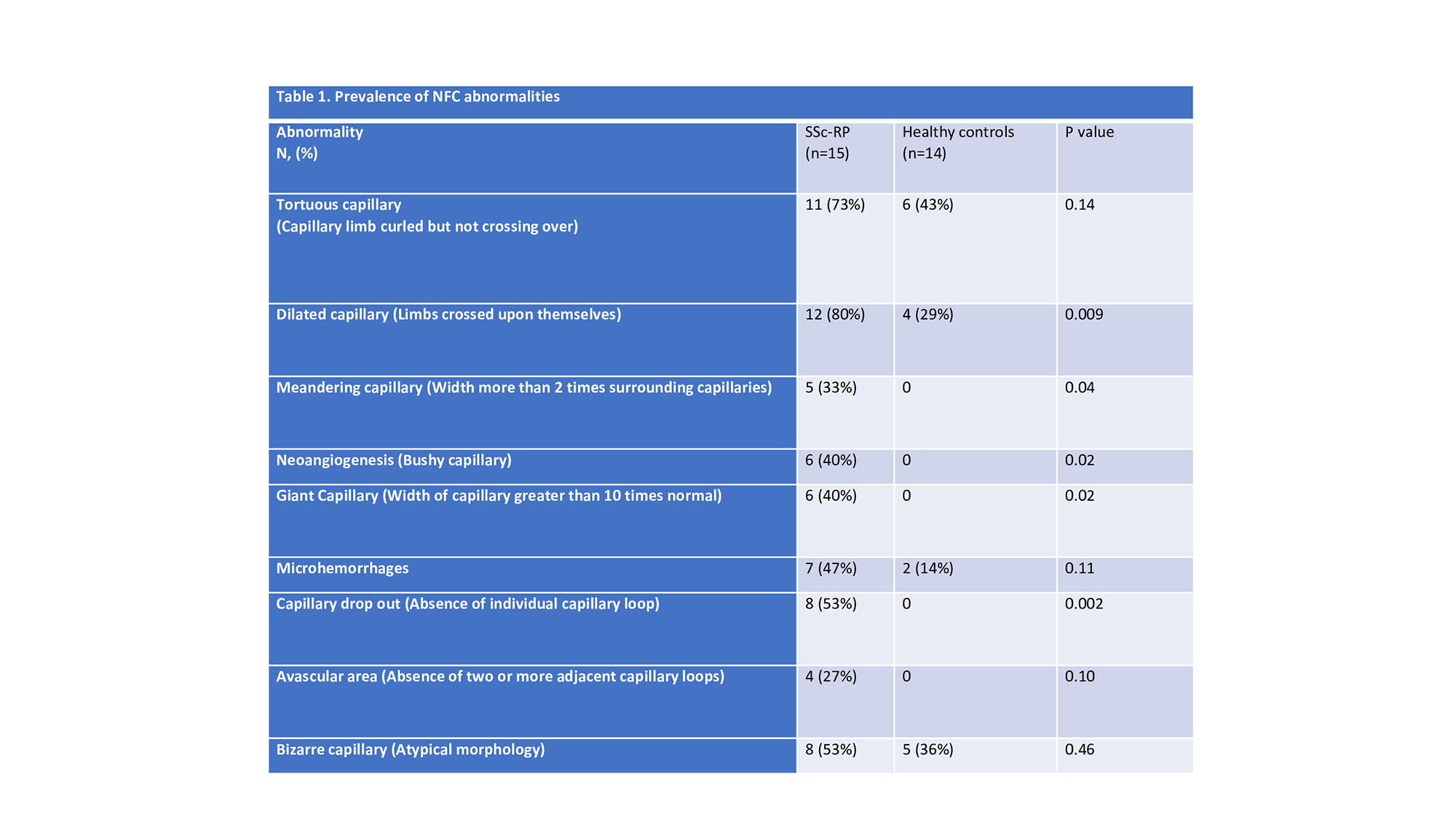
Results: Patients with RP and HC, respectively, were predominantly white (n=10, 67% vs. n=10, 71%) women (n=13, 87% vs. n=13, 93%) with a median (IQR) age of [59 (49-64) vs. 48 (39-57)]. Scleroderma NFC pattern was more prevalent in SSc compared to HC (87% vs. 0%, p< 0.001). Mean semi-quantitative score in SSc was 1.88 compared to 0 in HC (p< 0.001). Mean capillary density measured per linear mm was lower in SSc compared to HC (5.5 vs. 9.3, p< 0.001). Prevalence of various specific NFC abnormalities tended to be higher in SSc compared to HC (Table 1) with significantly more dilated capillaries, meandering capillaries, neoangiogenesis, giant capillaries, and capillary drop-out in SSc. Among SSc patients, mean (SD) ASRAP score was 53.2±11.9 and correlated significantly with mean semi-quantitative score (rho 0.59, p=0.02).
Conclusion: SSc patients have more NFC abnormalities and lower mean capillary densities than HC as assessed using Dinolite. More NFC abnormalities (mean semi-quantitative score) as assessed using Dinolite are present in SSc-RP who reported worse RP symptoms as assessed by the ASRAP instrument. Future work includes a larger longitudinal study with greater diversity to investigate associations between NFC abnormalities, ASRAP scores, and characteristics including disease duration and subtype, presence of digital ulcerations, medications, and laboratory parameters.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Madathanapalli K, Williams A, Gunes B, Wilson F, Pauling J, Domsic R, Yu L, Hinchcliff M. Clinical Nailfold Capillaroscopy Using Dinolite Microscope in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-nailfold-capillaroscopy-using-dinolite-microscope-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-nailfold-capillaroscopy-using-dinolite-microscope-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis/