Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Deucravacitinib is a first-in-class, oral, selective, allosteric tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) inhibitor approved in multiple countries for the treatment of adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis and is under investigation in phase 3 trials in SLE, Sjögren’s disease (SjD), and PsA. In the 48-week, double-blind, phase 2 PAISLEY trial (NCT03252587) in patients with active SLE, the primary endpoint and all key secondary endpoints were met with the deucravacitinib 3-mg twice-daily (BID) dose. Patients with SLE, especially those with anti-Ro/Sjögren’s syndrome–related antigen A (SSA) antibodies, share pathophysiological, genetic, and clinical similarities to patients with SjD, including common inflammatory signatures. Here, we describe clinical efficacy and patient-reported outcomes (PROs), including pain and fatigue, in a subpopulation of patients from PAISLEY who were anti-Ro/SSA positive and evaluate if outcomes remained consistent with those in the overall PAISLEY population.
Methods: In PAISLEY, patients with active SLE received placebo (PBO; n = 90) or deucravacitinib 3 mg BID (n = 91), 6 mg BID (n = 93), or 12 mg once daily (QD; n = 89). Patients with a positive anti-Ro/SSA antibody test result at baseline were included in this post hoc analysis (PBO, n = 48; deucravacitinib 3 mg BID, n = 52; 6 mg BID, n = 46; 12 mg QD, n = 42). Clinical efficacy outcome response rates, including those for SLE Responder Index-4 (SRI[4]) and British Isles Lupus Assessment Group–based Composite Lupus Assessment (BICLA), were reported with a prespecified nonresponder imputation. Mean change from day 1 (CFD1) at week 48 in PROs, including the Pain numerical rating scale (NRS) scored from 0 to 10 and Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS) Fatigue 7a short form, was calculated using a control-based pattern imputation for missing data. Results were descriptive.
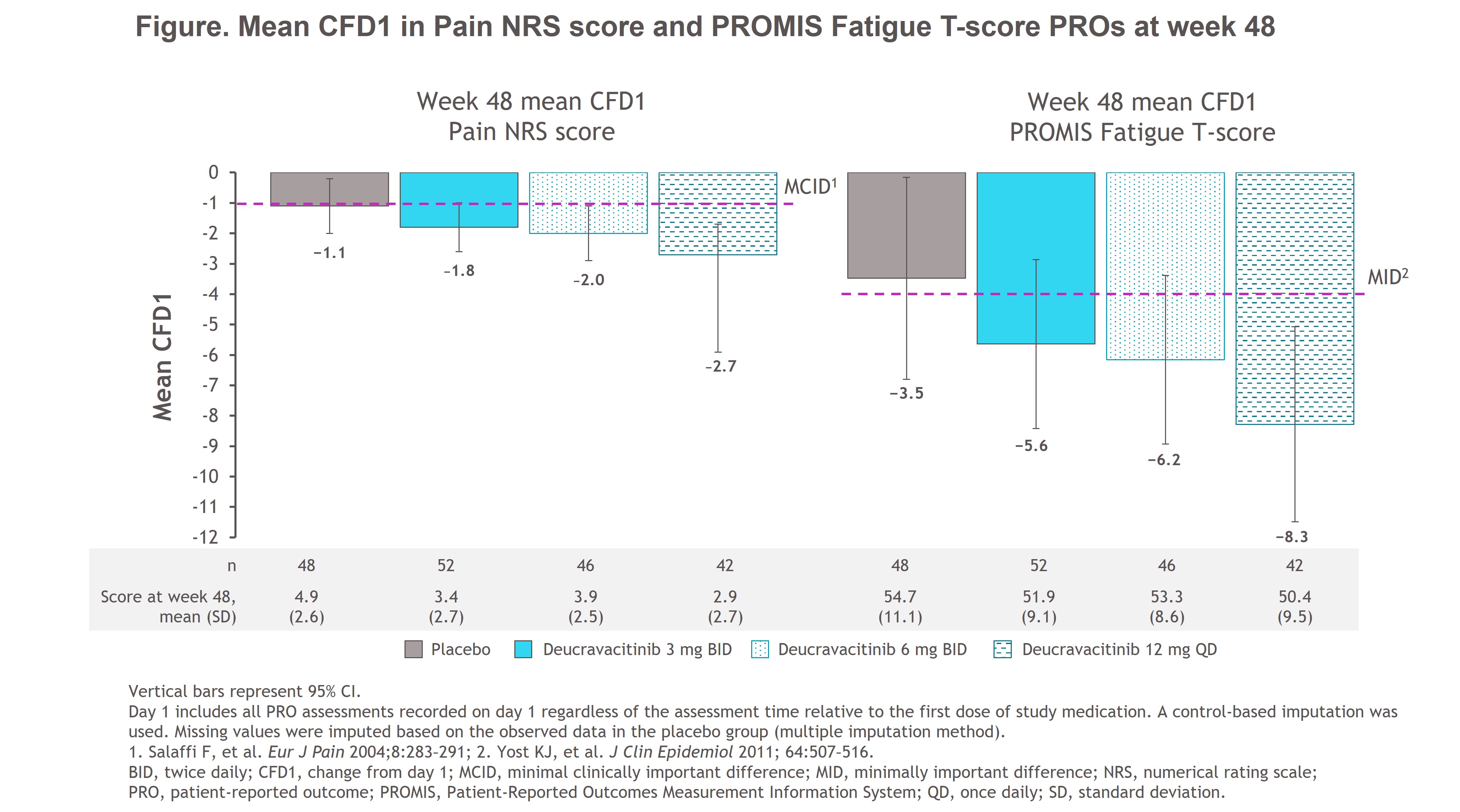
Results: At week 48, patients with SLE who were anti-Ro/SSA positive and receiving deucravacitinib had increased response rates vs those receiving PBO for SRI(4) (3 mg BID, 65.4%; 6 mg BID, 43.5%; 12 mg QD, 54.8%; PBO, 33.3%) and BICLA (3 mg BID, 51.9%; 6 mg BID, 32.6%; 12 mg QD, 42.9%; PBO, 25.0%). Greater mean CFD1 in pain and fatigue PROs was reported in all patients receiving deucravacitinib vs PBO; more patients receiving deucravacitinib reported improvements greater than or equal to the minimal clinically important differences of −1 for Pain and −4 for Fatigue T-score (Figure). Patients receiving deucravacitinib had numerical improvements in mean Pain NRS score and Fatigue T-score at week 48 vs those receiving PBO (Figure).
Conclusion: In a subpopulation of patients from PAISLEY with active SLE who were anti-Ro/SSA positive, those receiving deucravacitinib had improvements in key clinical outcomes, pain, and fatigue vs those receiving PBO. Results were consistent with those in the overall PAISLEY population. These findings warrant investigation of deucravacitinib for the treatment of SjD based on the similarities between SjD and SLE.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fisher B, Bootsma H, Strand V, Ng W, Wegman T, Becker B, Choi J, Sreih A, Chen L, Christodoulou A, Morand E. Clinical Efficacy and Patient-Reported Outcomes in Anti-Ro/Sjögren’s Syndrome–Related Antigen a Antibody–Positive Patients with Active SLE Treated WithDeucravacitinib in the Phase 2 PAISLEY Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-efficacy-and-patient-reported-outcomes-in-anti-ro-sjogrens-syndrome-related-antigen-a-antibody-positive-patients-with-active-sle-treated-withdeucravacitinib-in-the-ph/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-efficacy-and-patient-reported-outcomes-in-anti-ro-sjogrens-syndrome-related-antigen-a-antibody-positive-patients-with-active-sle-treated-withdeucravacitinib-in-the-ph/