Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Precapillary Pulmonary Hypertension (PPH) is a known complication of connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease (CTD-ILD) but at present requires right heart catheterization (RHC) for definitive diagnosis. Computed tomography (CT) imaging measures of vascular pruning have been associated with pulmonary vascular disease, but it is unknown whether these CT measures associate with PPH in patients with CTD-ILD. The aims of this study were to 1) compare clinical characteristics of patients with CTD-ILD with and without PPH, 2) assess if there are quantitative CT vascular measures that associate with the presence of PPH, and 3) determine if these comparisons differed across various rheumatic diseases.
Methods: We performed a retrospective review of adult patients ( >18 years old) with ICD-code diagnoses of ILD and connective tissue disease (CTD) with both a CT chest and RHC within two years of each other in the electronic medical record. Medical charts were reviewed for confirmation of ILD by a pulmonologist, CTD by a rheumatologist, and presence of PPH or absence of pulmonary hypertension by a pulmonologist. CT chest images underwent automated 3D vasculature reconstruction using the Chest Imaging Platform (www.chestimagingplatform.org) with vessel size estimation for calculation of blood vessel volume in arterial, venous, and total blood vessels of size greater than or less than 5 mm2 and 10 mm2; these values were divided by CTLV (total lung volume in Liters) to measure blood vessel volume normalized to total lung volume. Descriptive and comparative analyses using Chi-square (categorical variables) and Wilcoxon-ranked sum (continuous variables) tests were performed using R version 4.0.2.
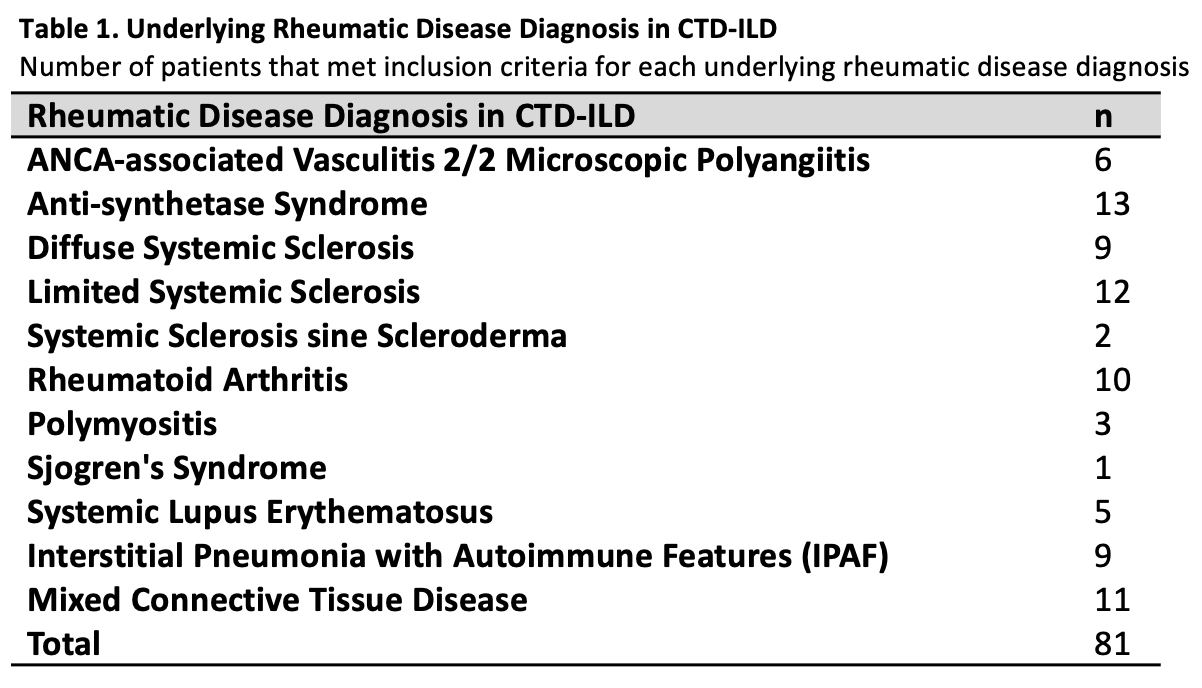
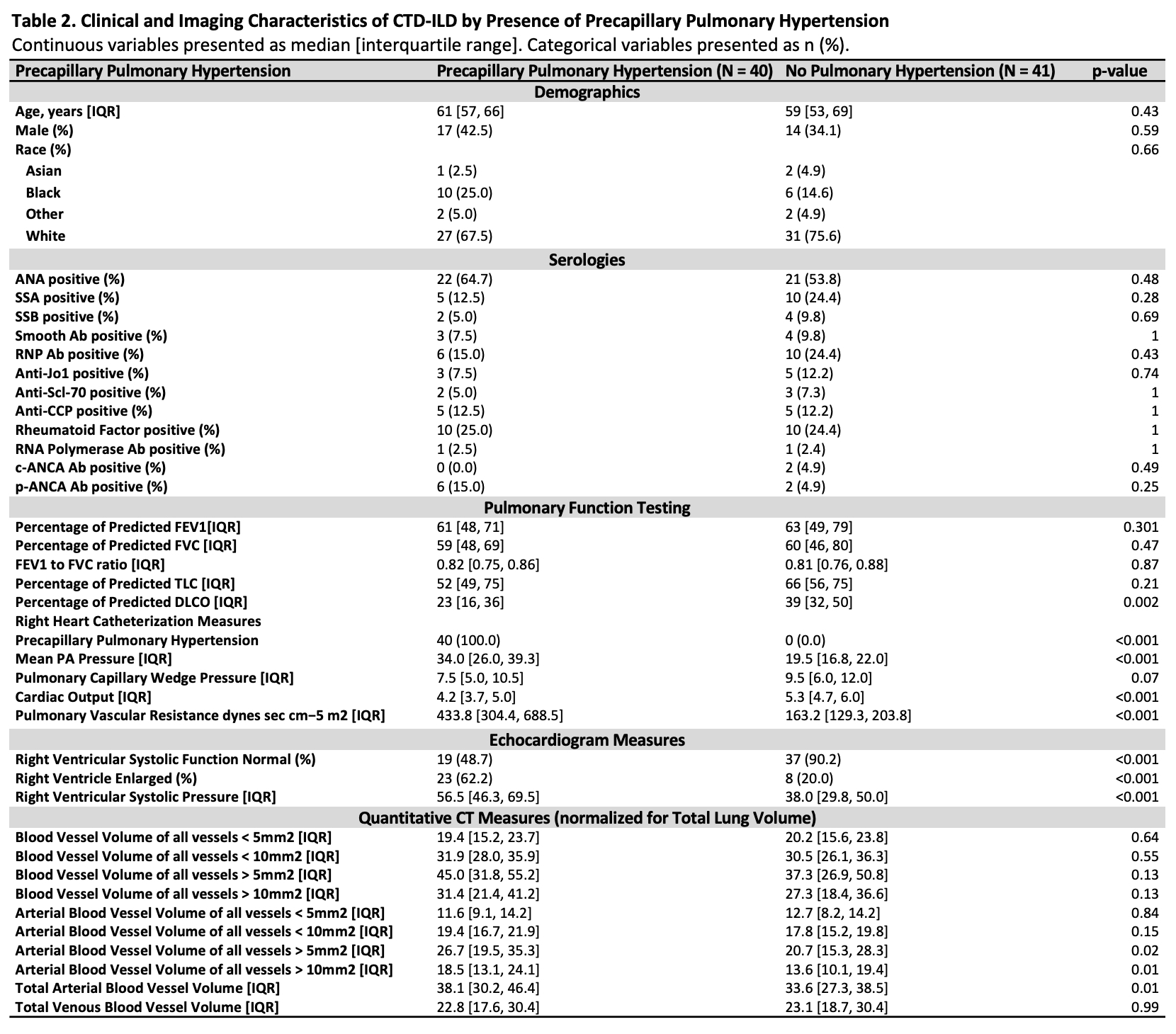
Results: 81 patients met our inclusion criteria (41 without PPH and 40 with PPH; 6 microscopic polyangiitis, 13 anti-synthetase syndrome, 9 diffuse systemic sclerosis (SSc), 12 limited SSc, 2 SSc sine scleroderma, 10 rheumatoid arthritis, 3 polymyositis, 1 Sjögren’s, 5 systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), 9 interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features (IPAF), and 11 mixed CTD). There were no statistical differences in age, sex, race, ethnicity, positive ANA, other autoimmune serologies, spirometry, and TLC measures in patients with PPH and patients without pulmonary hypertension. Predicted carbon monoxide diffusion capacity (DLCO) was significantly reduced in PPH (p=0.002). On quantitative CT compared to patients without pulmonary hypertension, patients with PPH had significantly greater blood vessel volume in arterial vessels (p=0.014), and in arterial vessels greater than 5 mm2 (p=0.016) and 10 mm2 (p=0.014), respectively.
Conclusion: Patients with CTD-ILD and precapillary pulmonary hypertension were found on quantitative CT to have greater arterial lung blood volume in vessels of size greater than 5 mm2 and 10 mm2. This suggests that distal increases in pulmonary vascular resistance lead to proximal arterial vascular dilation and an increased arterial blood volume on CT scan. Quantitative analysis of CT chest imaging in CTD-ILD may be a useful diagnostic tool for precapillary pulmonary hypertension; however, prospective studies are needed.
Number of patients that met inclusion criteria for each underlying rheumatic disease diagnosis
Continuous variables presented as median [interquartile range]. Categorical variables presented as n (%).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jesudasen S, Patel B, D'Silva K, Nardelli P, San José Estépar R, Washko G, San José Estépar R, Rahaghi F, Montesi S. Clinical Characteristics and Quantitative CT Findings in Connective Tissue Disease-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-characteristics-and-quantitative-ct-findings-in-connective-tissue-disease-associated-interstitial-lung-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-characteristics-and-quantitative-ct-findings-in-connective-tissue-disease-associated-interstitial-lung-disease/