Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 12, 2022
Title: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster I: Diagnosis
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Despite improvements in the treatment of lupus nephritis (LN), the prognosis remains unsatisfactory, and a need for non-invasive biomarkers for early detection endures. Previously, the usefulness of Serpin peptidase inhibitor clade C (antithrombin) member 1 (SERPINC1) and alpha-1-acid glycoprotein (ORM1) have been proposed as urine biomarkers for LN diagnosis through proteomics studies. However, their usefulness at the early disease stage has not yet been elucidated.
This study investigated the utility of urine SERPINC1 and ORM1 as early biomarkers for LN in the MRL-lpr mice, murine models of LN.
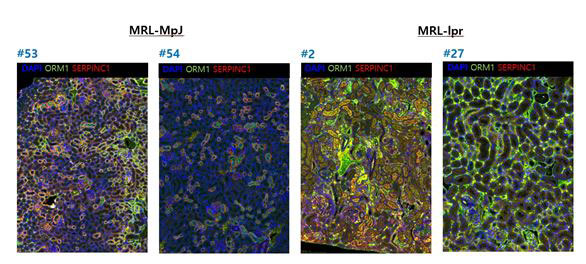
Methods: Urine samples were collected from MRL-lpr and MRL/MpJ mice at ages 13 and 23 weeks. Urine SERPINC1, ORM1, creatinine, and albumin were analyzed using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Levels of urine SERPINC1, ORM1, and albumin were corrected with creatinine concentration. Kidney biopsies of both sets of mice at 23 weeks were performed, and expression of ORM1 and SERPINC1 in kidney tissues was determined by opal multiplexed immunofluorescent staining. The activity and chronicity in kidney pathology were measured by an animal pathologist.
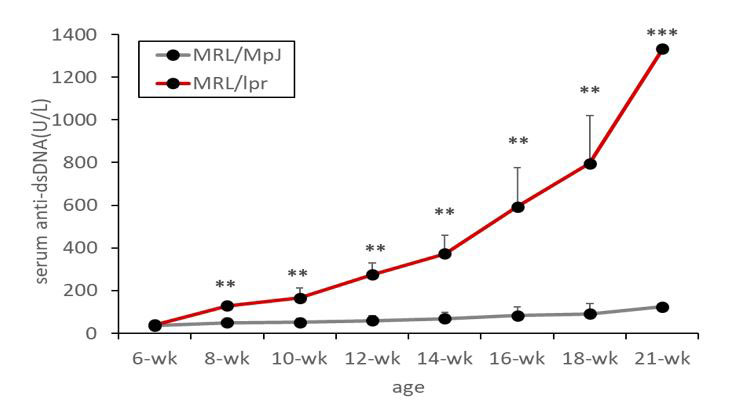
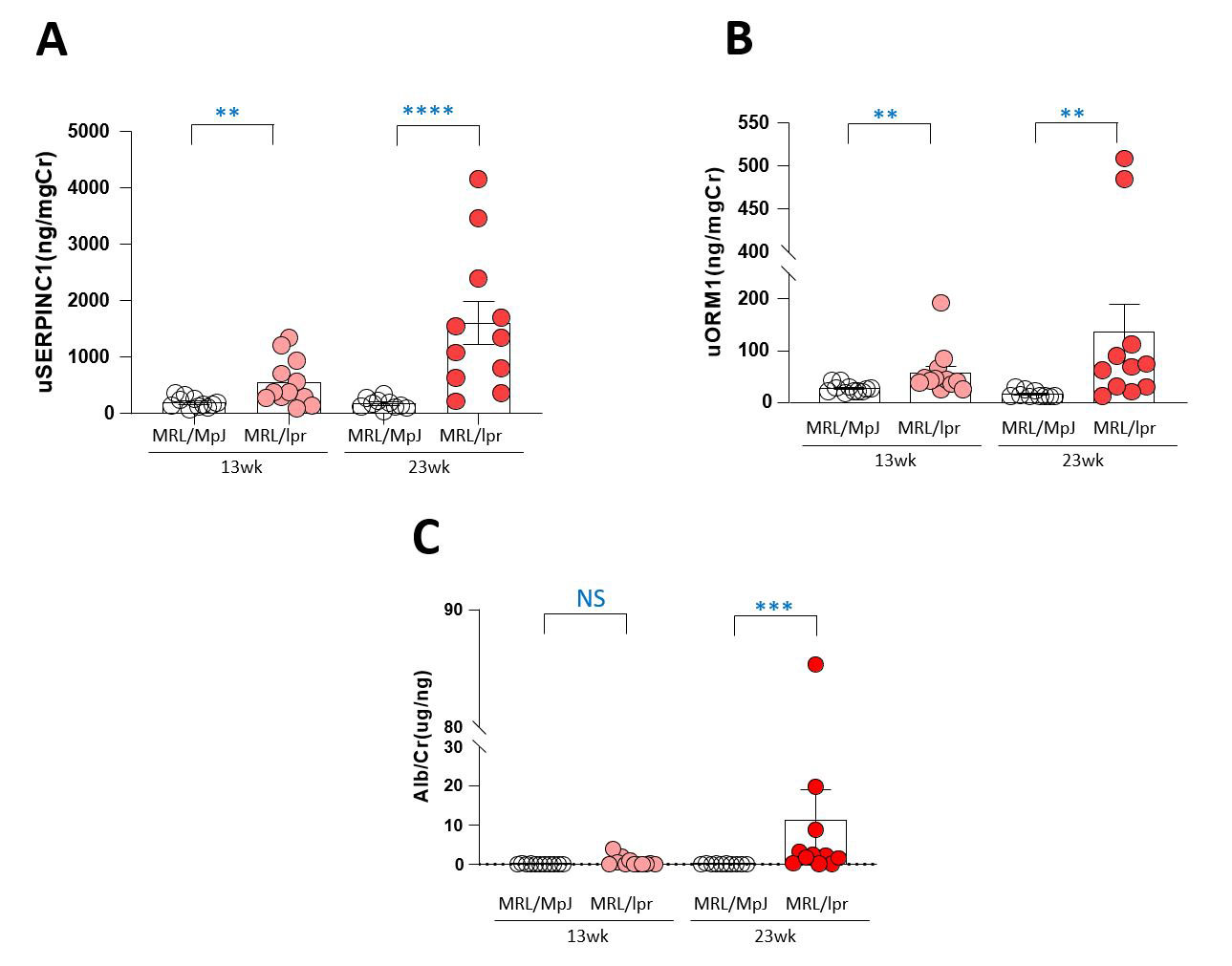
Results: A total of twenty-three of MRL-lpr (n=12) and MRL/MpJ (n=11) mice underwent analysis. Serum anti-dsDNA increased significantly in MRL-lpr mice according to the number of weeks compared with MRL-MpJ mice (Figure 1). The amount of urine SERPINC1 and ORM1 detected by ELISA was significantly higher in MRL-lpr mice than in MRL/MpJ mice at 13 and 23 weeks (SERPINC1: p< .01 and p< .001 at 13 and 23 weeks, respectively; ORM1: p< .01 at 13 and 23 weeks) (Figure 2). In contrast, no significant difference in urine albumin was observed between the two groups at 13 weeks (p=.83); however, a difference was detected at 23 weeks (p< .001). Regarding the kidney pathology of MPL-lpr mice, urine ORM1 had a significantly positive correlation with the activity index (rho =.879, p< .001) and chronicity index (rho =.947, p< .001). The correlation with the histopathology index was stronger than with urine albumin, the activity index (rho =.807, p=.003), and the chronicity index (rho =.869, p=< .001). SERPINC1 and ORM1 were primarily expressed in the tubular membrane in immunofluorescent-stained kidney tissue (Figure 3).
Conclusion: Urine SERPINC1 and ORM1 were detected in the LN murine model earlier than albumin. Additionally, urine ORM1 correlated with the degree of activity and chronicity index more than urine albumin. Therefore, we suggest urine SERPINC1 and ORM1 as novel biomarkers for early LN.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kim Y, Lee E, Ahn S, Oh J, Hong S, Lee C, Yoo B, Kim Y. Clinical Applications of Urine SERPINC1/ORM1 in MRL-lpr Lupus Nephritis-Prone Mice [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-applications-of-urine-serpinc1-orm1-in-mrl-lpr-lupus-nephritis-prone-mice/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-applications-of-urine-serpinc1-orm1-in-mrl-lpr-lupus-nephritis-prone-mice/