Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1147–1190) Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: IgG4-RD is a rare, chronic, fibroinflammatory disorder characterized by recurrent flares that can affect any organ and lead to permanent tissue damage. Inebilizumab (INEB) is a CD19-specific B cell depleting monoclonal antibody (mAb) approved for the treatment of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) and recently approved for the treatment of IgG4-RD (MITIGATE trial; NCT04540497). Three doses of INEB (days 1, 15 and 183) resulted in an 87% reduction in flare risk compared to placebo-treated participants in the MITIGATE trial. The aim was to evaluate clinical and molecular characteristics of INEB-treated participants who experienced a positively adjudicated and treated IgG4-RD flare during the randomized controlled period (RCP) of the MITIGATE trial.
Methods: Disease history and clinical characteristics of INEB-treated participants (n=7) with an on-study flare were analyzed. B cell counts, IgG4 levels, and other markers were evaluated and compared to the 61 INEB-treated participants who did not flare. Temporal relationships between disease flares, INEB dosing, and changes in biomarker levels were explored.
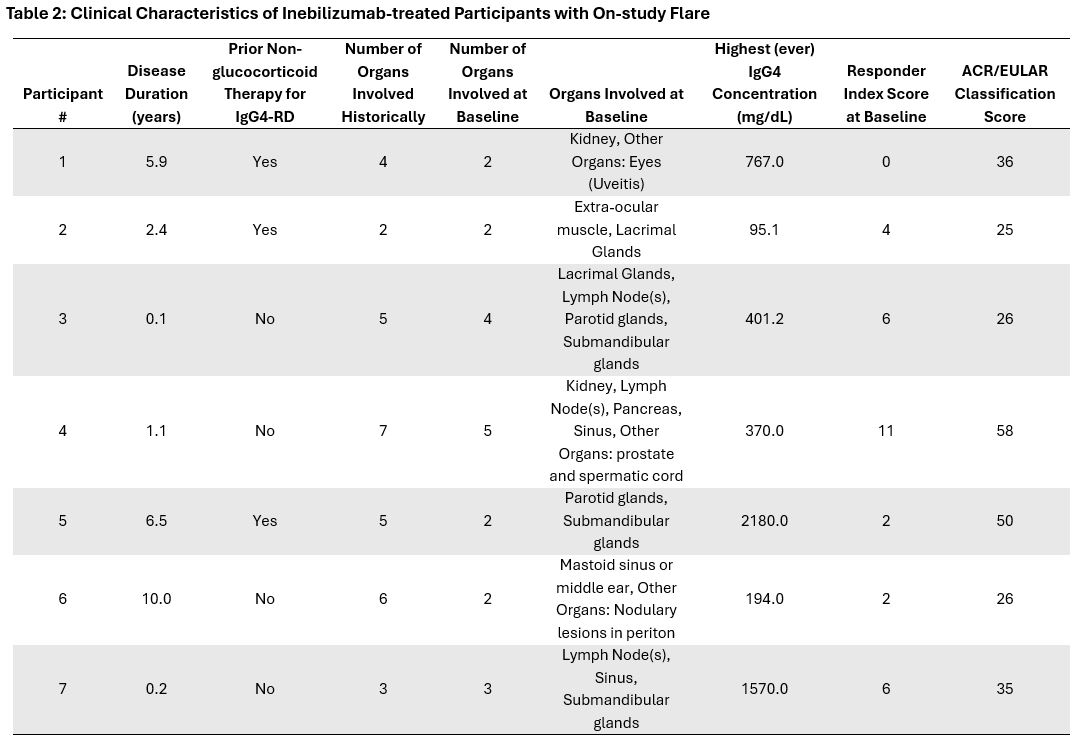
Results: Overall, the baseline characteristics of the 7 INEB-treated participants who experienced a flare are generally similar to those of the 61 INEB-treated participants who did not (Table 1), with lower historic IgG4 levels, longer duration of disease, and more prevalent prior non-GC therapy noted among the INEB-treated participants who flared. Clinical characteristics of the 7 INEB-treated participants who flared show diversity in disease duration, prior non-GC therapy, organ involvement, highest historic IgG4 levels, baseline Responder Index score, and ACR/EULAR classification criteria scores at study entry (Table 2).There is no consistent pattern in B cells, immunoglobulins, and other biomarkers among the INEB-treated participants who flared that distinguishes them from the 61 INEB-treated participants who did not flare. Analysis of the timing of biomarker changes (Figure 1) revealed no consistent pattern at the time of flare in INEB-treated participants. Of note:Participant 1 discontinued INEB after the first infusion (Day 1), and B cells were fully recovered at the time of flareParticipant 2 experienced a flare 2 weeks after the first infusion, prior to development of the full pharmacodynamic effects of INEBParticipant 3 displayed incomplete B cell depletion ( >5 cells/µL) at the time of flare despite receiving all prior doses of INEBThe remaining 4 participants experienced a flare in the setting of deep B cell depletion and reduced IgG4 levels compared to baseline
Conclusion: In this small cohort, baseline clinical and serologic characteristics did not reliably differentiate INEB-treated participants who experienced a flare (n=7) from those who did not (n=61). In INEB-treated participants, no clear patterns of biomarker changes are associated with occurrence of flare. Some participants experienced full apparent pharmacodynamic effect of INEB yet experience a flare. Two INEB-treated participants flared after discontinuing INEB or prior to development of the full pharmacodynamic effect.
.jpg) Figure 1. Relationship between B cell counts, serum IgG4 levels, inebilizumab administration, and flares in inebilizumab-treated MITIGATE participants who experienced an on-study flare (n=7). Dashed black lines represent inebilizumab dose received; dashed grey lines represent inebilizumab dose scheduled but not received; dashed red lines represent time of flare.
Figure 1. Relationship between B cell counts, serum IgG4 levels, inebilizumab administration, and flares in inebilizumab-treated MITIGATE participants who experienced an on-study flare (n=7). Dashed black lines represent inebilizumab dose received; dashed grey lines represent inebilizumab dose scheduled but not received; dashed red lines represent time of flare.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Stone J, Culver E, Khosroshahi A, Zhang W, Della Torre E, Okazaki K, Tanaka Y, Lohr M, schleinitz n, Martinez-Valle F, Nayar M, Rebours V, Perugino C, Clarkson K, Alexander T, Dong X, Huang Q, Cheng S, Cimbora D. Clinical and Biomarker Characteristics of Inebilizumab-Treated Participants Who Experienced an IgG4-RD Flare During the Phase 3 MITIGATE Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-and-biomarker-characteristics-of-inebilizumab-treated-participants-who-experienced-an-igg4-rd-flare-during-the-phase-3-mitigate-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-and-biomarker-characteristics-of-inebilizumab-treated-participants-who-experienced-an-igg4-rd-flare-during-the-phase-3-mitigate-trial/

.jpg)