Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-4:30PM
Background/Purpose: There is a lack of high-quality data to inform risk-stratified long-term thrombosis prevention strategies in patients with persistently positive antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL). The APS ACTION Registry aims to study the course of disease over at least 10 years in persistently aPL-positive patients; the primary objective of this study was to determine independent clinical and biologic predictors of thrombosis among persistently aPL-positive patients enrolled in the APS ACTION Registry.
Methods: Patients positive for aPL according to the Revised Sapporo Classification Criteria (tested within one year prior to enrollment) are eligible for inclusion in the registry. Follow up occurs every 12±3m with clinical data and blood collection. Registrants with at least one year of follow up were included in this study. We compared the baseline characteristics of those with or without new thrombosis during follow up, and calculated the incidence rate of first and recurrent thrombosis. We then conducted a time-to-event analysis, fitting Cox proportional hazards models to calculate the hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for independent predictors of thrombosis.
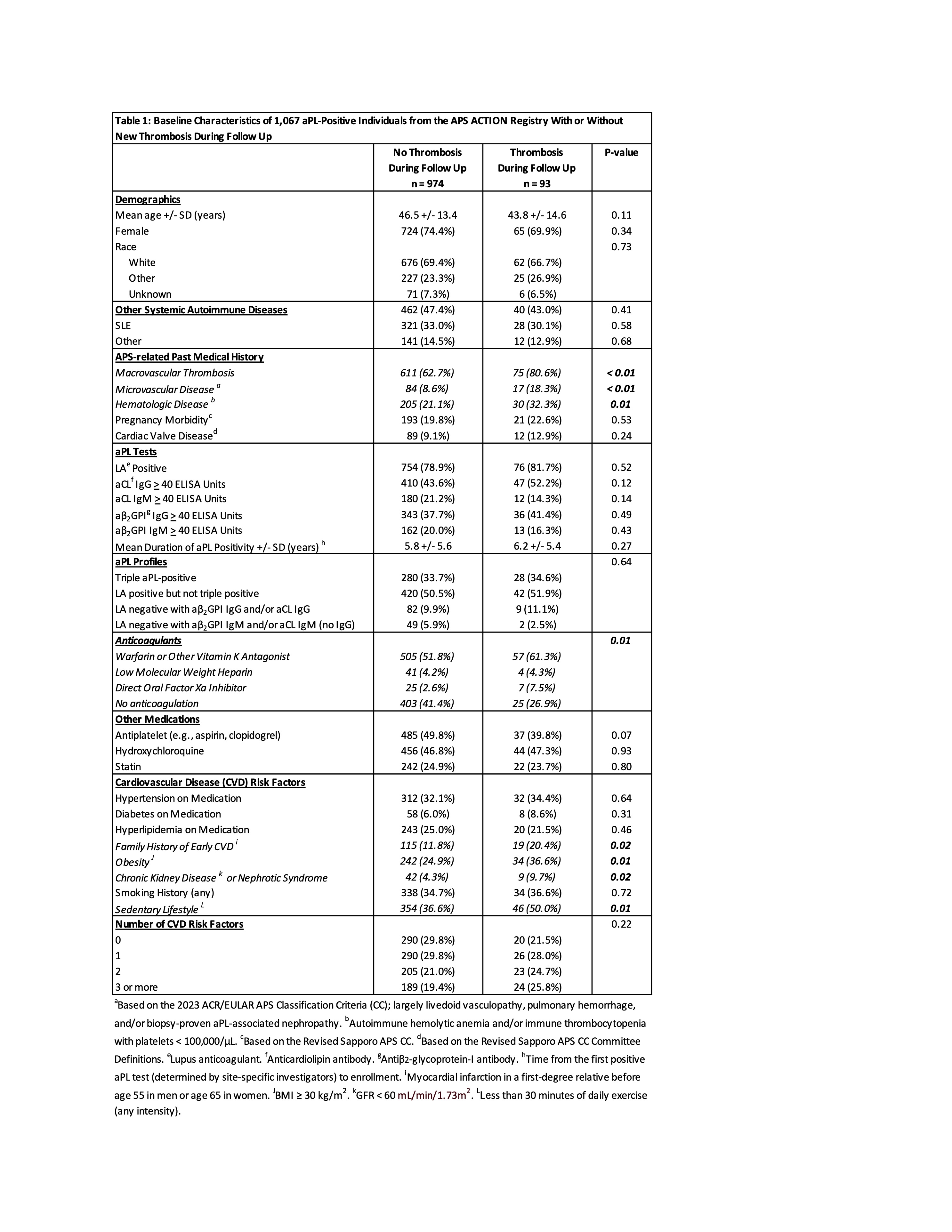
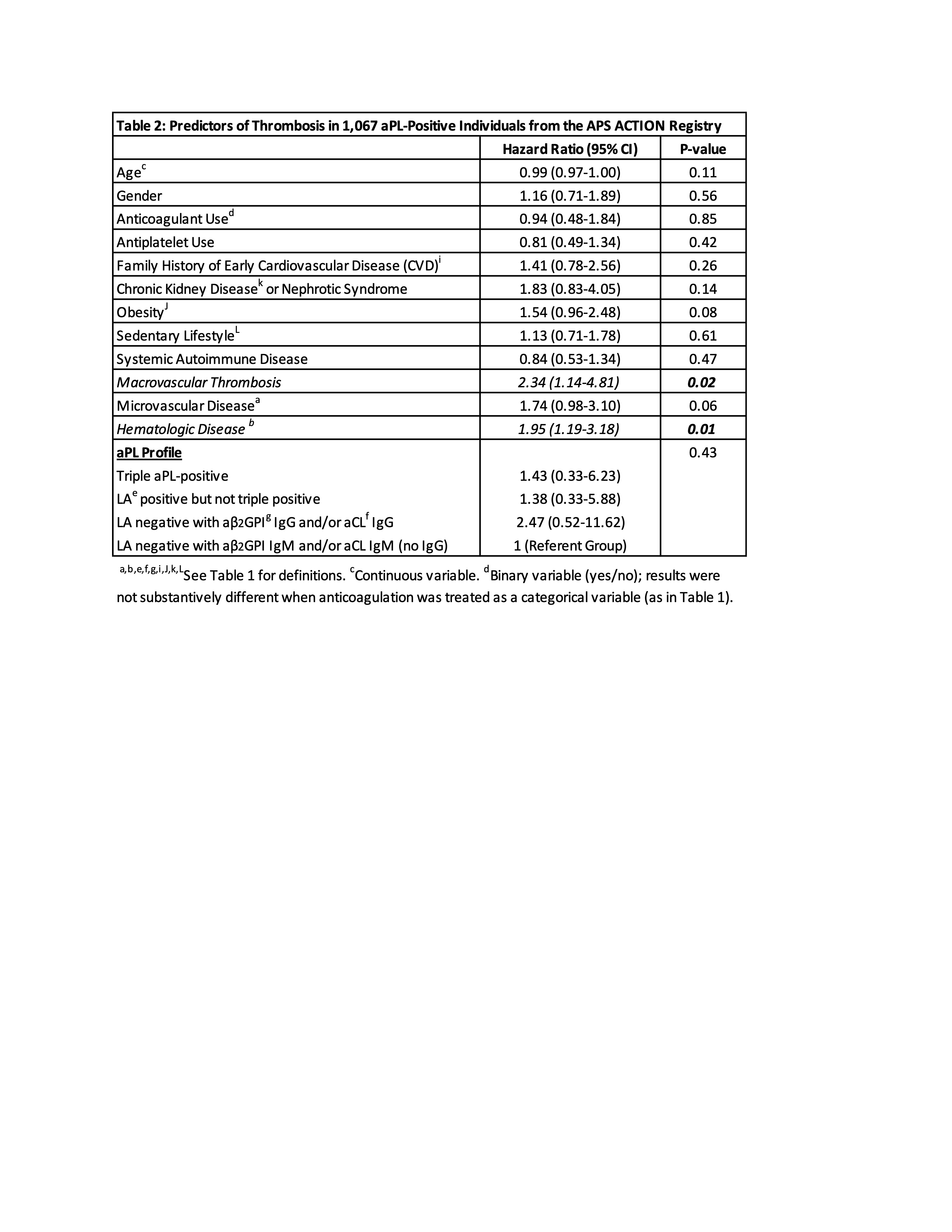
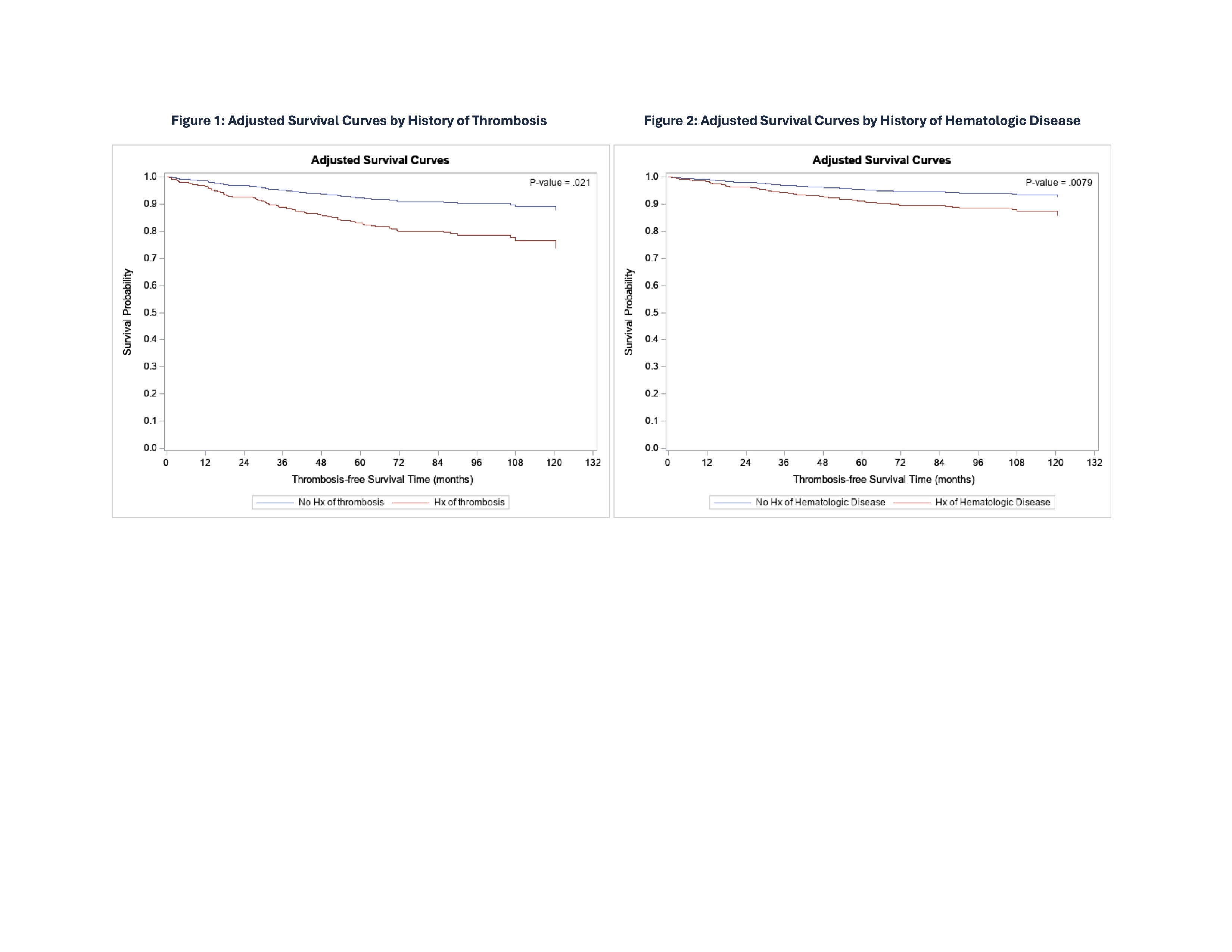
Results: As of May 2024, 1,196 persistently aPL-positive patients with or without APS by Sapporo classification were enrolled, of whom 1,067 (89%) had at least one year of follow up. Mean follow up (enrollment to first new thrombosis or most recent follow up) was 4.36 years (1890 person-years [p-y]) and 4.46 years (3405 p-y) for those without and with a history of thrombosis at enrollment, respectively. Based on 18 first events in 18 patients, and 98 recurrent events in 75 patients, new thrombosis incidence was 0.95 and 2.20 per 100 p-y in patients without and with a history of thrombosis, respectively. In unadjusted analyses, history of thrombosis, hematologic disease (autoimmune hemolytic anemia [AIHA] and/or immune thrombocytopenia with platelets < 100,000/μL), and microvascular disease, as well as baseline obesity, renal disease, sedentary lifestyle, anticoagulation, and family history of early cardiovascular disease were all more common (p < 0.05) among patients with new thrombosis (n = 93) than among those without new thrombosis (n = 974) (Table 1). After multivariable adjustment, independent predictors of new thrombosis included history of thrombosis (HR 2.34, 95% CI 1.14 – 4.81, p = 0.02; Figure 1) and hematologic disease (HR 1.95, 95% CI 1.19 – 3.18, p = 0.01; Figure 2); there was a trend for history of microvascular disease (p = 0.06) and obesity (p = 0.08) (Table 2).
Conclusion: In this prospective analysis, history of thrombosis and hematologic disease (AIHA and/or immune thrombocytopenia with platelets < 100,000/μL) each conferred an approximately two-fold increased risk of new thrombosis in persistently aPL-positive patients. No relationship between aPL profile and new thrombosis was identified, which may be related to the low number of events, heterogeneity of aPL results, and/or low number of LA-negative registrants. Future registry analyses using standardized core laboratory aPL results, and with longer follow up times and larger numbers of events, will help better define predictors of thrombosis in aPL-positive patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Thaler J, Parides M, Andrade D, Paredes-Ruiz D, Tektonidou M, Pengo V, Sciascia S, Nalli C, Ramires de Jesús G, Fortin P, Efthymiou M, Belmont H, Petri M, Cervera R, Skeith L, ATSUMI T, Lopez-Pedrera C, Zuo Y, Branch D, Willis R, Kello N, Zhang Z, Rodriguez-Almaraz E, Artim Esen B, Pardos-Gea J, Pons-Estel G, Pazzola G, Shi H, Duarte-Garcia A, Barbhaiya M, Yelnik C, Meroni P, Roubey R, Bertolaccini M, Cohen H, Rand J, Erkan D. Clinical and Biologic Predictors of Thrombosis in Persistently Antiphospholipid Antibody Positive Patients: Prospective Analysis of the International APS ACTION Clinical Database and Repository (“Registry”) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-and-biologic-predictors-of-thrombosis-in-persistently-antiphospholipid-antibody-positive-patients-prospective-analysis-of-the-international-aps-action-clinical-database-and-repository/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-and-biologic-predictors-of-thrombosis-in-persistently-antiphospholipid-antibody-positive-patients-prospective-analysis-of-the-international-aps-action-clinical-database-and-repository/