Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0066–0095) T Cell Biology & Targets in Autoimmune & Inflammatory Disease Poster
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
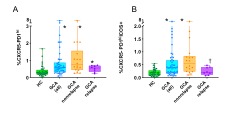
Background/Purpose: Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is a large-vessel granulomatous vasculitis. It is characterized by the presence at the inflamed arterial walls, of activated PD-1+ CD4 T cells; this contrasts with observations indicating that a defect of PD-1 signaling is implicated in the pathogenesis of GCA. A population of CD4+CXCR5-PD-1hi cells, termed Tph cells, has been described at the inflamed synovium and peripehral blood of patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis, and seem to play a pathogenic role in this condition. Our objective was to study the frequencies of circulating total Tph (cTph) and activated ICOS+Tph (cICOS+Tph) cells in the peripheral blood of patients with newly diagnosed GCA (nGCA) and examine whether they are related with the clinical outcome.
Methods: This is a prospective non-interventional study performed on consecutive patients referred to our ultrasound (US) GCA fast track clinic, in whom newly diagnosed GCA (nGCA) was clinically confirmed (2022 ACR/EULAR criteria) over a period of 18 months. Peripheral blood was drawn immediately upon confirmation and after obtaining written informed consent. For each patient, an age and gender-matched healthy control (HC) was also studied. PBMCs isolated by Ficoll- Hypaque gradient were stained with antibodies to CD3, CD4, CD45RA, CD45RO, CXCR5, ICOS, PD-1, and examined by flow cytometry. Patients were treated with standard therapy according to clinical response.
Results: A total of 48 nGCA patients were included (mean age 81,5 years, 50.0 % female). As compared with HC, nGCA patients presented at baseline with an increased frequency of cTph and cICOS+Tph cells. Among the 26 patients who could be followed up for 12 months (the remaining 22 have been diagnosed less than 12 months ago),8 experienced a relapse (2018 EULAR recommendations; symptoms plus: elevation of acute phase reactants and/or positive US). Interestingly, the basal frequency of cICOS+Tph cells had been significantly lower in patients who relapsed as compared with those who did not; the frequency of cTph cells also tended to be lower in relapsing subjects but the difference with non-relapsing patients was not statistically significant.
Conclusion: Newly diagnosed GCA patients demonstrate an increased frequency of cTph and cICOS+Tph cells. Lower basal proportions of cICOS+ Tph cells are associated with relapse.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Miranda-Carus M, Nieto-Carvalhal B, Monjo I, Uyaguari-Morocho M, Casado-Juárez I, Balsa A, De Miguel E. Circulating CD4+CXCR5-PD-1hiICOS+ Cells Are Elevated in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Giant Cell Arteritis and Associate with the Clinical Outcome [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/circulating-cd4cxcr5-pd-1hiicos-cells-are-elevated-in-patients-with-newly-diagnosed-giant-cell-arteritis-and-associate-with-the-clinical-outcome/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/circulating-cd4cxcr5-pd-1hiicos-cells-are-elevated-in-patients-with-newly-diagnosed-giant-cell-arteritis-and-associate-with-the-clinical-outcome/