Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2022
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Axial spondyloarthritis [AxSpA and particularly non-radiographic (nr)AxSpA] has one of the longest diagnostic delays in rheumatology. Although improving, lack of radiographic evidence of disease and competing diagnoses continue to hamper early detection and treatment.
Methods: This study utilized data from the OM1 AxSpA Premium Dataset (OM1, Inc; Boston, MA), which follows approximately 30,000 AxSpA patients in the U.S. managed by rheumatologists longitudinally with deep clinical data, including laboratory, patient-reported and disease activity information, and linked administrative claims starting from 2013. Study inclusion criteria included diagnoses of ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and non-radiographic AxSpA [as determined by diagnosis codes and a machine-learning (ML) based algorithm]. The nrAxSpA cohort excluded patients who were later characterized as having AS. Demographics, comorbidities and associated manifestations, biologic DMARD exposure and maximum BASDAI during follow-up were evaluated.
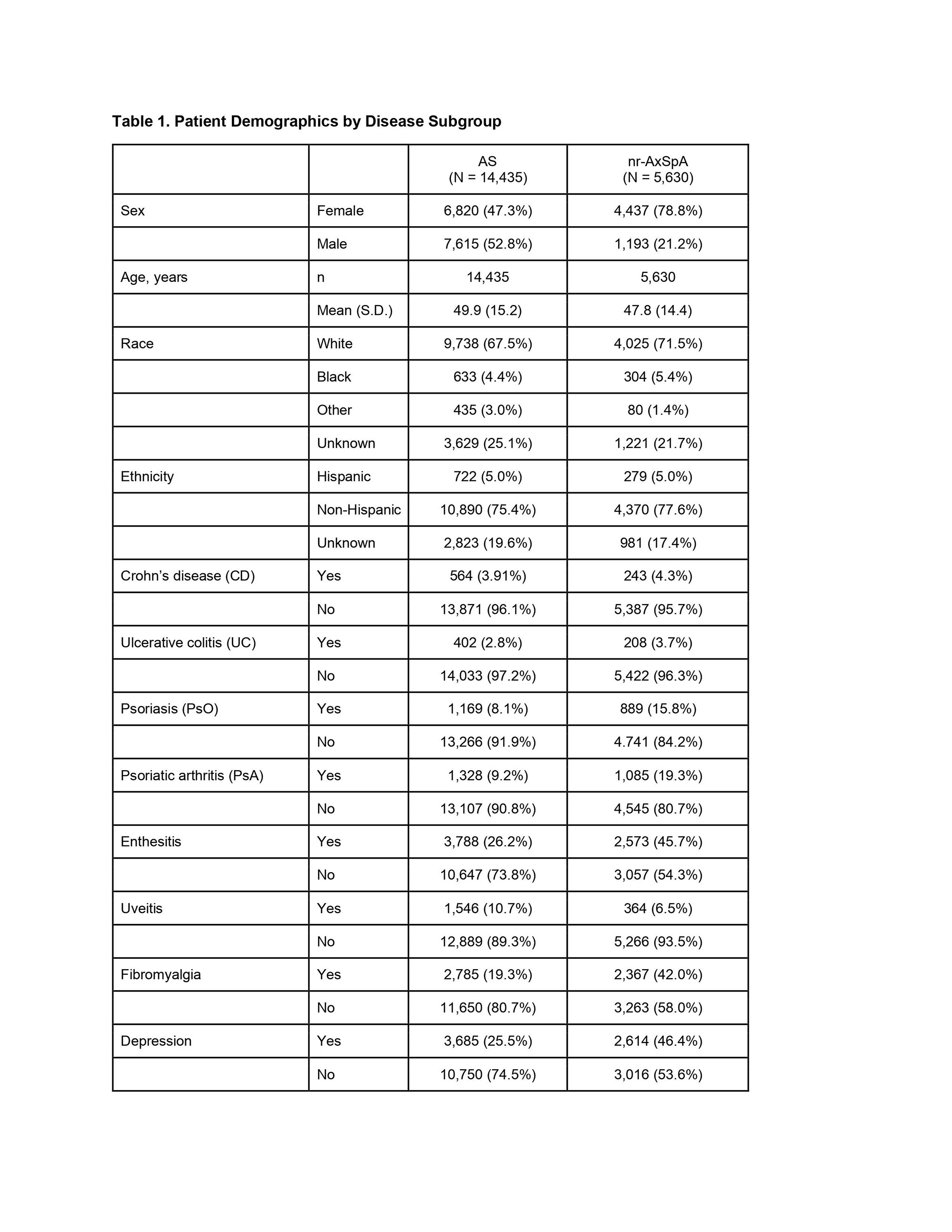
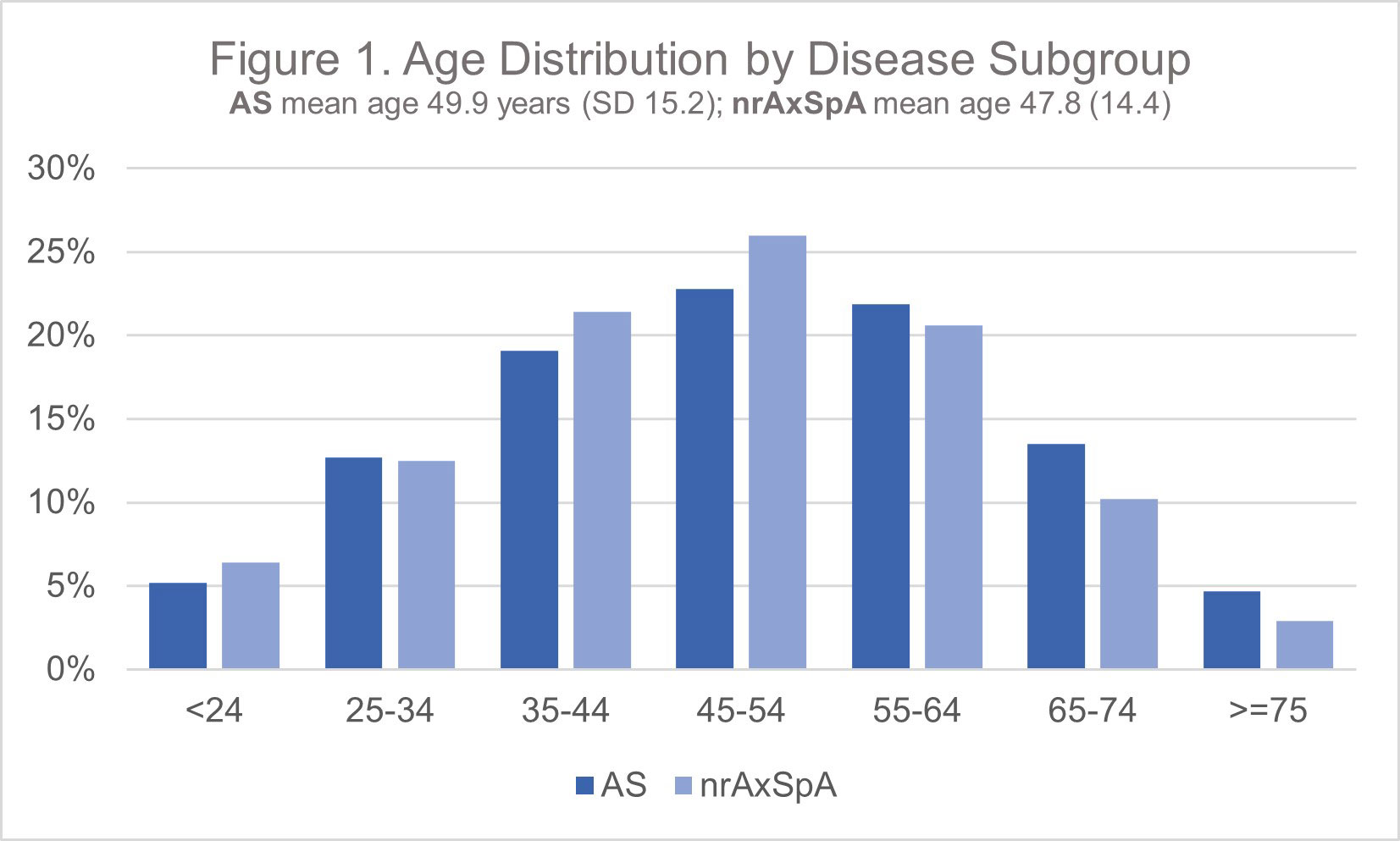
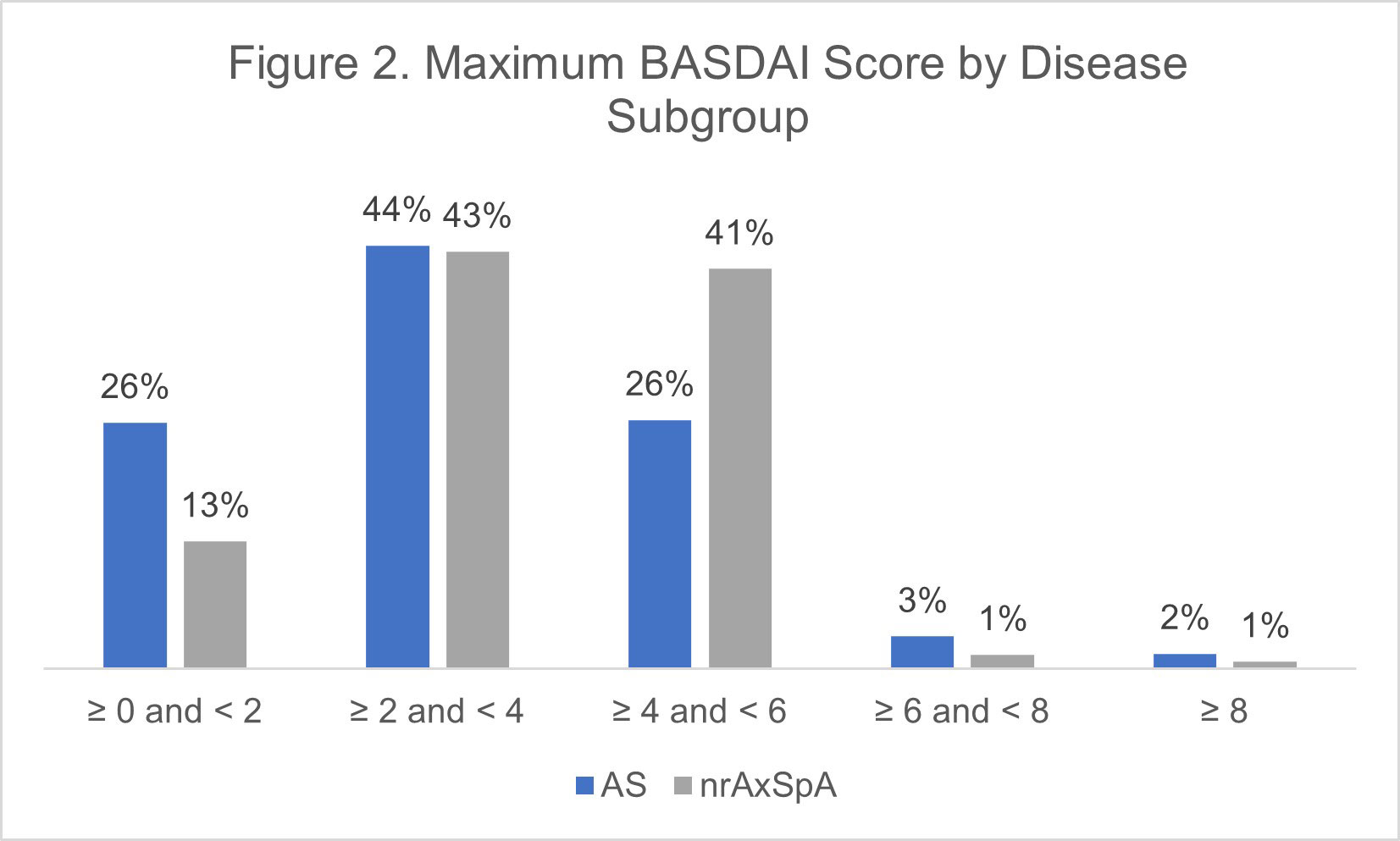
Results: A total of 20,065 AxSpA patients were included in the study, including 11,171 (81%) with at least one BASDAI score available. Mean age at start of follow-up was 49.9 years (SD 15.2) in the AS cohort (N=14,435) and 47.8 (SD 14.4) in the AS and nrAxSpA (N=5,630) cohorts, respectively (Figure 1). Ratio of male to female was close to 1:1 in AS, but closer to 1:3 in nrAxSpA (Table 1). Rates of ‘ever’ treatment with a biologic DMARD was similar (85.0% AS, 80.0% nr-AxSpA), and the proportion of patients with a maximum BASDAI in the “active” disease range (≥4) during follow-up was higher in the nr-AxSpA group (43% versus 31% AS) (Figure 2). Comorbidity patterns differed in the two groups, with nrAxSpA patients more commonly diagnosed with psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, enthesitis, fibromyalgia, and depression. Uveitis was more commonly recorded in the AS cohort (10.7% vs. 6.5%). Rates of concomitant inflammatory bowel disease were similar in the two cohorts (Table 1).
Conclusion: In this real-world cohort of patients managed by rheumatologists, patients identified as having nrAxSpA had a high burden of disease and comorbidities. Machine learning may provide an effective means of identifying likely patients early in their disease and speed referral to rheumatologists. Improved appreciation of nrAxSpA is necessary to optimize patient outcomes now that advanced therapies are available for both AS and nrAxSpA, particularly for female patients who may be overlooked in what was commonly considered a male-dominated disease.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Starzyk K, Kumparatana P, Meng r. Characterization of Non-radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis Patients and the Burden of Disease in Routine Clinical Practice [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterization-of-non-radiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis-patients-and-the-burden-of-disease-in-routine-clinical-practice/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterization-of-non-radiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis-patients-and-the-burden-of-disease-in-routine-clinical-practice/