Session Information
The 2020 Pediatric Rheumatology Symposium, originally scheduled for April 29 – May 2, was postponed due to COVID-19; therefore, abstracts were not presented as scheduled.
Session Type: Poster Breakout Session
Session Time: 5:10PM-5:40PM
Background/Purpose: Cytokine storm syndromes (CSS), such as macrophage activation syndrome (MAS) and secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), are life threatening conditions that commonly present with unremitting fever and shock like multi-organ dysfunction (MOD). Laboratory studies show pancytopenia, elevated liver enzymes, elevated ferritin, and hemophagocytosis. Familial forms of HLH result from homozygous defects in genes involved in perforin mediated cytolysis by NK cells and CD8 T cells. As many as 30-40% of CSS patient cohorts studied have heterozygous defects in the same HLH genes resulting in decreased cytolytic function, prolonged interaction with antigen presenting cells, and subsequent increased pro-inflammatory cytokines resulting in MOD. Since NK cell dysfunction is common in CSS, there are likely other genes that contribute to CSS via decreased cytolysis. Using gene sequencing, mutations in potentially novel HLH genes present in 3 or more CSS patients were explored.
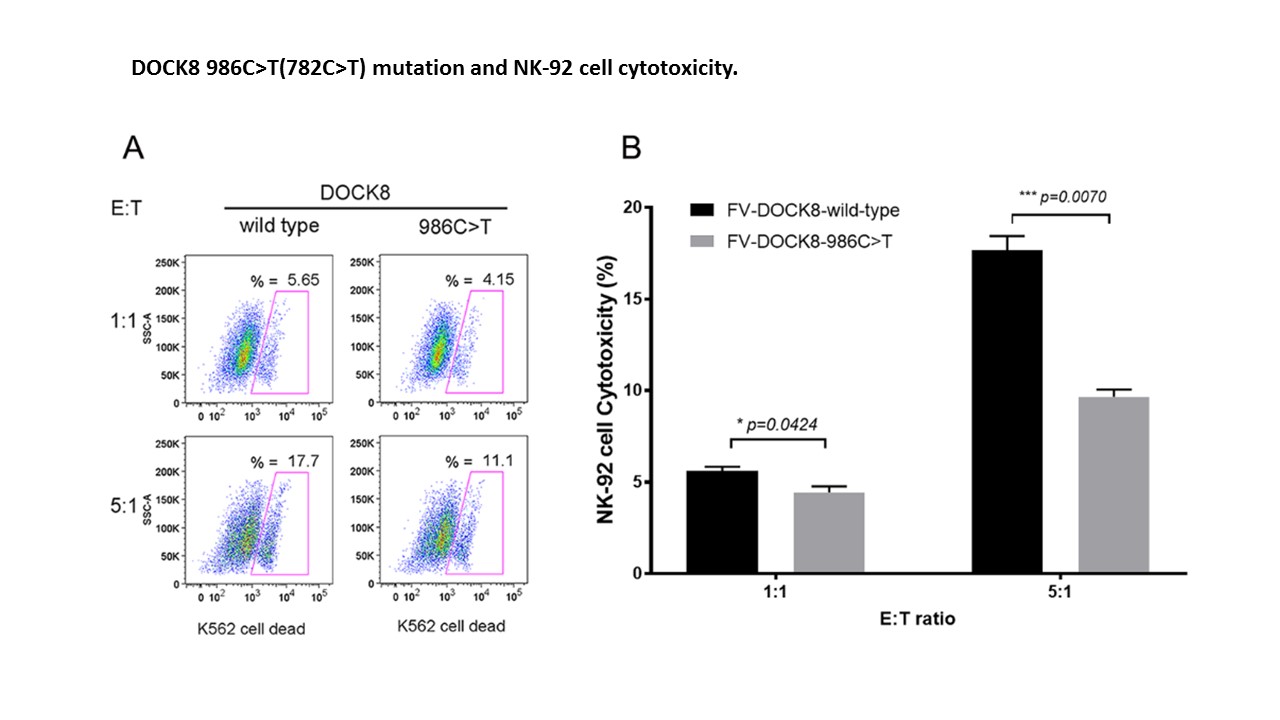
Methods: Pediatric and adult patients with CSS at UAB were screened for genetic mutations, potentially contributing to CSS, via whole genome sequencing or a commercial immunodeficiency exomic genetic panel of 207 genes. Several patients were noted to have mutations in the guanine nucleotide exchange factor DOCK8 critical to NK cell function. DOCK8 mutations from this CSS cohort, or wild-type (WT) sequence controls, were introduced exogenously into human NK-92 NK cell lines by foamy virus (FV) transduction. Alternatively, the endogenous NK-92 DOCK8 genes were cut and repaired to express WT sequence or patient derived DOCK8 mutations by CRISPR/Cas9 technology. WT and mutant DOCK8 expressing NK-92 cells were incubated with K562 target cells and compared for cytolytic activity, degranulation (CD107a), and cytokine [interferon-γ (IFNγ), tumor necrosis factor (TNF)] production by flow cytometry. The splice variant was tested by exon trapping.
Results: Two CSS patients were identified with rare heterozygous DOCK8 mutations, and 2 others with CSS were noted to have the same DOCK8 polymorphism (c.187G >A, p.Asp63Asn) present in 12% of the population (Table). One of the rare mutations was missense (c.782C >T, p.Ala261Val – novel), and one was a splice acceptor variant (c.54-1G >T, 0.03%). The novel DOCK8 mutant consistently decreased NK cell lytic activity when introduced by either CRISPR/Cas9 (n=2) or FV (n=3, decreased by ~50% compared to WT, p=0.007) (Fig. 1). Similarly, the novel mutant decreased degranulation by >50% (n=3, p=0.0129) (Fig. 2). During the incubation of the NK-92 cells with K562 targets, NK cells expressing the novel DOCK8 mutant increased expression of IFNγ and TNF by >200% (p=0.0192 & p=0.0027, respectively). In addition, the DOCK8 polymorphism consistently statistically decreased NK cell function (cytolysis and degranulation) but to a lesser degree. The DOCK8 splice variant also abolished splicing as tested by exon trapping.
Conclusion: Heterozygous mutations in DOCK8, a novel CSS associated gene, likely contribute to pathology through a partial dominant-negative effect resulting in decreased cytolysis and increased pro-inflammatory cytokine production.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zhang M, Cron R, Absher D, Atkinson P, Chatham W, Cron R. Characterization of DOCK8 as a Novel Gene Associated with Cytokine Storm Syndrome [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 4). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterization-of-dock8-as-a-novel-gene-associated-with-cytokine-storm-syndrome/. Accessed .« Back to 2020 Pediatric Rheumatology Symposium
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterization-of-dock8-as-a-novel-gene-associated-with-cytokine-storm-syndrome/