Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 12, 2022
Title: Abstracts: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes I: Renal Aspects
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: A decline of urine protein-to-creatinine ratio (UPCR) to < 0.5 is associated with better long-term preservation of kidney function in lupus nephritis (LN). UPCR < 0.5 defines complete response in guidelines and clinical trials when achieved after 1 or 2 years. Biomarkers of early response are needed to guide early treatment changes. We studied longitudinal urine proteomic profiles in LN to identify early predictors of proteinuric response.
Methods: We quantified 1200 biomarkers (Kiloplex, RayBiotech) in urine samples collected on the day of (73%) or within 3 weeks (27%) of kidney biopsy and week 12, 24, or 52 in LN patients (ISN class III, IV, V, or mixed) with proteinuria > 1 g/d. Response was defined at one year from renal biopsy: Complete = UPCR < 0.5, serum creatinine (sCr) < 125% of baseline, prednisone ≤ 10mg/d; Partial = UPCR < 50% from baseline but >0.5, sCr < 125% of baseline, but prednisone allowed to 15 mg/d; Non responder = not meeting previous definitions.
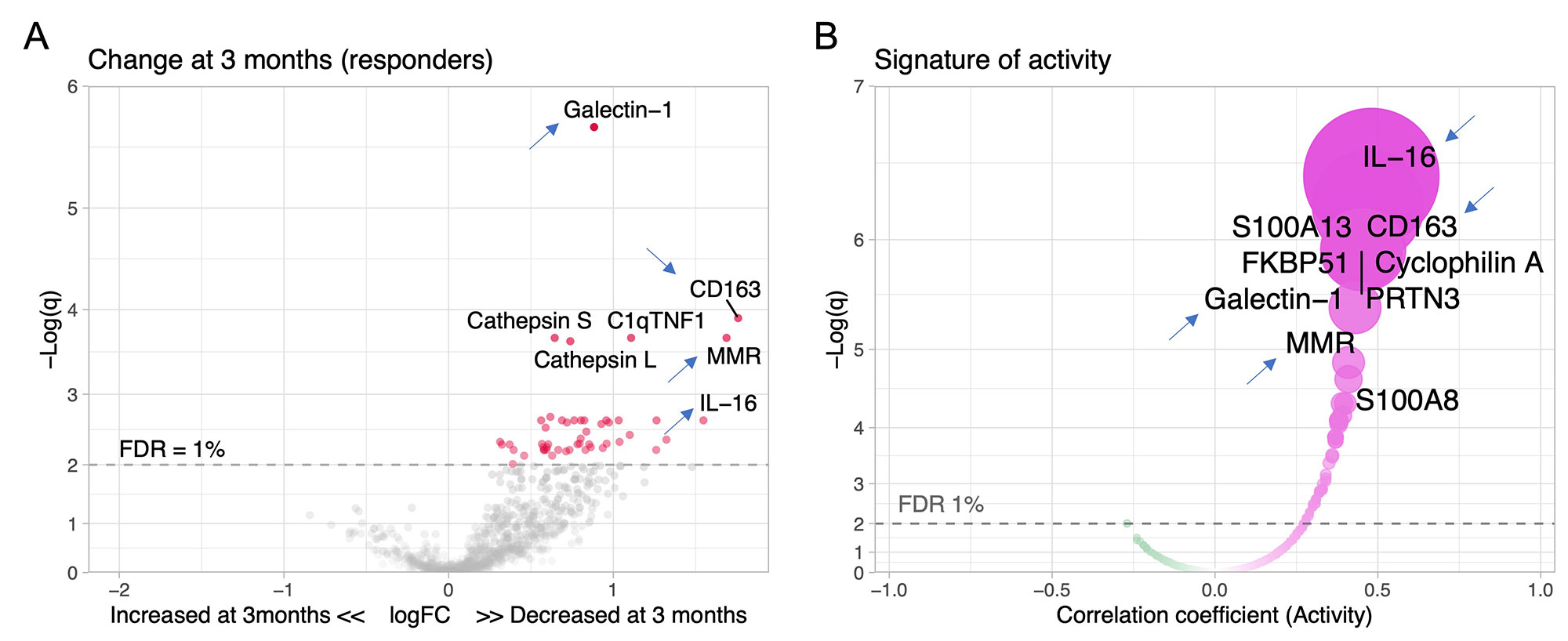
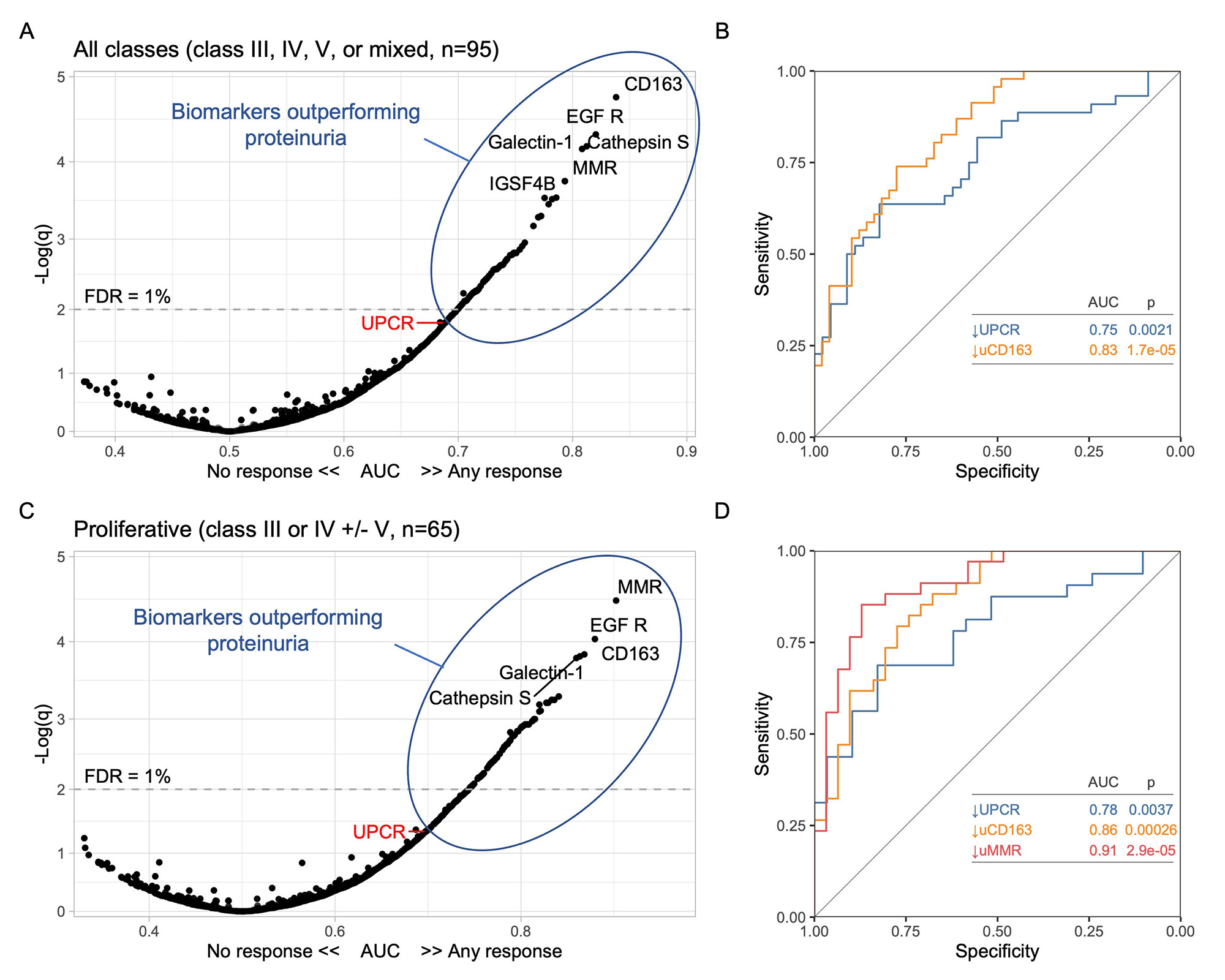
Results: A total of 127 patients were included: 48 (38%) with pure proliferative LN (class III or IV), 41 (32%) with mixed LN (III or IV +/- V), and 38% (30%) with pure membranous LN. Response was complete in 34 (27%), partial in 29 (23%), and none in 64 (50%). There were no urinary biomarkers at baseline that predicted response. We then analyzed the changes in urinary proteins at 3 months compared to baseline. Patients who responded at 1 year showed an early decline in 51 urinary proteins led by CD163, IL-16, and macrophage mannose receptor (MMR, CD206) (Figure 1A) which matched the proteomic signature associated with histological activity (Figure 1B). No changes were observed in nonresponders. The decline of several urinary biomarkers at 3 months outperformed a decline in UPCR (clinical standard) in predicting the 1 year response (Figure 2A). In particular, a decline of CD163 predicted 1 year response in ROC analysis with an area under the curve (AUC) of 83% compared to an AUC of 75% for UPCR decline (Figure 2B). In proliferative LN, urinary biomarkers displayed superior performance with an AUC of 91%, 86%, and 78% for the decline of MMR, CD163, and UPCR, respectively (Figure 2C-D). Pathway enrichment analysis identified leukocyte activation, neutrophil degranulation, and matrix degradation as the main pathways reduced at 3 months in responders.
Conclusion: An early decline in urinary biomarkers of histological activity is associated with proteinuric response at 1 year. These findings indicate that effective immunosuppression induces by three months an immunological response in the kidney that can be noninvasively monitored in the urine. Biomarkers of immunological response outperformed early decline of UPCR, the standard of care, in predicting 1-year proteinuric response, especially in proliferative LN. Because biomarkers of immunological response parallel intrarenal activity, they could detect early treatment response/failure and allow early treatment changes. They could serve as surrogate endpoints in clinical trials. Longitudinal studies are needed to confirm that this immunological response is a better predictor of long-term kidney function preservation than proteinuric responses.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fava A, Magder L, Goldman D, Buyon J, Diamond B, Guthridge J, Apruzzese W, Fine D, Monroy-Trujillo J, Atta M, Izmirly P, Belmont H, Davidson A, Dall'Era M, Rao D, Arazi A, Hacohen N, Raychaudhuri S, (AMP) RA/SLE t, Petri M. Change in Urinary Biomarkers at Three Months Predicts 1-year Treatment Response of Lupus Nephritis Better Than Proteinuria [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/change-in-urinary-biomarkers-at-three-months-predicts-1-year-treatment-response-of-lupus-nephritis-better-than-proteinuria/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/change-in-urinary-biomarkers-at-three-months-predicts-1-year-treatment-response-of-lupus-nephritis-better-than-proteinuria/