Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: Abstracts: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical I
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-2:30PM
Background/Purpose: Clinical trials in patients with interstitial lung diseases (ILDs) generally include a 52-week treatment period. Shorter trials would help speed up drug development and reduce the time that patients receive placebo. We assessed the prognostic value of change in FVC at week 12 or 24 for change in FVC at week 52, and for ILD progression over 52 weeks, in patients with autoimmune disease-related ILDs.
Methods: We analyzed data from patients with fibrosing ILD associated with systemic sclerosis (SSc-ILD) in the placebo group of the SENSCIS trial and patients with progressive fibrosing autoimmune disease-related ILDs in the placebo group of the INBUILD trial. Using logistic regression models (unadjusted and adjusted for factors that may affect ILD progression), we assessed absolute changes in FVC % predicted at week 12 or 24 as predictors of ILD progression (absolute decline in FVC % predicted ≥5% or death) over 52 weeks.
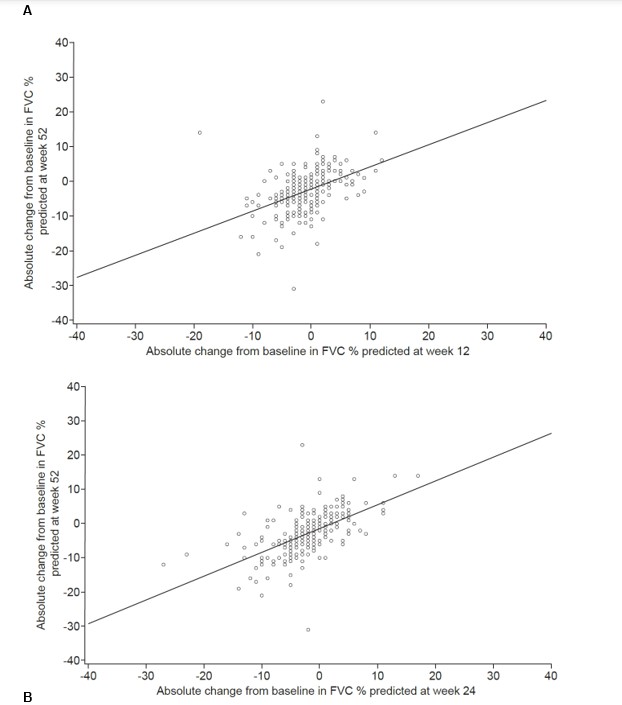
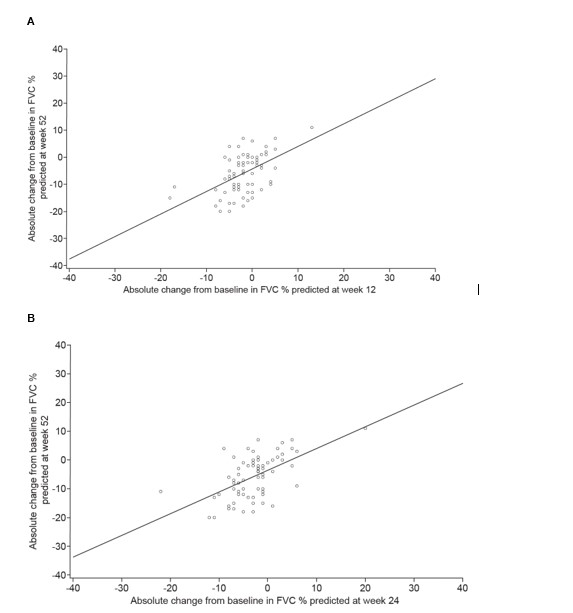
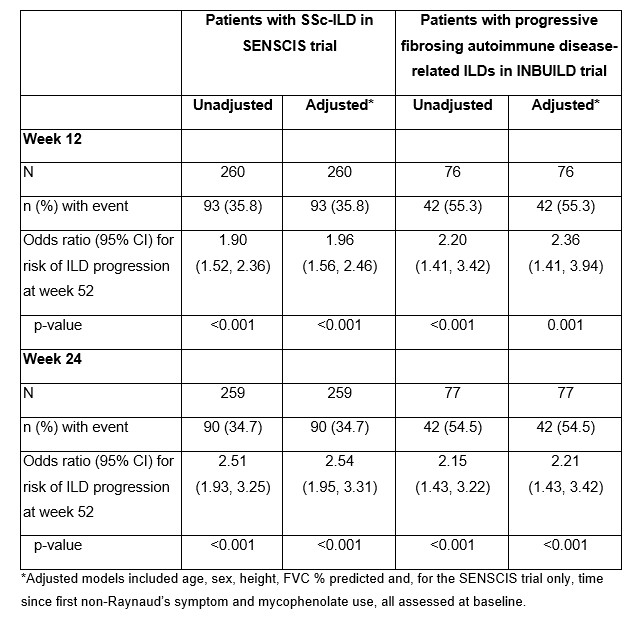
Results: Among patients with SSc-ILD in the SENSCIS trial, the correlation with absolute change in FVC % predicted at week 52 was stronger for the change at week 24 (r=0.59; n=256) than for the change at week 12 (r=0.43; n=255) (Figures 1A and 1B). In unadjusted analyses, the risk of ILD progression over 52 weeks was 1.90 (95% CI 1.52, 2.36) or 2.51 (95% CI 1.93, 3.25) times higher for each 2.5% decrease in FVC % predicted from baseline to week 12 or week 24, respectively (Table). Among patients who had ILD progression at week 52, 50% had an absolute decline in FVC % predicted ≥3.0 at week 12 and 75% had an absolute decline in FVC % predicted ≥3.0 at week 24. Among patients with progressive fibrosing autoimmune disease-related ILDs in the INBUILD trial, the correlation with absolute change in FVC % predicted at week 52 was similar for the change at week 12 (r=0.51; n=71) and week 24 (r=0.55; n=72) (Figures 2A and 2B). In unadjusted analyses, the risk of ILD progression over 52 weeks was 2.20 (95% CI 1.41, 3.42) or 2.15 (95% CI 1.43, 3.22) times higher for each 2.5% decrease in FVC % predicted from baseline to week 12 or week 24, respectively (Table). Among patients who had ILD progression at week 52, 50% had an absolute decline in FVC % predicted ≥3.5 at week 12 and 75% had an absolute decline in FVC % predicted ≥2.0 at week 24.
Conclusion: In clinical trials in patients with autoimmune disease-related ILDs, changes in FVC at week 12 and 24 were associated with the risk of ILD progression over 52 weeks. Among patients who had ILD progression at week 52, the majority showed FVC decline at week 24. This suggests that it is feasible to conduct trials in this patient population of shorter than 52 weeks’ duration.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hoffmann-Vold A, Alves M, Miede C, Distler O. Change in Forced Vital Capacity at Week 12 or 24 Has Prognostic Value for Outcome at Week 52 in Patients with Autoimmune Disease-Related Interstitial Lung Diseases [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/change-in-forced-vital-capacity-at-week-12-or-24-has-prognostic-value-for-outcome-at-week-52-in-patients-with-autoimmune-disease-related-interstitial-lung-diseases/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/change-in-forced-vital-capacity-at-week-12-or-24-has-prognostic-value-for-outcome-at-week-52-in-patients-with-autoimmune-disease-related-interstitial-lung-diseases/