Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: RA – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: In patients (pts) with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), including those treated with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, high rheumatoid factor (RF) levels are a poor prognostic factor, associated with higher disease activity and risk of radiographic progression.1,2,3 Such pts have reduced response to monoclonal antibodies targeting TNF,4 but may experience greater clinical response to TNF inhibitors without a fragment crystallizable (Fc) portion, such as certolizumab pegol (CZP).5,6,7 This post-hoc analysis assessed radiographic progression in CZP+methotrexate (MTX) vs placebo (PBO)+MTX-treated pts with RA, stratified by RF level, in the C-EARLY (NCT01519791) and C-OPERA (NCT01451203) phase 3 randomized trials.
Methods: A pooled analysis of pts with early (≤1 year active disease) moderate-to-severe RA with poor prognostic factors in the C-EARLY and C-OPERA trials is presented (full analysis set). At Week (Wk)24, PBO-treated non-responders could switch to CZP for the remaining 28 wks (early escapers). Pts were stratified by baseline (BL) RF level (low: < 200 IU/mL; high: ≥200 IU/mL), per published strata.1,6 Change from BL in modified total sharp score (mTSS) and proportions of pts experiencing minimum clinically important difference (worsening) of mTSS ( >5) at Wk24 and Wk52, and mTSS over time are reported.
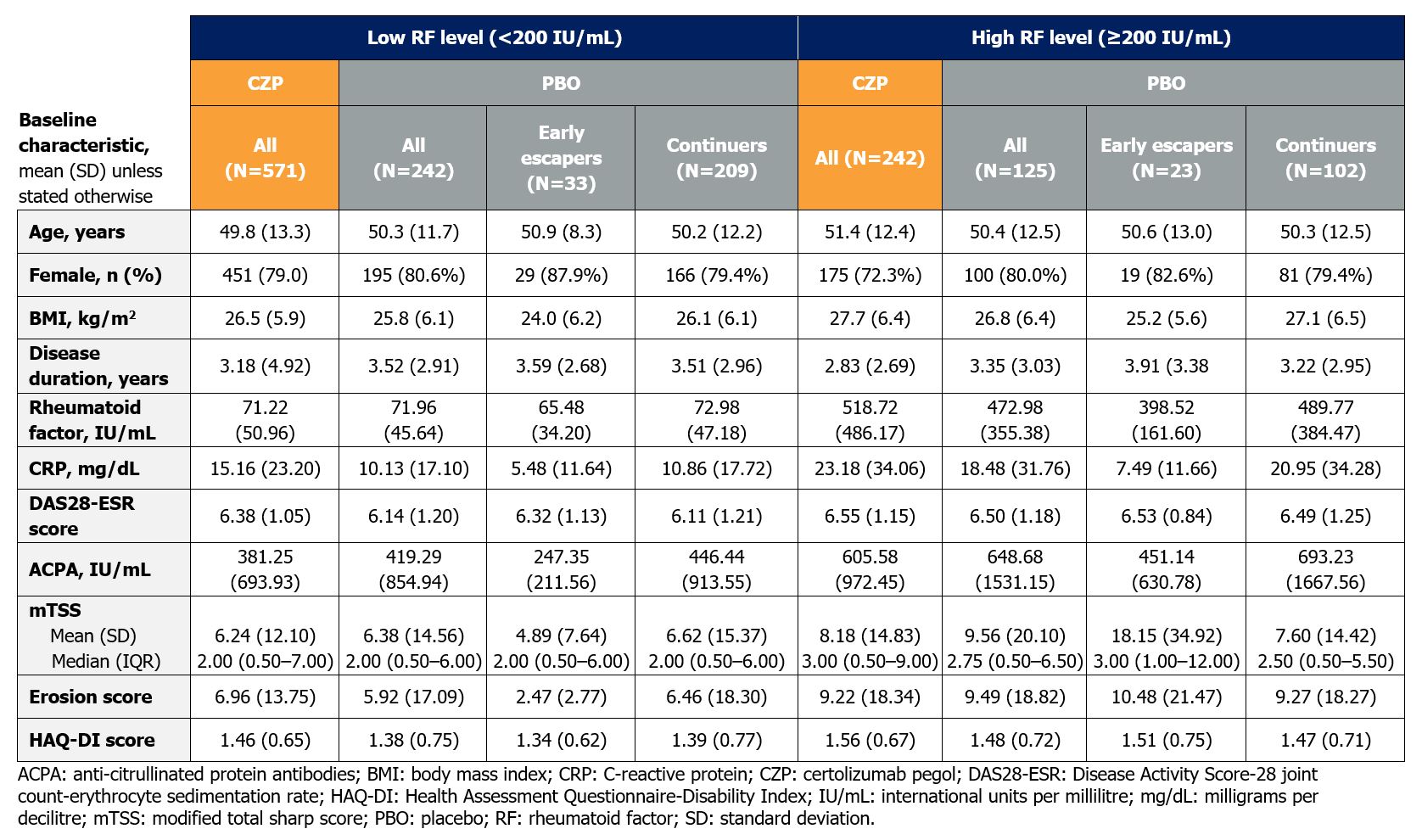
Results: 813 CZP-treated (low RF: N=571; high RF: N=242) and 367 PBO-treated (low RF: N=242; high RF: N=125) pts with BL RF measurements were included; 56 PBO-treated pts were early escapers. BL characteristics were similar between CZP- and PBO-treated pts within each RF stratification. However, pts with high RF had more severe disease at BL than those with low RF, with higher mean C-reactive protein, anti-citrullinated protein antibodies, mTSS, and erosion scores (Table 1).
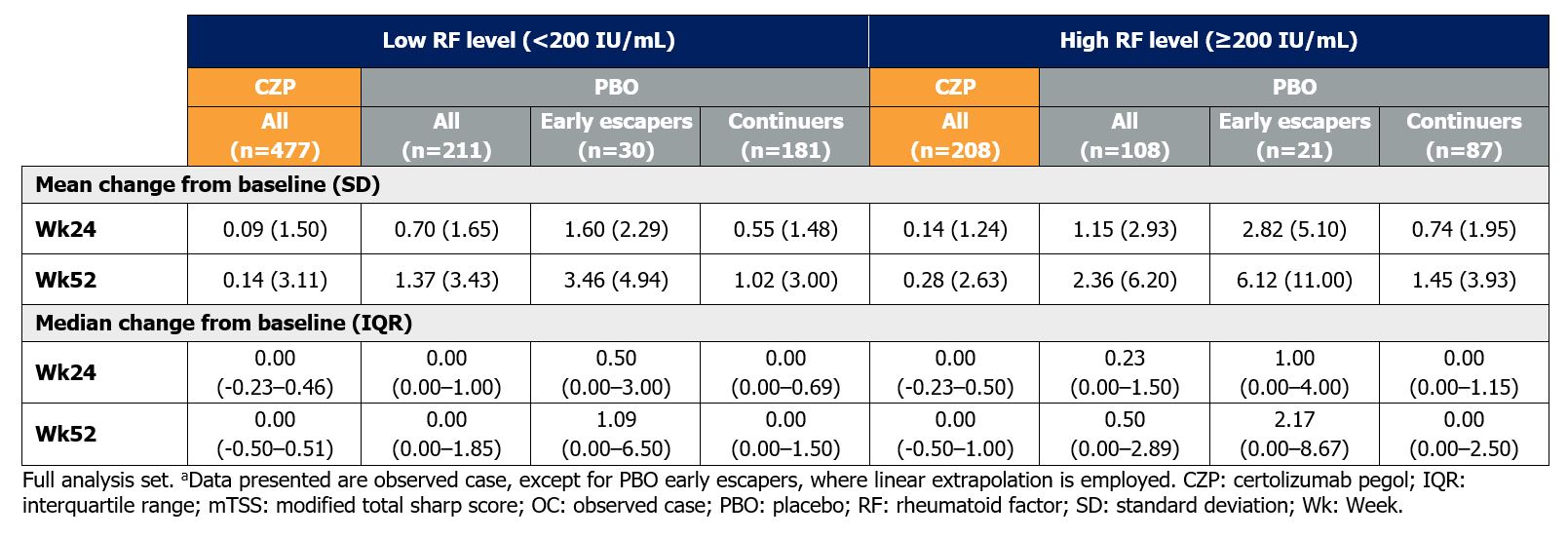
By Wk52, mean mTSS increased from BL in PBO-treated pts with both high RF (change from BL [CfB]: 2.36±6.20) and low RF (CfB: 1.37±3.43), but was comparable in CZP-treated pts (high RF: CfB: 0.28±2.63; low RF: CfB: 0.14±3.11) (Table 2).
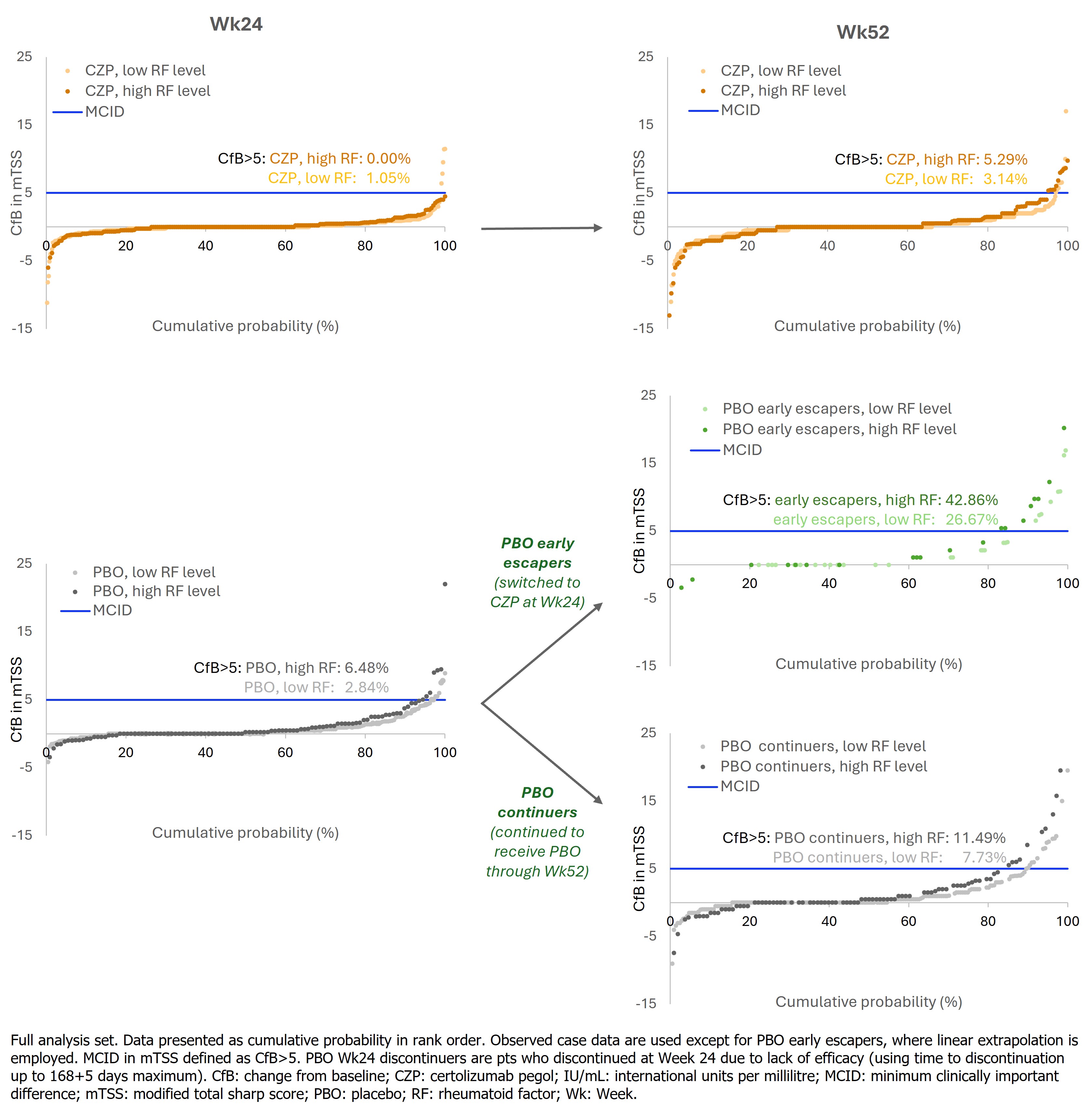
The proportion of pts with meaningfully worsening radiographic progression was higher in PBO-treated pts with high RF compared to low RF at both Wk24 (6.48% vs 2.84%) and Wk52 (17.59% vs 10.43%) (Figure 1). By contrast, a smaller proportion of CZP-treated pts experienced meaningful worsening and was similar between pts with high and low RF (Wk24: 0.00% vs 1.05%; Wk52: 5.29% vs 3.14%, respectively).
Conclusion: Pts with high BL RF levels had more severe RA and BL radiographic damage than those with low RF. Worsening radiographic damage was observed in PBO-treated pts, with slightly greater progression in high-RF pts than low-RF. In contrast, irrespective of BL RF levels, CZP-treated pts demonstrated consistently lower radiographic progression, suggesting RF does not adversely influence radiographic response to CZP.
References: 1. Vastesaeger N. et al, Rheum 2009;48:1114–21. 2. Cuchacovich M. et al, Clin Rheumatol 2014;33(12):1707–14. 3. Smolen J. et al, Ann Rheum Dis 2023;82(1):3–18. 4. Takeuchi T. et al, Arthritis Res 2017;19:194. 5. Nakayama Y. Rheumatol Int 2022;42:1227–1234. 6. Smolen J. Arthritis Rheumatol 2023;75(suppl 9). 7. Bidgood S. et al, Ann Rheum Dis 2024;83 (suppl 1):727.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Smolen J, Burmester G, Tanaka Y, Takeuchi T, Curtis J, Mikuls T, López Medina C, Taylor P, Tilt N, Lauwerys B, Ufuktepe B, Huizinga T. Certolizumab Inhibits Radiographic Progression Even in RA Patients with High Rheumatoid Factor Levels: A Pooled, Post-Hoc Analysis of Two Phase 3 Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/certolizumab-inhibits-radiographic-progression-even-in-ra-patients-with-high-rheumatoid-factor-levels-a-pooled-post-hoc-analysis-of-two-phase-3-trials/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/certolizumab-inhibits-radiographic-progression-even-in-ra-patients-with-high-rheumatoid-factor-levels-a-pooled-post-hoc-analysis-of-two-phase-3-trials/