Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: Abstracts: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes III: Predicting & Optimizing Outcomes
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:00PM-3:30PM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease with persistent synovial inflammation. Despite early diagnosis and the treatment-to-target strategy in ERA, the treatment response rate is not optimal. Analyzing synovial tissue in ERA may help to find useful biomarkers to optimize the remission rate. Therefore, this study aimed to analyze the histology features together with the presence and distribution of cells by immunohistochemistry (IHC) of ERA synovial biopsies, to better characterize the disease and identify the presence of predictive factors of treatment response.
Methods: According to ACR/EULAR 2010, ERA patients were enrolled as part of the UCLouvain Arthritis Cohort at Cliniques Universitaires Saint Luc, Brussels. All patients were naïve to steroids and DMARDs therapy. Patients underwent ultrasound (US)-guided or mini-arthroscopy synovial biopsy. After the biopsy, patients started DMARD therapy and were evaluated every 3-4 months. Synovial samples were analyzed for histology (Synovial Hyperplasia, Fibrinoid Necrosis, Hypervascularization, Inflammatory Infiltrate), pathotypes (lymphoid, myeloid, or pauci-immune), and IHC (CD3, CD20, CD138, and CD68) with a semiquantitative score from 0 to 3 for each feature.
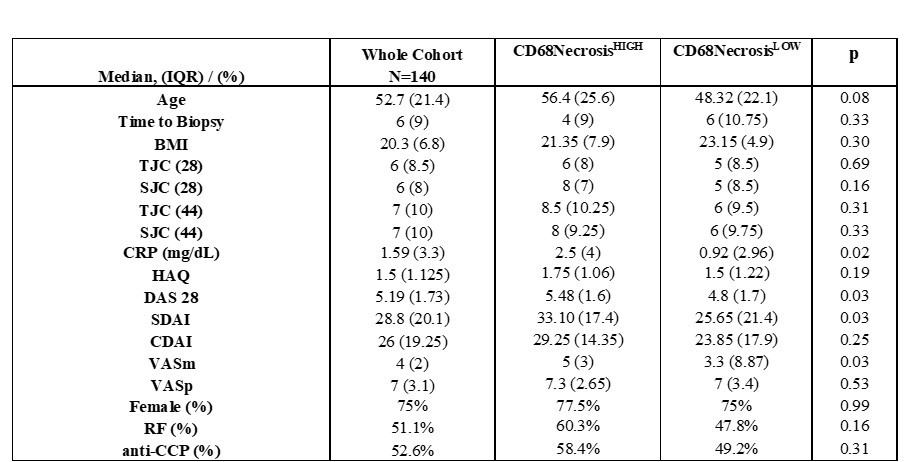
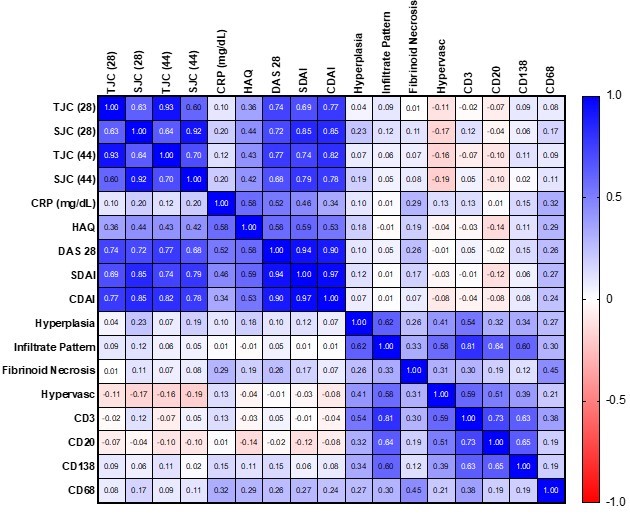
Results: 140 patients were included. Clinical and demographic features are reported in Table 1. CD68 and Fibrinoid Necrosis score were strongly associated [r= 0,44 (0,27-0,56); p< 0,0001]. CD68 score showed a good correlation with CRP [r=0.31 (0.13-0.46); p=0.0013], DAS28 [r=0,26 (0,07-0,43); p=0,005], SDAI [r=0,28 (0,07-0,47); p=0,008] and CDAI [r=0,25 (0,03-0,44); p=0,018]. The Fibrinoid Necrosis score showed a good correlation with CRP [r=0,29 (0,11-0,45); p=0,001] and DAS28 [r=0,26 (0,06-0,43); p=0,009].Based on the sum of the CD68 and Necrosis semiquantitative score [0-6], patients were then categorized as CD68NecrosisHIGH (≥3) and CD68NecrosisLOW (< 3). CD68NecrosisHIGH patients had higher CRP values [2.5 mg/dL (4) versus 0.92 mg/dL (2.96); p=0.02], DAS28 [5.48 (1.6) versus 4.8 (1.7); p=0.03] and SDAI [33.10 (17.4) versus 25.65 (21.4); p=0.03). At three months of observation, CD68NecrosisHIGH patients, compared to CD68NecrosisLOW showed a greater fall of DAS28 [1.99 (2.06) versus 1.1 (2.27), p=0.03], SDAI [21.45 (IQR 23.3) versus 11.65 (IQR 17.5); p=0.003] and CDAI [16 [14.9] versus 10.5 (20.1), p=0.04].Moreover, CD68NecrosisHIGH patients had a higher EULAR Moderate/Good Response rate compared to CD68NecrosisLOW (90% versus 71.43%; p=0.036). CD68Necrosis score was then included in a predictive matrix model together with baseline disease features (SJC44 and DAS28) with a Moderate/Good EULAR Response Criteria at 3 months as the outcome (AUC 0.724, 95%CI [0.58-0.86]; p=0.0028, Figure 2). Classification into pathotypes did not identify patients with better responses to treatment or requiring therapy with bDMARDs/tsDMARDs.
Conclusion: The evaluation of Macrophages and Fibrinoid Necrosis in ERA synovial biopsies identifies patients with higher disease activity and with a better DAS28 fall at three months. The semiquantitative score can predict the achievement of EULAR Response Criteria, alone or with clinical baseline features.
The values reported expressing the 3 months predictive probability of reaching a Moderate/Good EULAR Response [0_1 = 0% – 100%] for each combination of included categorized variables. For example, a patient with CD68 + Necrosis Score <3, SJC ≥ 14, and DAS28 ≥ 6 has a 3-month predicted probability of reaching at least a Moderate EULAR Response of 87%.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Natalucci F, triaille c, Sapart E, VAN MULLEM C, Sokolova T, MERIC de BELLEFON L, NZEUSSEU TOUKAP A, GALANT C, Lauwerys B, Durez P. CD68 and Fibrinoid Necrosis Are Synovial Biomarkers of Severity in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis and Are Associated with a Better Response to Methotrexate: Analysis of the UCLouvain Brussels ERA Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cd68-and-fibrinoid-necrosis-are-synovial-biomarkers-of-severity-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-are-associated-with-a-better-response-to-methotrexate-analysis-of-the-uclouvain-brussels-era-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cd68-and-fibrinoid-necrosis-are-synovial-biomarkers-of-severity-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-are-associated-with-a-better-response-to-methotrexate-analysis-of-the-uclouvain-brussels-era-cohort/