Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) is a disease characterized by the presence of auto-antibodies, immune complex deposition, and a robust type I interferon (IFN) signature. It is widely known that patients with SLE often have Coombs positivity, but the presence of anti-erythrocyte autoantibodies in the absence of hemolytic anemia has long been thought to be clinically insignificant. Recently, these antibodies have been proposed to play a pathogenic role in childhood-onset SLE (cSLE) via opsonization of mitochondria-containing erythrocytes and induction of type-I IFN production by myeloid cells in-vitro (Caielli et al., 2021). In this study we investigated whether peripheral myeloid cells from children with SLE demonstrate evidence of subclinical erythrocyte uptake.
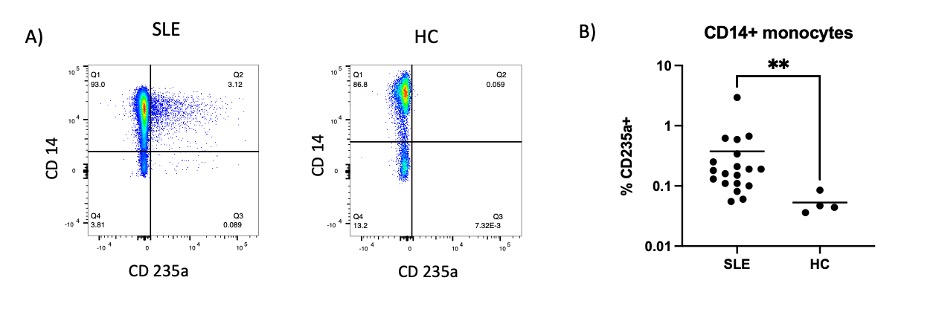
Methods: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated from cSLE (n=20) and healthy children (n=4). PBMCs were stained for lineage surface markers prior to fixation and permeabilization followed by intracellular staining for the erythrocyte membrane protein CD235a. Intracellular positivity was measured by flow cytometry. Subsequently, PBMC samples from a well-characterized longitudinal cohort of children with SLE were screened for the presence of CD235a+ monocytes.
Results: A subset of patients with cSLE display intracellular CD235a positivity within blood monocytes, which is absent in healthy children (Figure 1). CD235a intracellular positivity is most prevalent within CD14+ monocytes and did not correlate with clinical measures of anemia. Preliminary results from the longitudinal cohort suggest a correlation between frequency of blood CD235a+ CD14+ monocytes and disease activity per the SLEDAI-2K over time in a subset of patients.
Conclusion: This study confirms the presence of subclinical erythrocyte uptake within peripheral myeloid cells of patients with childhood-onset SLE in the absence of anemia. Future work will focus on the longitudinal nature of the anti-erythrocyte response in children with SLE with a specific focus on immunological phenotyping of the peripheral CD14+ monocytes demonstrating erythrocyte uptake.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Robinson L, Balasubramanian P, Wan Z, Rodriguez Alcazar J, Lima Silva Santos M, Walters L, Baisch J, Onel K, Wright T, Pascual V, Caielli S. CD14+ Monocytes Demonstrate Subclinical Erythrocyte Uptake in Childhood Onset Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cd14-monocytes-demonstrate-subclinical-erythrocyte-uptake-in-childhood-onset-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cd14-monocytes-demonstrate-subclinical-erythrocyte-uptake-in-childhood-onset-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/