Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Basic Science Poster
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Tagraxofusp is a novel targeted therapy directed to the interleukin-3 receptor (CD123). Tagraxofusp is comprised of human IL-3 recombinantly fused to a truncated diphtheria toxin (DT) payload engineered such that IL-3 replaces the native DT receptor-binding domain. In this way, the IL-3 domain of tagraxofusp directs the cytotoxic DT payload to cells expressing CD123. Upon internalization, tagraxofusp irreversibly inhibits protein synthesis and induces apoptosis of the target cell.
Tagraxofusp was recently approved by the FDA for the treatment of patients with blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm (BPDCN), a malignancy derived from the plasmacytoid dendritic cell (pDC) precursor. pDCs are immune cells that express CD123, secrete IFN-α, and play a role in inflammation and disease pathogenesis observed in systemic sclerosis (SSc) patients1,2. Therapeutic depletion of pDCs or attenuation of pDC function may represent a novel approach to treating SSc patients.
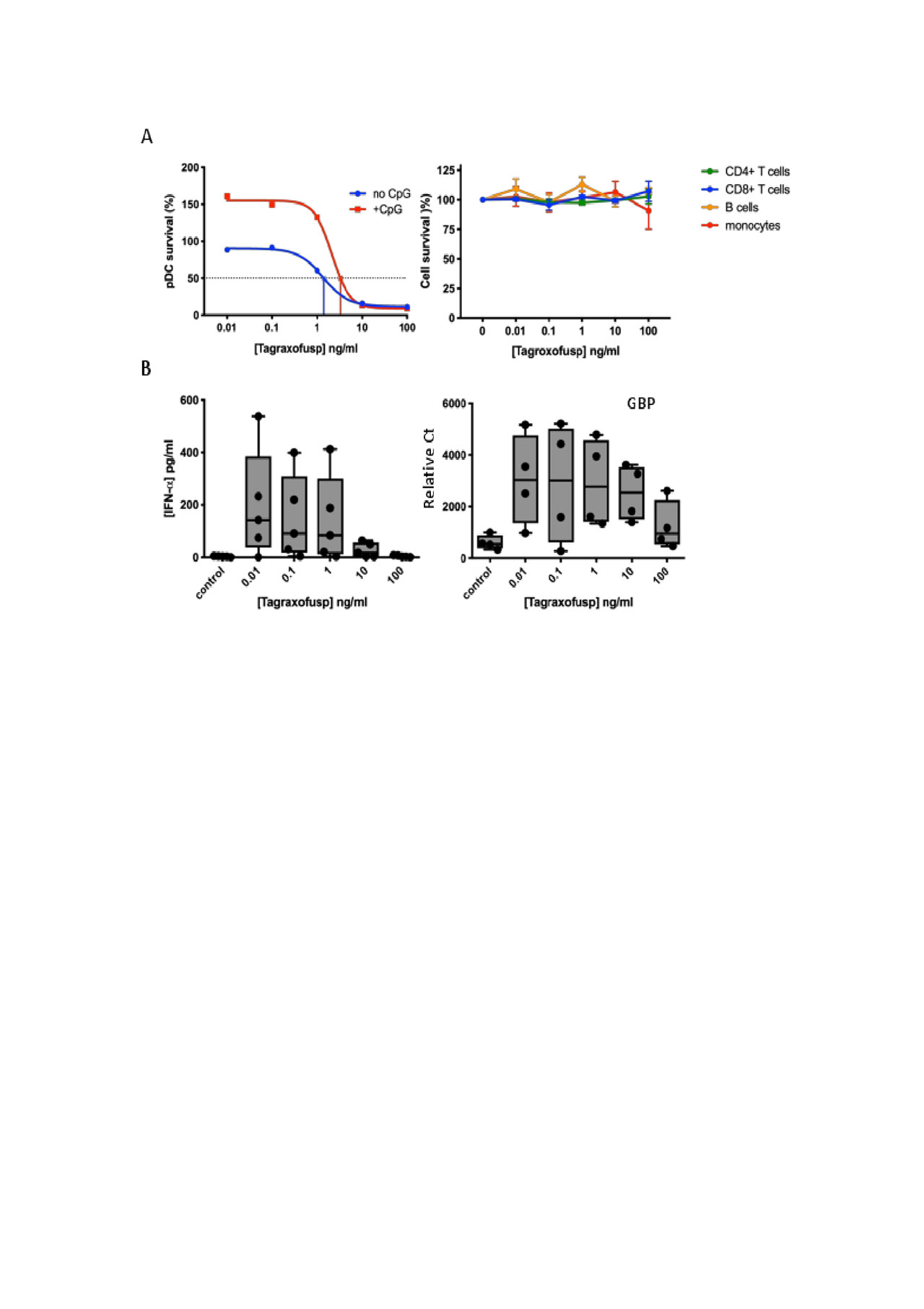
Methods: Patients fulfilled the 2013 ACR/EULAR classification criteria for SSc3. PBMCs from either SSc patients or healthy volunteers (HV) were prepared using Ficoll-Paque density gradient from fresh blood. pDCs were isolated from PBMCs as previously described and used to enrich the frequency of pDCs in an additional draw of PBMCs4. pDC-enriched PBMCs (3-6% pDCs) were cultured at 2×105 cells per well in the presence or absence of CpG-274 (0.5 μM) to activate pDCs and then incubated with tagraxofusp (0.01-100 ng/ml, 0.17 pM-1.7 nM) at 37°C, 5% CO2, and 95% humidity. After 24 h of culture, pDC survival was assessed by flow cytometry (CD14-, CD3- BDCA4+ CD123+), and supernatants were collected for cytokine quantification by a multiplexed Luminex assay. Changes in gene expression were measured by PCR on 10 μg cDNA, and calculated based on relative threshold cycle and expression of a ubiquitin housekeeping gene.
Results: Tagraxofusp was cytotoxic towards pDCs from both HV (n=5) and SSc donors (n=5) to a similar extent. The ED50 of tagraxofusp in pDCs from HV and SSc was 4.3 and 3.2 ng/ml (74.4 and 55.4 pM), respectively; no effect was observed on B or T cells across the tagraxofusp dose range tested (Fig.1A). Tagraxofusp-mediated pDC depletion was further accompanied by a 68-fold reduction in secreted IFN-α and a 3-fold downregulation of GBP, a type 1 IFN-induced gene (Fig. 1B).
Conclusion: Tagraxofusp is a novel CD123-targeted therapy that is cytotoxic towards pDCs from SSc patients. These data present a novel approach of targeting pDCs in the treatment of SSc, and a clinical trial is under design.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lindsay R, Chen J, Spiera R, Gordon J, Ah Kioon M, Barrat F, Brooks C. CD123+ Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells from Systemic Sclerosis Patients Are Susceptible to the Cytotoxic Activity of Tagraxofusp, a CD123-Targeted Therapy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cd123-plasmacytoid-dendritic-cells-from-systemic-sclerosis-patients-are-susceptible-to-the-cytotoxic-activity-of-tagraxofusp-a-cd123-targeted-therapy/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cd123-plasmacytoid-dendritic-cells-from-systemic-sclerosis-patients-are-susceptible-to-the-cytotoxic-activity-of-tagraxofusp-a-cd123-targeted-therapy/