Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: CD3+CD4–CD8– “double negative” T cells are expanded in the peripheral blood of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and lupus-prone mice. Double negative T cells infiltrate tissues, induce immunoglobulin production and secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines. Although double negative T cells have been claimed to derive from CD8+ T cells through down-regulation of CD8 surface co-receptors, the molecular mechanisms orchestrating this process remain unclear. The transcription factor cAMP responsive element modulator (CREM)α, that is overexpressed in T cells from SLE patients, has been demonstrated to trans-regulate lupus-relevant genes and orchestrate epigenetic remodeling in mature T cells. Thus, CREMα is a promising candidate in the search for molecular mechanisms in T cell pathology in SLE.
Methods: Primary human and murine T lymphocytes were isolated to assess epigenetic differences of the CD8 cluster in CD8+, CD4+, and double negative T cells using MeDIP and ChIP techniques. CD8 mRNA and protein expression was monitored in response to forced expression or knock-down of CREMα. CREMα-mediated effects on chromatin conformation were assessed using over-expression and knock-down techniques, followed by MeDIP or ChIP. Interactions between CREMα and epigenetic modifiers were established using Co-IPs and proximity ligation assays (PLA).
Results: We link CREMα with transcriptional silencing of CD8A and CD8B in T cells from SLE patients and lupus prone MRL/lpr mice. CREMα trans-represses CD8 and mediates chromatin remodeling of the CD8 cluster through the recruitment of DNA methyltransferase (DNMT)3a and histone methyltransferase G9a.
Conclusion: We conclude that CREMα is essential for the expansion of double negative T cells in SLE and propose that CREMα may be utilized as disease biomarker and therapeutic target.
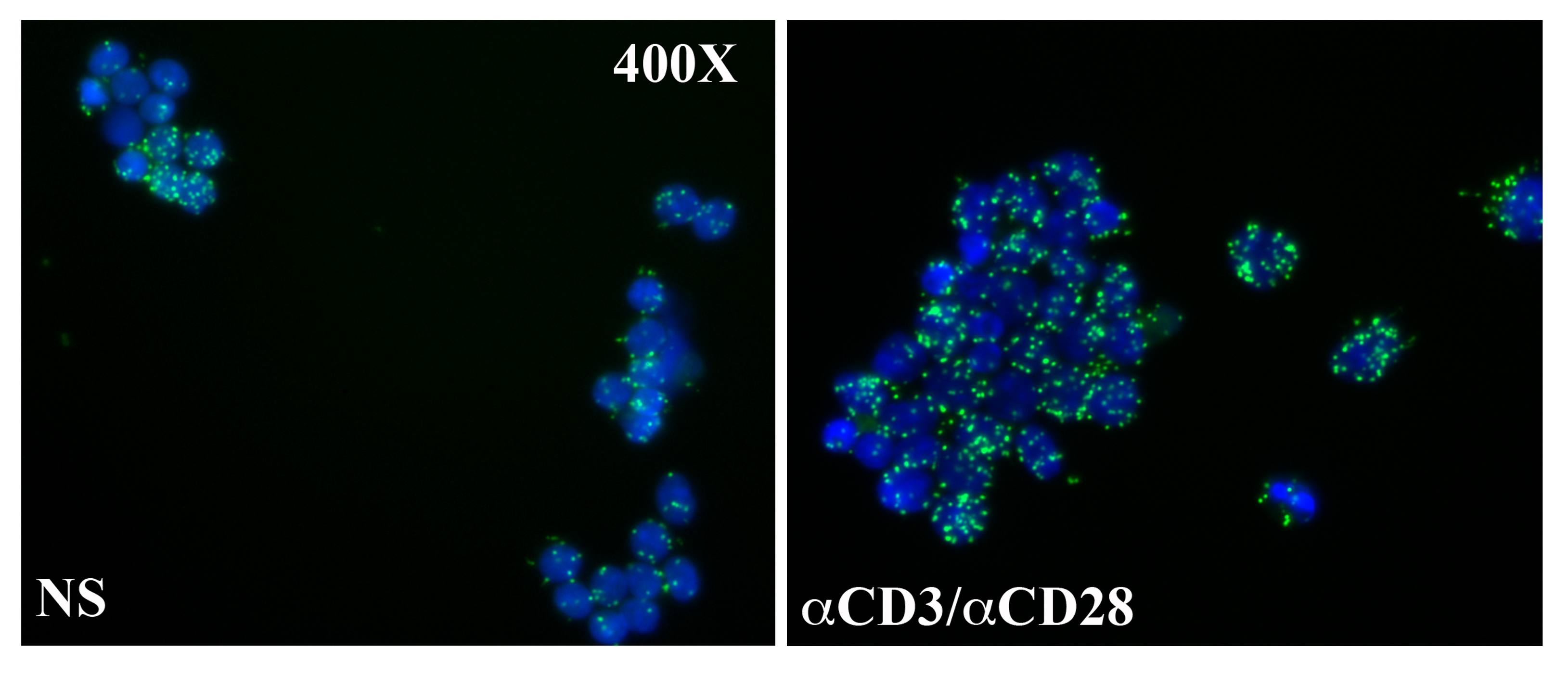
An interaction between CREMα and G9a has been established applying proximity ligation assays. Ex vivo isolated CD8+ T cells exhibit interactions between CREMα and G9a that are enhanced after TCR-stimulation (120h). Nuclei are stained with DAPI, green signals represent CREMα:G9a interactions.
Disclosure:
C. M. Hedrich,
None;
J. C. Crispín,
None;
T. Rauen,
None;
C. Ioannidis,
None;
T. Koga,
None;
N. Rodriguez Rodriguez,
None;
S. A. Apostolidis,
None;
V. C. Kyttaris,
None;
G. C. Tsokos,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/camp-responsive-element-modulator-crem%ce%b1-governs-cd8-expression-and-contributes-to-the-generation-of-cd3cd4cd8-t-cells-in-lupus/