Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Immunoglobulin A Vasculitis (IgAV) is an inflammatory disease caused by the accumulation of immune complexes of IgA in the walls of small blood vessels [1]. These immunocomplexes have been shown to activate the mannan-binding lectin and the alternative complement pathway [2]. Moreover, complement system components have been observed in skin and kidney biopsies in IgAV patients [3]. In this context, the complement protein C5a (a fragment cleaved from the C5 complement factor), together with its receptor, C5aR1, have been proposed as therapeutic targets in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV) [4], another small-vessel vasculitis [1]. Nevertheless, the molecular mechanisms by which the complement is involved in IgAV are poorly understood. In light of this, this work aimed to determine whether C5 and C5AR1 represent novel genetic risk factors for IgAV.
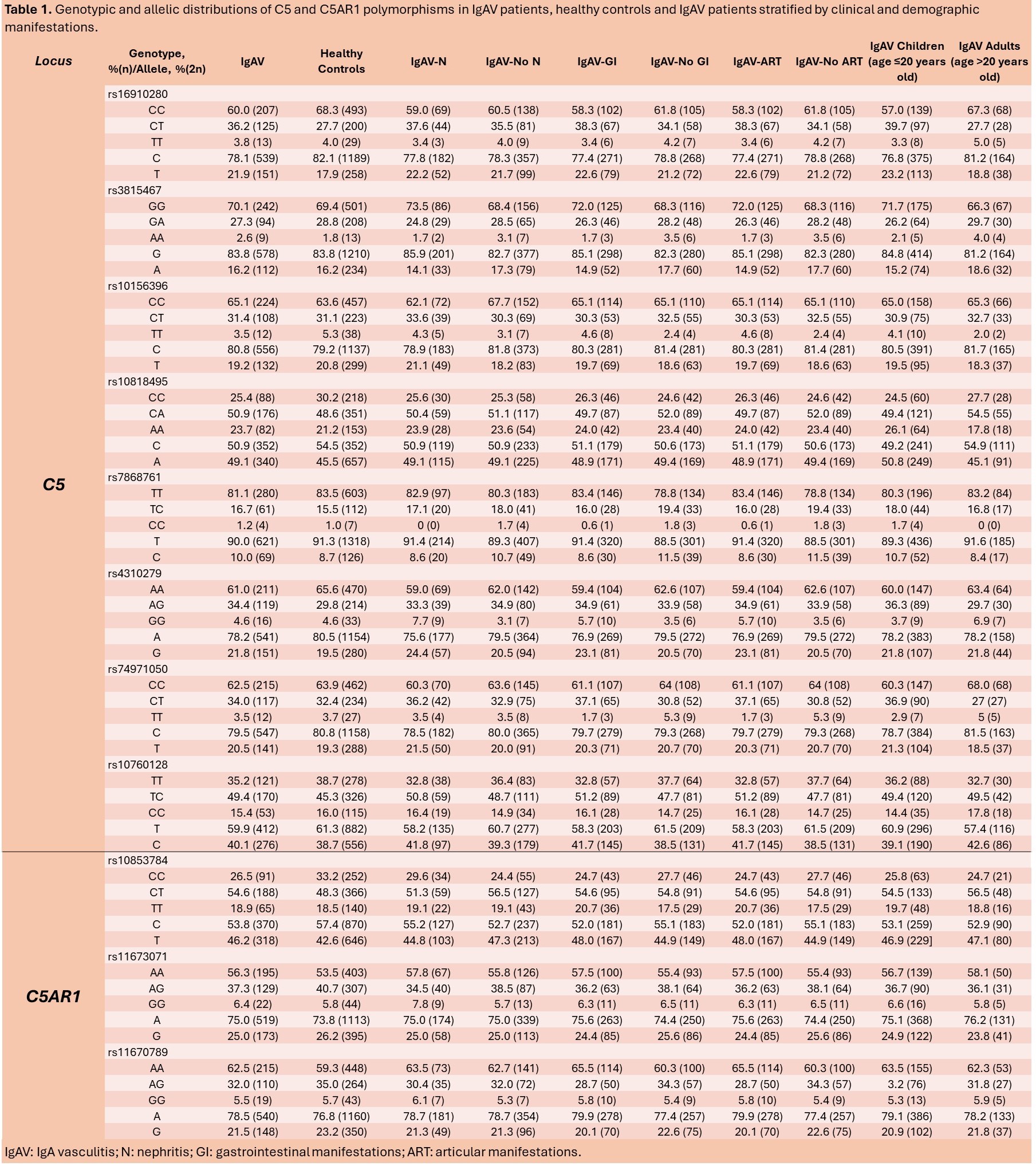
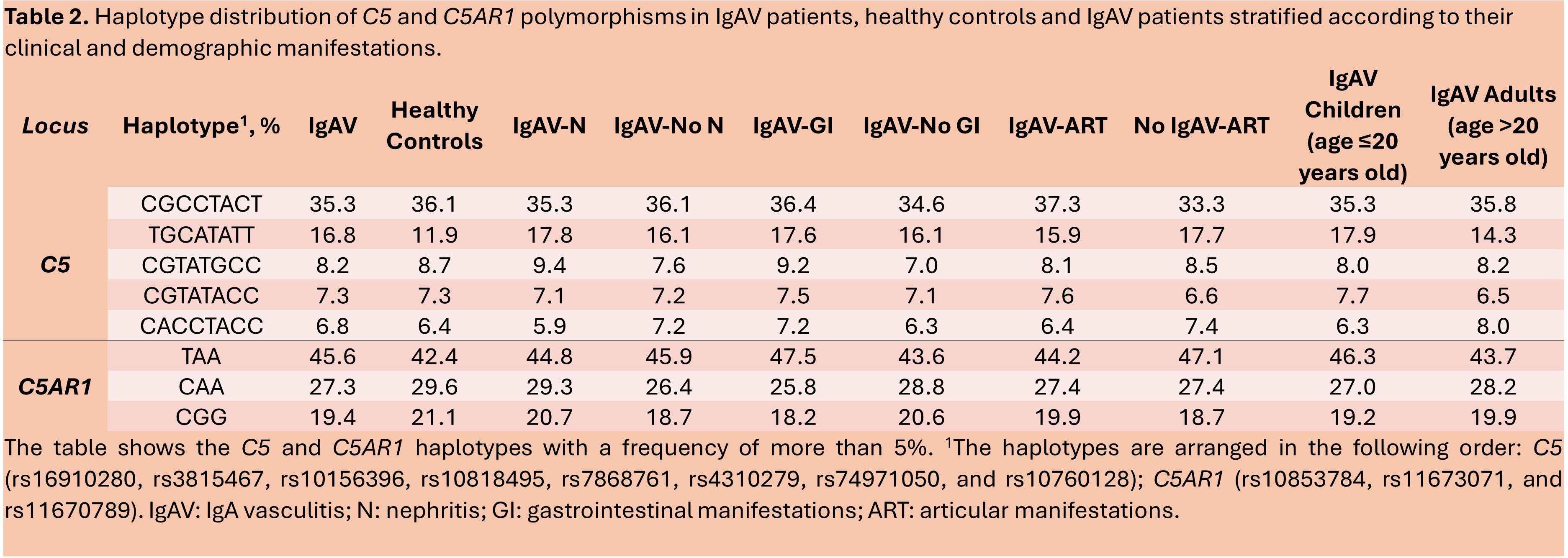
Methods: 346 patients with IgAV, the largest series of Caucasian patients with IgAV ever assessed for genetic studies, and 764 healthy ethnically matched controls (HC), were recruited for this study. Among the IgAV patients, 33.8% (117) presented nephritis (IgAV-N). Eight tag single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within C5 (rs16910280, rs3815467, rs10156396, rs10818495, rs7868761, rs4310279, rs74971050, and rs10760128) and 3 C5AR1 tag SNPs (rs10853784, rs11673071, and rs11670789) were genotyped by qPCR using TaqMan Probes. p-values < 0.05 after Benjamini-Hochberg correction for an FDR of 5% were considered statistically significant.
Results: No statistically significant difference was found in C5 and C5AR1 genotype and allele frequencies between patients with IgAV and HC (Table 1). Likewise, when IgAV patients were stratified according to the severity of the disease, represented by the presence or absence of renal manifestations, we did not observe differences of statistical significance in the genotype and allele frequencies of C5 and C5AR1. Moreover, when IgAV patients were stratified according to other clinical aspects, such as the age at disease onset or the presence/absence of articular and gastrointestinal manifestation, no significant differences were observed in the genotype and allele frequencies in C5 and C5AR1 (Table 1). Furthermore, no differences in the haplotype frequencies of C5 and C5AR1 were observed between IgAV patients and HC (Table 2), and between IgAV patients stratified according to the severity of the disease (Table 2) as well as to other clinical manifestations (Table 2).
Conclusion: Our results suggest that C5 and C5AR1 do not seem to be involved in the pathogenesis of IgAV.
References: [1] Arthritis Rheum. 2013 Jan;65(1):1-11, [2] Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 3:13:921864, [3] Autoimmun Rev. 2017 Dec;16(12):1246-1253, [4] Immunobiology. 2023 Sep;228(5):152413.
Research funded by FEDER funds (EU) and “Fondo de Investigaciones Sanitarias” (ISCIII, Health Ministry, Spain), grant number PI21/00042. JCBL: PFIS program fellowship (ISCIII-ESF: FI22/00020); RL-M: Miguel Servet type II (ISCIII-ESF: CPII21/00004).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Batista-Liz J, Calvo-Rio V, Sebastián Mora-Gil M, Gabrie-Rodriguez L, Gálvez Sánchez R, Sevilla-Pérez B, Callejas J, Leonardo M, Peñalba A, Narvaez-García J, Martín-Penagos L, Caminal-Montero L, COLLADO P, Quiroga Colina P, Vicente-rabaneda E, Rubio E, León Luque M, Blanco-Madrigal J, Galindez-Agirregoikoa E, Castañeda S, Blanco-Alonso R, Pulito-Cueto V, Lopez-mejias R. C5 Signaling Pathway Genes as Key Drivers of the Pathogenesis of IgA Vasculitis? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/c5-signaling-pathway-genes-as-key-drivers-of-the-pathogenesis-of-iga-vasculitis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/c5-signaling-pathway-genes-as-key-drivers-of-the-pathogenesis-of-iga-vasculitis/