Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) is a key therapy for lupus (or SLE). Yet, challenged to weigh benefits vs. harms, ~80% of patients self-discontinue HCQ. Shared decision-making (SDM) tools, like HCQ-SAFE© (Garg, 2023), can support patients and clinicians in complex treatment decisions. In a clinical trial, HCQ-SAFE SDM intervention (Fig. 1A) was used by 12 clinicians during 200 visits in 8 clinics of 2 health systems. Still adoption of SDM tools can be challenging in non-research settings, particularly busy clinics and low-resource settings. We aimed to: 1) examine implementation outcome metrics mapped to the RE-AIM framework for using the HCQ-SAFE SDM intervention; 2) develop strategies based on clinician experiences using the Normalization Process Theory (NPT) to revise HCQ-SAFE implementation workflow for easier integration in clinics.
Methods: The HCQ-SAFE SDM intervention (Fig. 1A) was implemented in 200 unique visits by 6 MDs, 3 PharmDs, and 3 RNs (NCT05922722). Clinicians completed a questionnaire to report intervention details (version, topics, language), time, and rated feasibility & likelihood to use on a 1-9 Likert scale (9=best). Clinicians also participated in a cognitive interview to share experiences, barriers, & facilitators to HCQ-SAFE use. Quantitative data from 200 questionnaires estimated RE-AIM implementation metrics. Reach: % eligible visits completing HCQ-SAFE. Effectiveness: change in decisional conflict scores (overall/by role). Adoption: % clinicians completing intervention. Implementation: Fidelity (% visits covering ≥1 benefit/harm, language) & Feasibility (median score ≥7, time ≤5 min).
Maintenance: monthly completion rate & Net Promoter Score (NPS ≥80%, motivators – detractors). Qualitative data from interviews were analyzed using a coding scheme informed by 4 NPT domains to identify strategies to refine workflows for easier integration of HCQ-SAFE in clinics.
Results: In 200 visits, MDs (50%), PharmDs (28%), and RNs (22%) completed the HCQ-SAFE intervention (Table 1). Data analysis showed excellent completion rates (100%) across MDs, PharmDs, RNs, with equally effective resolution of decisional conflicts regardless of clinician role (98% PharmD/RN vs. 99% MD; Table 1). Adoption was slightly lower among MDs (75%) vs. PharmDs/RNs (100%). HCQ-SAFE was rated highly feasible (median score 9, median time 5 mins) and received 100% NPS, indicating strong clinician willingness for continued use. Content analysis of clinician experiences using NPT yielded 6 strategies for HCQ-SAFE implementation (Table 2; Fig. 1B). Key recommendations included: tailoring training by role, simplifying eligibility to include all SLE patients, using PharmDs/RNs to lead reviews. Clinicians preferred this equally effective staff-led model for easier integration and facilitate team-based care. The revised clinical workflow (Fig. 1B) gained unanimous endorsement from participating clinicians.
Conclusion: The impact of this study is 2-fold. First, it establishes HCQ-SAFE is a highly feasible and effective SDM intervention for clinical use. Second, it delivers an end-user-informed practical workflow to ensure sustainable integration in clinics to promote medication adherence via SDM.
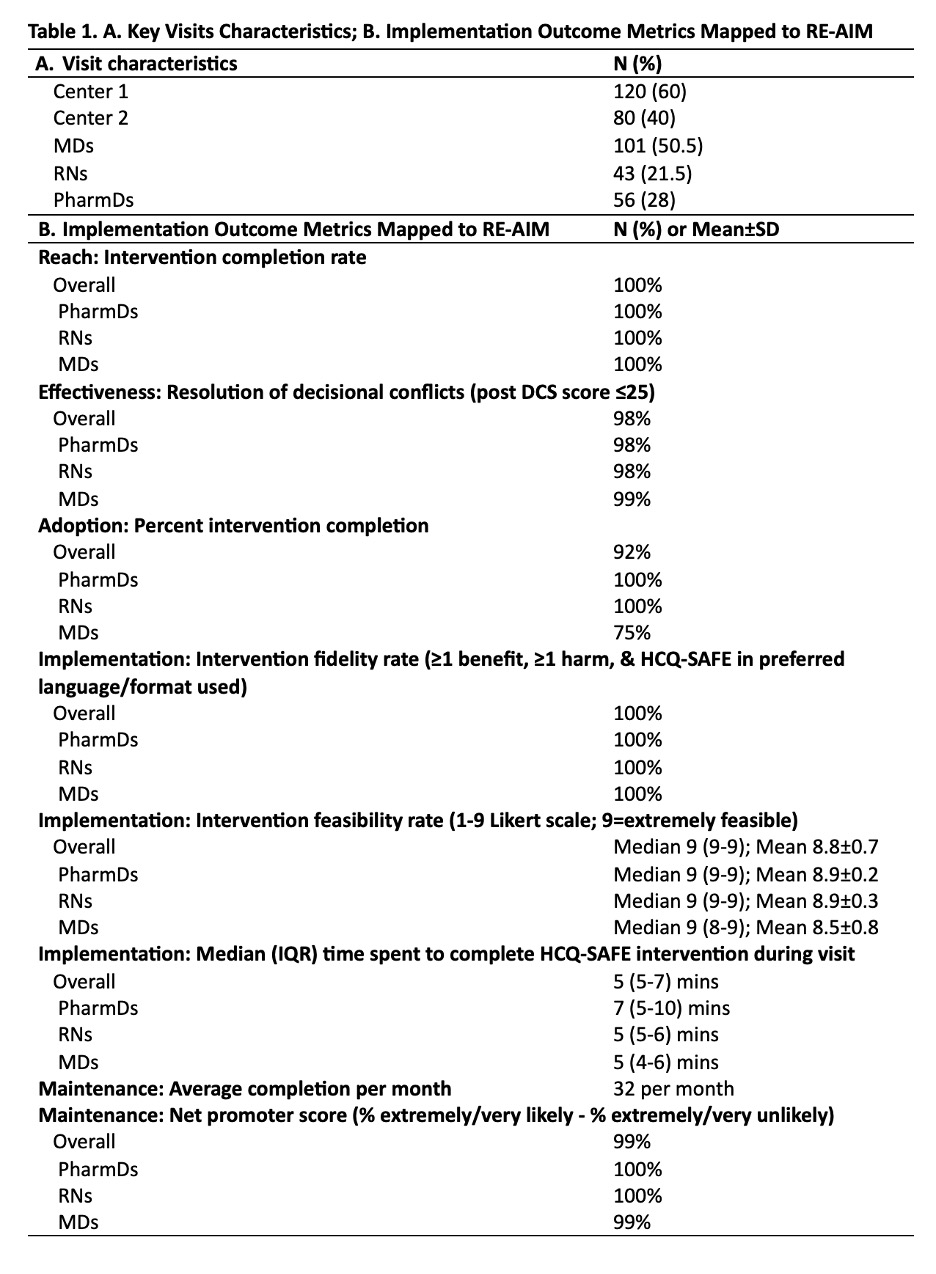 Table 1. A. Key Visits Characteristics; B. Implementation Outcome Metrics Mapped to RE-AIM
Table 1. A. Key Visits Characteristics; B. Implementation Outcome Metrics Mapped to RE-AIM
.jpg) Table 2. Qualitative Analysis of Clinician Interviews Informed by Normalization Process Theory Domains to Deliver Strategies to Develop Practical Workflow for HCQ-SAFE Integration in Clinics
Table 2. Qualitative Analysis of Clinician Interviews Informed by Normalization Process Theory Domains to Deliver Strategies to Develop Practical Workflow for HCQ-SAFE Integration in Clinics
.jpg) Figure 1A. Swim Lane diagram showing the study workflow used to implement the HCQ-SAFE shared decision-making intervention across 200 unique patient visits in 8 clinics of 2 health systems; Figure 1B. An end-user-informed practical workflow for routine use of HCQ-SAFE shared decision-making intervention in clinics
Figure 1A. Swim Lane diagram showing the study workflow used to implement the HCQ-SAFE shared decision-making intervention across 200 unique patient visits in 8 clinics of 2 health systems; Figure 1B. An end-user-informed practical workflow for routine use of HCQ-SAFE shared decision-making intervention in clinics
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hartel I, Patel J, Gazeley D, Johnson D, Levinson J, Campbell C, Youngchild B, Gomez S, Weber A, Michaud J, Dickmann L, Ferguson S, Chewning B, Bartels C, Garg S. Bridging the Gap: A Mixed-Methods Study to Enhance Integration of HCQ-SAFE, A Shared Decision-Making Tool for Hydroxychloroquine Use, in Routine Lupus Care [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bridging-the-gap-a-mixed-methods-study-to-enhance-integration-of-hcq-safe-a-shared-decision-making-tool-for-hydroxychloroquine-use-in-routine-lupus-care/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bridging-the-gap-a-mixed-methods-study-to-enhance-integration-of-hcq-safe-a-shared-decision-making-tool-for-hydroxychloroquine-use-in-routine-lupus-care/
