Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (0978–1006) T Cell Biology & Targets in Autoimmune & Inflammatory Disease Poster
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Despite advances in therapies for chronic autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), significant unmet needs persist, including therapeutic ceiling effects, adverse events, and suboptimal remission rates. We hypothesized that a rationally designed, dual-targeting molecule could enhance remission rates and reduce required dosing, thereby improving the safety profile. ELN28 is a first-in-class bi-functional soloMER drug conjugate (SDC) targeting soluble TNFα and delivering the JAK inhibitor Tofacitinib directly to inflamed tissues. The payload is released in the presence of neutrophil elastase, which is enriched in inflammatory microenvironments. We evaluated ELN28’s functional activity and compared it to mono-specific anti-TNFα therapies across multiple ex vivo and in vivo models of autoimmune inflammation.
Methods: Dual immunomodulatory activity of ELN28 was assessed in phytohemagglutinin (PHA)-stimulated healthy donor PBMCs. To model synovial inflammation, a 3D co-culture system was developed comprising primary RA synovial fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and monocytes (2:2:1 ratio). Organoids were treated with ELN28, followed by quantification of cytokine and chemokine production. In vivo efficacy was tested in an LPS-induced acute inflammation model (Tg1278TNFKOhTNFR1KI), where ELN28 was administered 2 hours pre-LPS exposure and cytokine levels measured after 5 hours. Chronic efficacy was evaluated in the Tg197 transgenic mouse model of polyarthritis, with biweekly ELN28 dosing over 7 weeks. Comparative treatments included Adalimumab and a mono-specific anti-TNFα soloMER (ELN22).
Results: ELN28 exhibited high-affinity (~100 pM) binding to soluble TNFα and potent neutralization in TNFα-stimulated L929 fibrosarcoma assays. Structural analysis via X-ray crystallography confirmed binding to a recessed epitope unique to soluble TNFα, enabling discrimination from membrane-bound TNFα. ELN28 inhibited PHA-induced PBMC proliferation and significantly reduced secretion of CXCL1, CXCL5, CXCL10, IL-6, and CCL2 in the RA synovial organoid model, outperforming mono-specific comparators. In vivo, ELN28 demonstrated dose-dependent, superior efficacy versus Adalimumab and ELN22 in the LPS-induced Tg1278 model. In the Tg197 chronic arthritis model, ELN28 improved histopathological outcomes—including reductions in bone erosion, cartilage destruction, and inflammatory scores—and achieved twofold superiority in normalizing disease-associated gene expression (RNA-seq) toward a wild-type baseline.
Conclusion: ELN28 is a novel bi-functional drug conjugate that combines selective TNFα neutralization with inflammation-targeted JAK inhibition. Its unique targeting of soluble TNFα and elastase-triggered delivery mechanism offer a promising strategy for overcoming limitations of current RA therapies. ELN28 demonstrated robust dual activity and disease-modifying effects in preclinical models of autoimmune inflammation. IND-enabling studies are underway to advance ELN28 toward clinical development in RA and related autoimmune diseases, including Psoriatic Arthritis, Hidradenitis Suppurativa, and IBD.
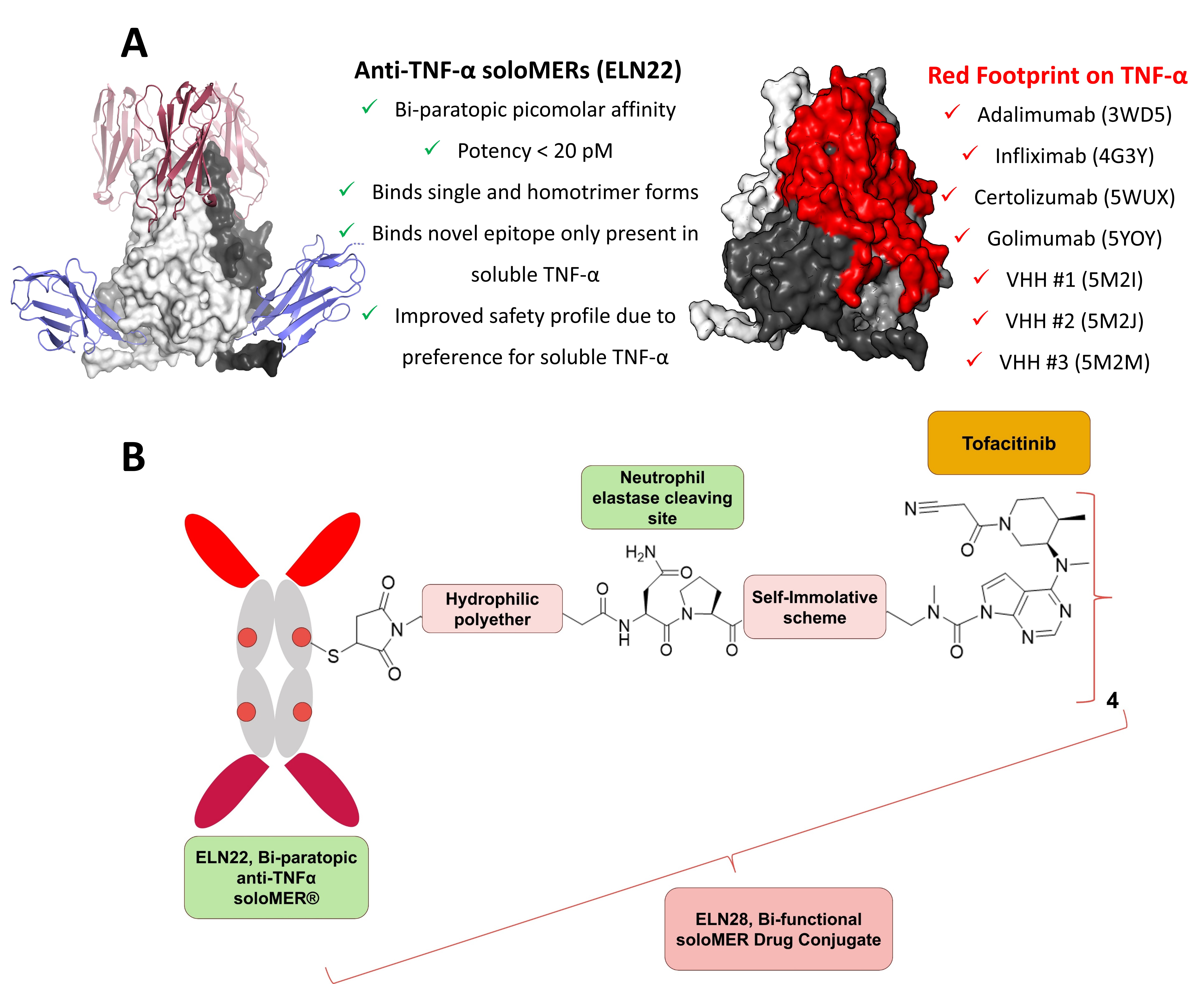 (A) X-ray structures of anti-TNF-α soloMERs expose novel TNF-α epitopes (left). On the right, crystallography data of existing anti-TNFα binding domains illustrating in red their overlapping footprint on TNF-α molecule (B) ELN28 SDC targets both soluble TNFα and Janus kinases. The overexpression of soluble TNFα in the inflamed tissues drives preferential accumulation of SDC at these sites. Tofacitinib payload is efficiently and safely released in the inflamed tissue by the action of human neutrophil elastase (HNE).
(A) X-ray structures of anti-TNF-α soloMERs expose novel TNF-α epitopes (left). On the right, crystallography data of existing anti-TNFα binding domains illustrating in red their overlapping footprint on TNF-α molecule (B) ELN28 SDC targets both soluble TNFα and Janus kinases. The overexpression of soluble TNFα in the inflamed tissues drives preferential accumulation of SDC at these sites. Tofacitinib payload is efficiently and safely released in the inflamed tissue by the action of human neutrophil elastase (HNE).
.jpg) (A) Inhibition of TNF-α mediated cytotoxicity in L929 mouse fibrosarcoma cell line (left), and Anti-TNF-α independent inhibition of JAK/STAT phosphorylation signalling in human IL23-JAK/STAT HEK Blue™ Reporter cells (right). Functional Tofacitinib is released from ELN28 SDC in the presence of HNE. ELN0-2V is an isotype control soloMER (B) In the presence of HNE, ELN28 inhibited phytohemagglutinin (PHA) induced PBMC proliferation (donors A, C, D E). In a pooled PBMC sample, ELN28 +/- HNE demonstrated the additive (bifunctional) activity. ELN0-2V is an isotype control soloMER drug conjugate with a non-binding soloMER conjugated to Tofacitinib.
(A) Inhibition of TNF-α mediated cytotoxicity in L929 mouse fibrosarcoma cell line (left), and Anti-TNF-α independent inhibition of JAK/STAT phosphorylation signalling in human IL23-JAK/STAT HEK Blue™ Reporter cells (right). Functional Tofacitinib is released from ELN28 SDC in the presence of HNE. ELN0-2V is an isotype control soloMER (B) In the presence of HNE, ELN28 inhibited phytohemagglutinin (PHA) induced PBMC proliferation (donors A, C, D E). In a pooled PBMC sample, ELN28 +/- HNE demonstrated the additive (bifunctional) activity. ELN0-2V is an isotype control soloMER drug conjugate with a non-binding soloMER conjugated to Tofacitinib.
.jpg) (A) ELN28 attenuates the release of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines in an LPS induced acute inflammation human TNF-α transgenic mouse model (Tg1278TNFKohTNFR1K1). In this acute inflammation model, LPS was administered 2 h after intraperitoneal administration of test articles, and terminal blood sampling 5 h post-LPS dosing (B) Test articles were dosed at 3 mg/kg twice weekly for 7 weeks. ELN28 and ELN22 were comparable in the clinical arthritis score assessment (left panel). Histopathology analysis demonstrated superior disease control by ELN28 (C) RNAseq analysis of disease associated genes (DAGs). Two dimensional scatterplots, regression lines show deviation of the treatment profile from disease group
(A) ELN28 attenuates the release of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines in an LPS induced acute inflammation human TNF-α transgenic mouse model (Tg1278TNFKohTNFR1K1). In this acute inflammation model, LPS was administered 2 h after intraperitoneal administration of test articles, and terminal blood sampling 5 h post-LPS dosing (B) Test articles were dosed at 3 mg/kg twice weekly for 7 weeks. ELN28 and ELN22 were comparable in the clinical arthritis score assessment (left panel). Histopathology analysis demonstrated superior disease control by ELN28 (C) RNAseq analysis of disease associated genes (DAGs). Two dimensional scatterplots, regression lines show deviation of the treatment profile from disease group
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ubah O, Murray E, Priyanka S, Martinez Fraile J, Porter A, Boyd R, Barelle C. Breaking Inflammatory Pathways: ELN28, a Novel Dual TNFα/JAK Inhibitor Drug Conjugate for Chronic Inflammation [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/breaking-inflammatory-pathways-eln28-a-novel-dual-tnf%ce%b1-jak-inhibitor-drug-conjugate-for-chronic-inflammation/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/breaking-inflammatory-pathways-eln28-a-novel-dual-tnf%ce%b1-jak-inhibitor-drug-conjugate-for-chronic-inflammation/
