Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Clinical Aspects - Poster II: Co-morbidities and Complications
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is associated with muscle loss, obesity, and osteoporotic fractures. Body composition and muscle quality are important regulators of bone strength among healthy adults. This study determined if patients with RA have deficits in cortical bone thickness (CBT; a structural measure highly correlated with fracture load) and trabecular bone density (TBD; a measure of volumetric bone mineral density) relative to their body mass. The study also assessed the degree to which these deficits are related to deficits in skeletal muscle.
Methods: Participants with RA, ages 18-75 years, were recruited from academic practices (2012-2016) and compared to a reference sample of healthy controls (ages 21 to 80). Participants underwent peripheral quantitative CT (pQCT) of the tibia to measure CBT and TBD as well as muscle cross-sectional area and density and fat area. Whole-body DXA measured appendicular lean mass index (ALMI), and fat mass index (FMI). BMI and body composition measures were converted to age-, sex, and race-specific Z-Scores. Multivariable linear regression models evaluated independent associations between body composition exposures and bone outcomes in RA and controls with assessment for altered associations in RA.
Results: The study consisted of 102 RA patients (50 men) and 416 controls (192 men). Patients with RA had greater BMI (p=0.004), greater total fat mass (p=0.02) and lower adiposity-adjusted ALMI Z-Scores (p=0.004), and low muscle density Z-Scores (p<0.0001). TBD and CBT Z-Scores were similar in RA and controls. However, RA patients had lower Z-Scores for bone outcomes compared to controls with similar BMI Z-Score (Figure). Sequential adjustment for ALMI, FMI, and muscle density Z-Scores in linear regression models attenuated these associations. Results were similar in analyses incorporating pQCT muscle and fat cross-sectional area Z-Scores. Relationships between body composition and bone outcomes were similar in RA and controls (no interaction) (Table). Men with RA had lower TBD Z-Scores than women with RA (p=0.005). Disease duration >10 years was associated with lower TBD (p=0.07) and CBT (p=0.04) independent of sex, ALMI, and FMI.
Conclusion: Patients with RA have bone structure and density that is maladapted to their weight. Muscle deficits in RA likely contribute to bone deficits through a loss of mechanical loading. Deficits in muscle mass and quality are, therefore, under-recognized risk factors for maladapted bone structure in RA; potentially impacting the long-term risk of fracture. 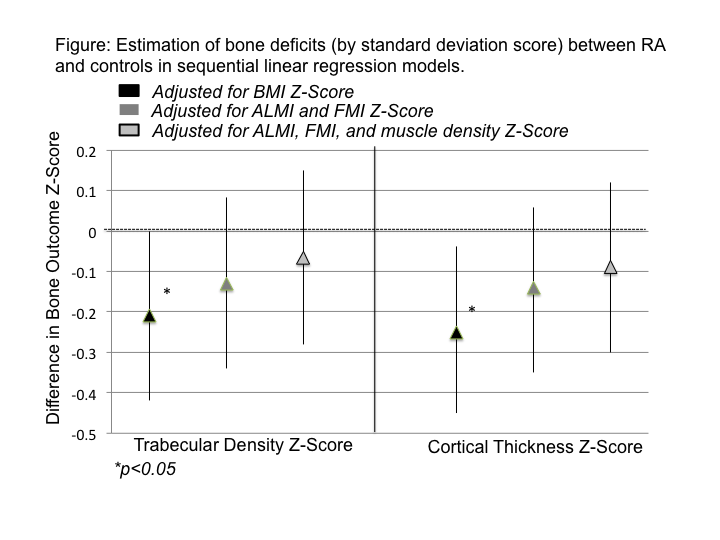
| Table: Beta-coefficients representing associations between body composition and bone structure outcomes in patients with RA and controls. RA has similar relationships (no significant disease interaction) between body composition, muscle quality and bone outcomes. | ||||
|
Rheumatoid Arthritis (N=102) |
Controls (N=416) |
|||
|
TRABECULAR DENSITY Z-SCORE |
||||
| β (95%CI) | p-value | β (95%CI) | p-value | |
| ALMI Z-Score | 0.33 (0.053, 0.61) | 0.02 | 0.34 (0.21, 0.47) | 0.001 |
| FMI Z-Score | 0.12 (-0.12, 0.36) | 0.33 | 0.0062 (-0.088, 0.15) | 0.90 |
| Muscle Density Z-Score | 0.099 (-0.099, 0.30) | 0.33 | 0.10 (0.011, 0.20) | 0.03 |
|
CORTICAL THICKNESS Z-SCORE |
||||
| β (95%CI) | p-value | β (95%CI) | p-value | |
| ALMI Z-Score | 0.35 (0.11, 0.59) | 0.004 | 0.45 (0.33, 0.58) | <0.001 |
| FMI Z-Score | -0.04 (-0.23, 0.17) | 0.77 | -0.027 (-0.15, 0.092) | 0.66 |
| Muscle Density Z-Score | 0.12 (-0.039, 0.29) | 0.14 | 0.089 (-0.0023, 0.18) | 0.06 |
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Baker J, Long J, Zemel BS, Dinnella JE, Sharma P, Ibrahim S, Leonard MB. Bone Structural Deficits in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Impact of Muscle Mass and Density [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bone-structural-deficits-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-impact-of-muscle-mass-and-density/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bone-structural-deficits-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-impact-of-muscle-mass-and-density/
