Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1264–1307) RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rapid radiographic progression (RRP) is selected as one of the risk factors for difficult- to- treat RA, which needs to be resolved as soon as possible. On the other hand, EULAR recommendations for imaging were published, in which MRI bone oedema was an independent and strong predictor for joint destruction.
To clarify, association of BE with RRP using the clinical data in RA patients treated with conventional synthetic (cs) DMARDs. This study was undertaken for patients as post-hoc analysis of the paper (Trial Registration Number: UMIN000012200): Etiology of autoimmune diseases: Commensal bacterial pathogens overwhelming antibody defence function evoke serological marker levels and aggravate disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. (K. Terato et al. Published: February 6, 2018, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0190588).
Methods: All patients were mainly treated with methotrexate (MTX) or MTX +other csDMARDs combination therapy. The majority of patients did not respond to medication. None of the patients received biologics during the study. Hand and feet X-rays were taken for all patients and MRI was taken for affected hand. The modified total Sharp score (mTSS) was evaluated by KK and TO over a period of one year. MRI hand BE (rarely other large joints) were also checked by same reader by OMERACT MRI method as BE score.
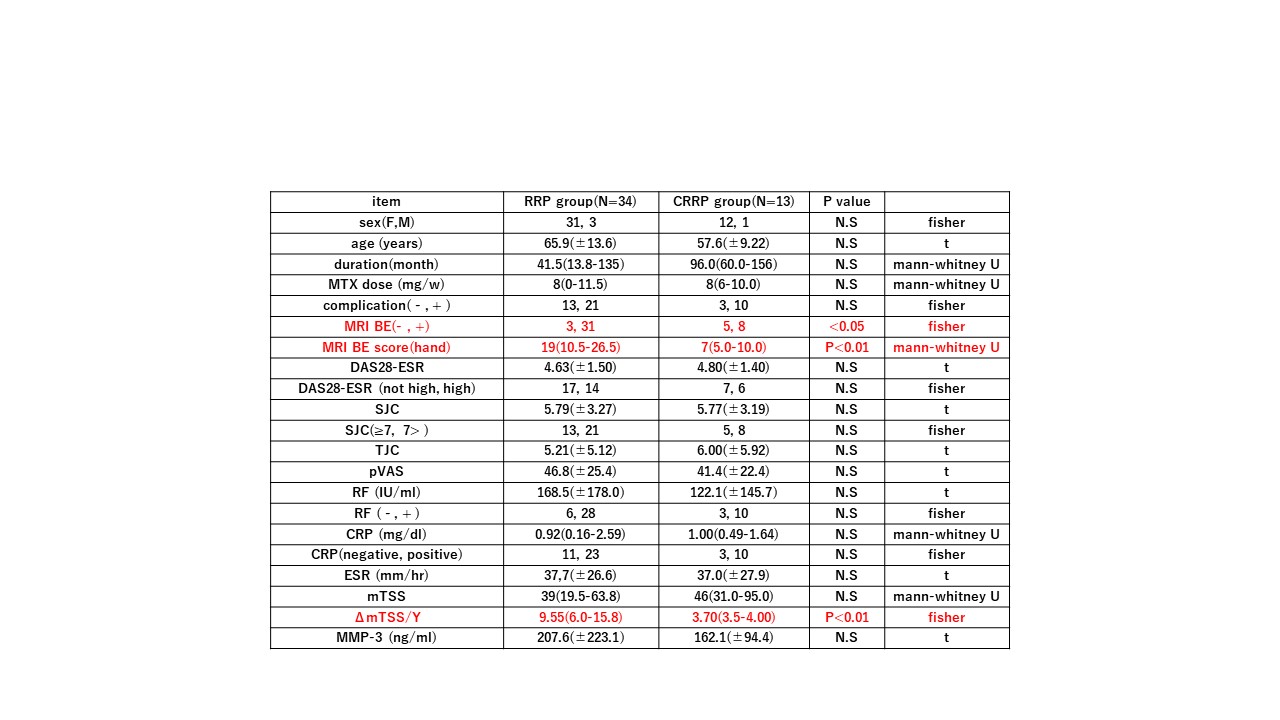
Results: 1) At first, baseline data of 108 non-RRP patients and 47 Clinically relevant radiographic progression (CRRP:5 >ΔmTSS /year≥3)+RRP patients (ΔmTSS /year ≥5) were statistically compared. Short duration, high BE rate and MRI BE score (hand), high DAS28-ESR , high CRP levels, high mTSS, high yearly progression of mTSS were significantly increased in RRP+CRRP group compared with non RRP group. Secondly, background data of 13 CRRP and 34 RRP patients were compared. Only percentages of BE, MRI BE score (hand) were significantly increased in RRP group compared with CRRP group (table 1)
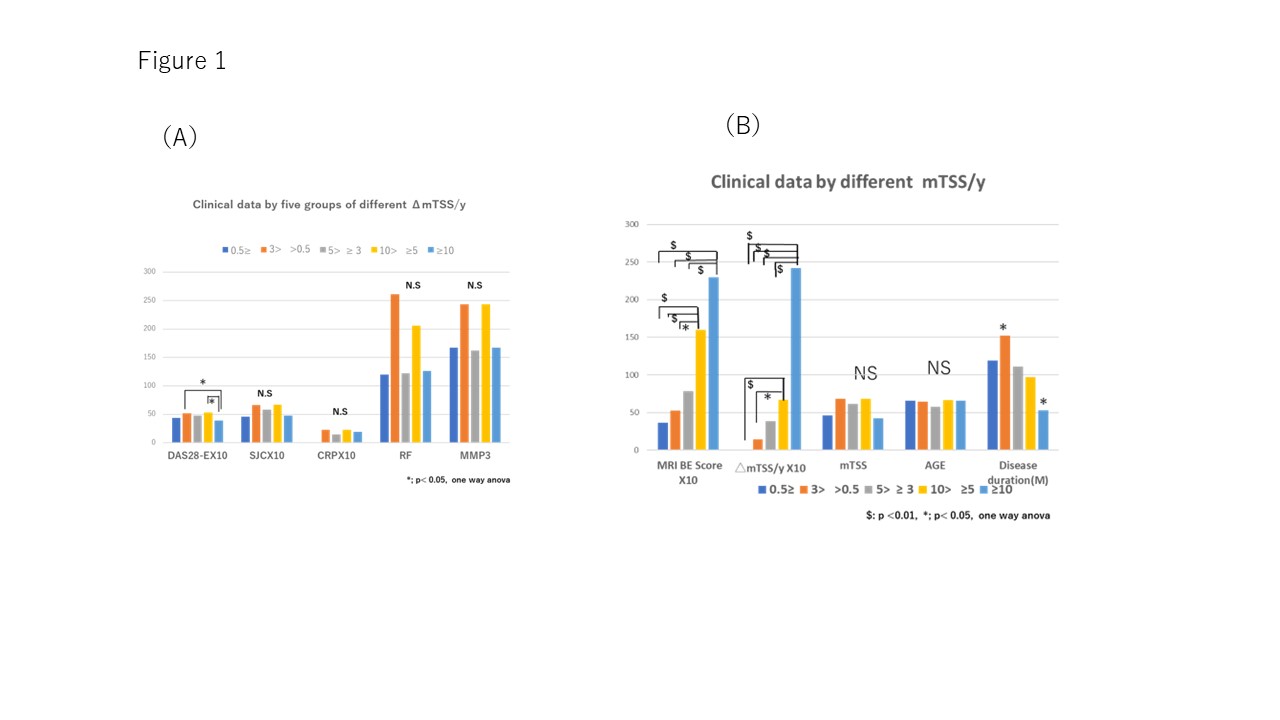
2)Secondly, patient data were divided into 5 groups according to rate of 1) ΔmTSS/year– ≥10, 2)< 10 and ≥5 (both 1)2) are in RRP group), 3) < 5 and ≥3 (in CRRP group), 4) < 3 and >0.5, and 5)) ≤ 0.5(both 4)5) are in non RRP group). Mean of DAS28-ESR in the group of ΔmTSS /year ≥10 was significantly lower in the group of ΔmTSS /year < 10 and ≥5 and < 3 and >0.5, respectively(P< 0.05). No significant changes were observed in SJC (x10), CRP value (x10), RF, MMP3 (ng/ml) (figure 1A). We also compared mean BRI BE score (hand)(x10), ΔmTSS /year (x10), mTSS, age, disease duration among 5 groups. As a results, MRI BE score (hand) and and ΔmTSS /year in the group of ΔmTSS /year-≥10 or < 10 and ≥5 (both 4)5) are in RRP group) was significantly higher than another group (figure 1B).
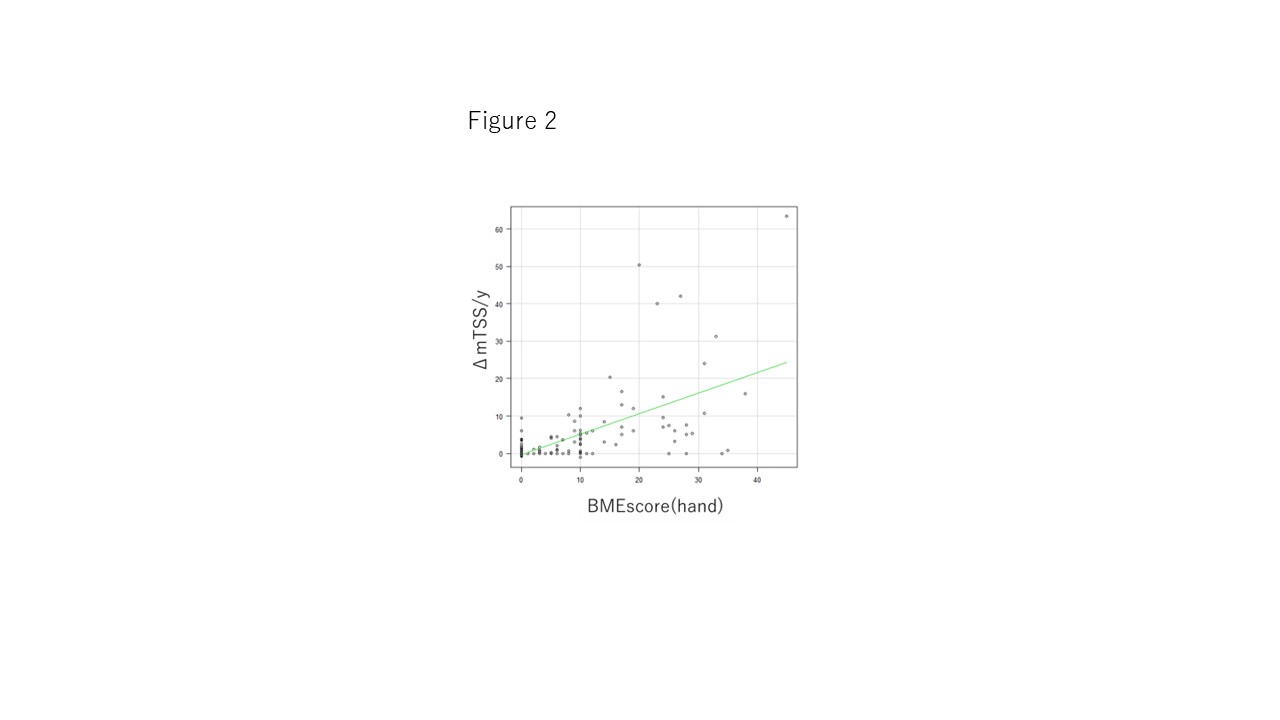
3) Finally, we investigated correlation between MRI BE score and ΔmTSS /year(x10). We found slight correlation between them. r = 0.57 P = 0.001(Pearson Correlation Coefficient) (Figure 2).
Conclusion: BE may be a possible prognostic factor for RRP and more associated with RRP than CRRP.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Katayama K, Okubo T, Sato T, Tanaka K, Kawahata T, Makino Y, Ito H. Bone Marrow Edema in MRI Is More Associated with Rapid Radiographic Progression Than Clinically Relevant Radiographic Progression [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bone-marrow-edema-in-mri-is-more-associated-with-rapid-radiographic-progression-than-clinically-relevant-radiographic-progression/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bone-marrow-edema-in-mri-is-more-associated-with-rapid-radiographic-progression-than-clinically-relevant-radiographic-progression/