Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1124–1154) Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Inflammatory musculoskeletal diseases including rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) are characterized by physical function impairment due to progressive inflammatory and structural changes. This becomes apparent even in the early disease stages before arthritis onset, such as in psoriasis (PsO). Chronic inflammation triggers an accelerated remodeling of the extracellular matrix (ECM), resulting in the release of specific degradation products of proinflammatory and collagen molecules that can be measured in blood. In this study, we explored whether levels of ECM biomarkers differ among patients with RA, PsA and PsO, and controls. In addition, we investigated the association between biomarkers and functional impairment by measures of hand function.
Methods: This is a secondary analysis of serum samples obtained from participants of three hand function studies with identical study conditions for sample collection and assessments (FAU ethics approval #125_16B, #357_20B). Serum samples from patients with RA, PsA, and PsO, and controls were obtained in the outpatient clinic of the Rheumatology and Dermatology Department, Universitätsklinikum Erlangen, Germany. Serum ECM catabolic markers (C1M, C2M, C3M, C4M, PRO-C4, C6M, ARG), formation markers (PRO-C1, PRO-C3, PRO-C6), and inflammation markers (VICM) were measured by immunoassay (Nordic Bioscience, Herlev, Denmark). Fine motor skills were assessed by the Moberg-Picking-Up Test (MPUT) and isometric grip strength was measured using a dynamometer. The Michigan Hand Questionnaire (MHQ) was used to evaluate patient-perceived hand function. The best out of two and three attempts was used for the analysis of MPUT and grip strength, respectively. Linear regression models with robust standard errors were used to compare biomarker levels between groups, adjusting for age and gender. Correlations between biomarker data and hand function were assessed by Spearman’s rank correlation (ρ) and p-values were adjusted by false discovery rate method.
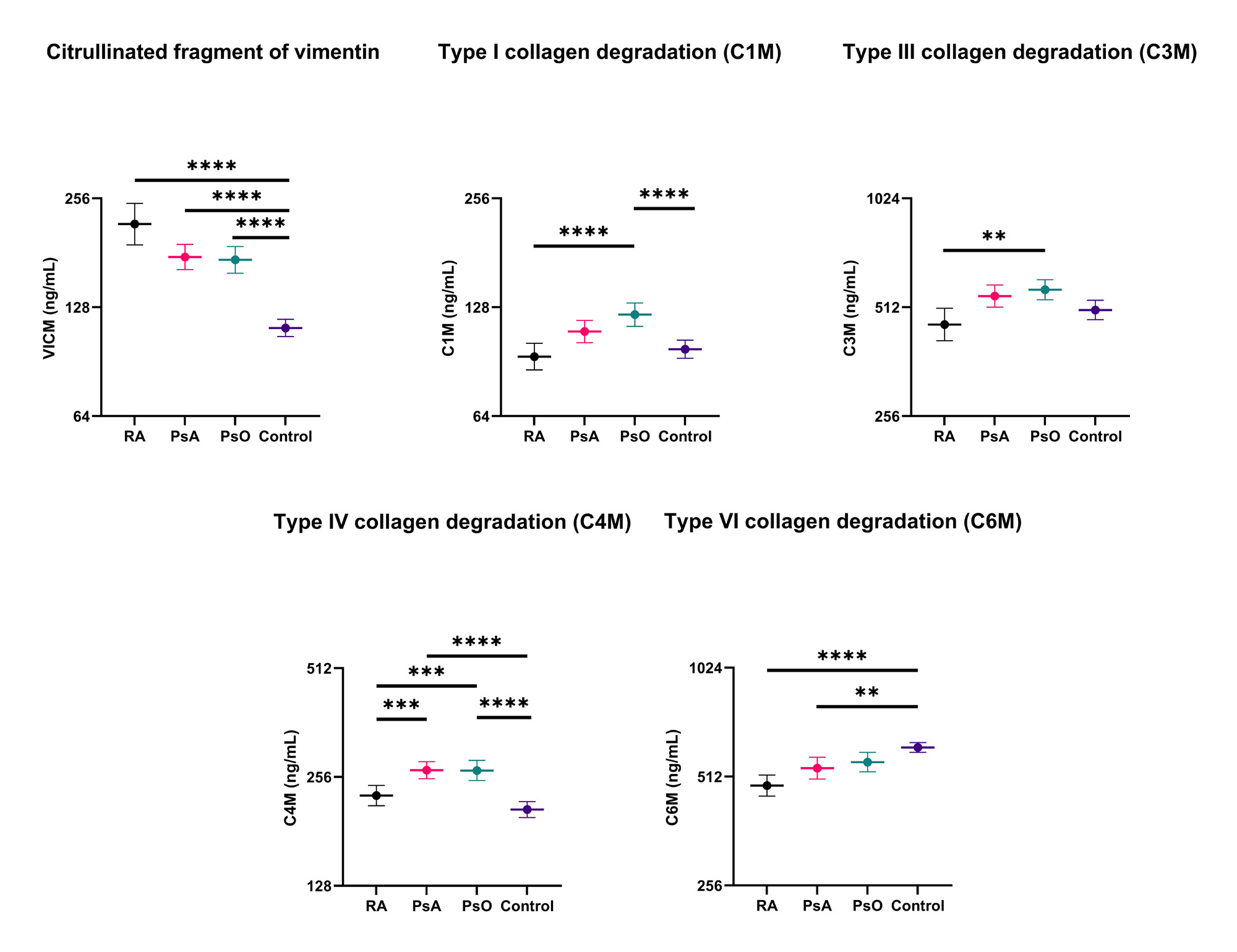
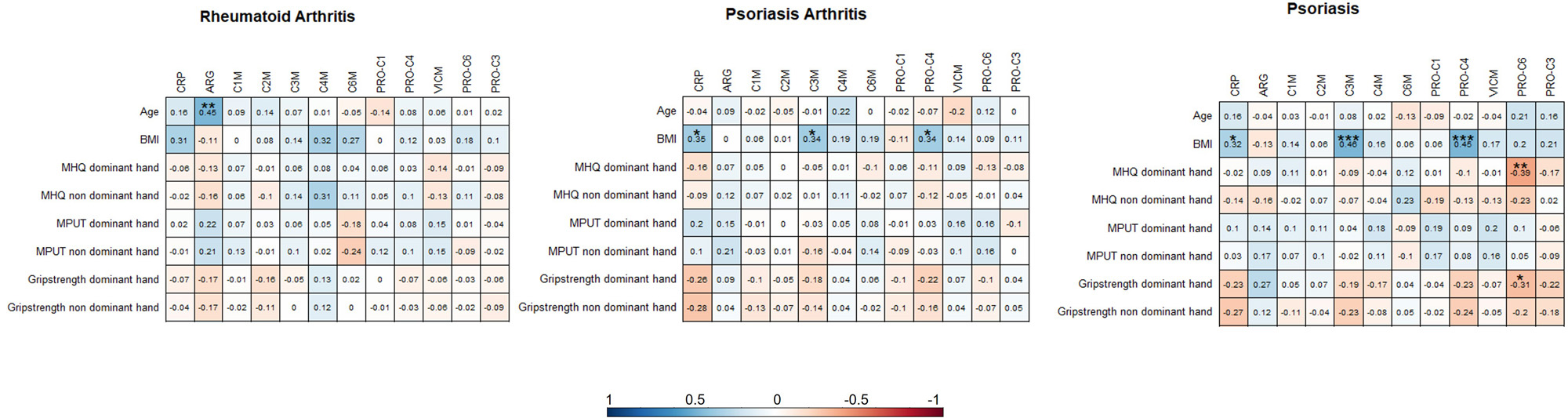
Results: 85 patients with RA, 115 with PsA, 102 with PsO and 110 controls (mean age, years: 58.4, 53.7, 45.8, 46.6; % male: 35.3, 49.6, 60.8, 45.0, respectively) were included. VICM levels were significantly higher in RA, PsA, and PsO than in controls (Figure 1, p< 0.0001). PsA and PsO showed significantly higher C4M levels compared to RA and controls, while C6M was lower in patients with RA and PsA than in controls (Figure 1, p< 0.001). C1M presented higher levels in PsO compared to controls, and together with C3M higher levels than RA (Figure 1, p< 0.004). The remaining biomarkers did not show any significant differences. Weak correlations were observed between the biomarkers and the hand function scores (all ρ<±0.2-0.3, Figure 2), while only PRO-C6 showed a significant negative correlation with MHQ (ρ=-0.39, p< 0.01) and grip strength (ρ=-0.31, p< 0.05) in patients with PsO.
Conclusion: Patients with RA, PsA, and PsO showed significant alterations in ECM remodeling biomarkers and specially PsA and PsO had higher levels of inflammatory biomarkers compared to RA and controls. Furthermore, predominantly in PsO, ECM formation biomarkers were associated with hand function impairment.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Port I Linares H, Coppers B, Bayat S, Elie-Tino G, Valor-Mendez L, Simon D, Fagni F, Corte G, Bay-Jensen A, Tascilar K, Hueber A, Schoenau V, Sticherling M, Heinrich S, Bohr D, Schett G, Kleyer A, Leyendecker S, Holm Nielsen S, Liphardt A. Blood-Based Biomarkers of Inflammation and Tissue Remodeling Can Discriminate Between Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriasis, and Psoriatic Arthritis and Are Associated with Hand Function [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/blood-based-biomarkers-of-inflammation-and-tissue-remodeling-can-discriminate-between-rheumatoid-arthritis-psoriasis-and-psoriatic-arthritis-and-are-associated-with-hand-function/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/blood-based-biomarkers-of-inflammation-and-tissue-remodeling-can-discriminate-between-rheumatoid-arthritis-psoriasis-and-psoriatic-arthritis-and-are-associated-with-hand-function/