Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Innate immune activation plays a key role in granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA), contributing to vascular inflammation via neutrophil extracellular traps, immune complexation (IC), and endothelial injury. Its role in response to rituximab (RTX) remains unclear. We aimed to evaluate changes in innate immune markers before and after RTX and assess their ability to predict remission and treatment response.
Methods: Ten plasma biomarkers reflecting neutrophil and platelet activation, endothelial injury, and IC were measured pre- and 6–12 months post-RTX. Skewed biomarkers were log-transformed or dichotomized. Changes over time were assessed using linear or generalized linear mixed-effects models. Confounders were selected systematically using iterative linear regression models, excluding aliased and collinear variables. Non-response was defined as < 50% BVAS/WG reduction without new symptoms; non-remission as BVAS/WG > 0. Wilcoxon and Fisher’s tests compared trajectories by outcome. ROC curves and Youden index thresholds were used to evaluate predictive performance. Combined biomarker scores we constructed to predict non-response/non-remission and calculated individual biomarker thresholds based on ROC-derived Youden index from pre-treatment samples. These thresholds were applied to generate a simple score (0–4), summing the number of positive biomarkers within those that significantly changed post-RTX. Areas under the curve (AUC) were calculated for each cutoff (score 0–4). A weighted score was derived from logistic regression, and DeLong’s test was used to compare performance.
Results: Forty GPA patients were included (median age 53 [interquartile range 38–65], 58% female, 90% White). Thirty-four (85%) were PR3-ANCA+, 3 (7.5%) MPO-ANCA+ and 3 (7.5%) missing. Pre-RTX median BVAS/WG was 3.0, dropping to 0.0 post-RTX. Ten patients (25%) did not reach remission; 9 (23%) failed to respond.Citrullinated histone H3-DNA complexes (CitH3-DNA), IC, and neutrophil elastase–DNA complexes (NE-DNA) levels decreased significantly post-RTX; vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM) increased (Figure 1). Baseline biomarkers individually did not differentiate outcomes. However, a combined score of 4 positive biomarkers according to the thresholds and direction specified in Figure 2 best identified non-responders across definitions: AUC ranged from 0.767 to 0.651. For lack of remission, score 4 had: sensitivity = 0.93, specificity = 0.60, positive predictive value (PPV) = 0.88, negative predictive value (NPV) = 0.75; for lack of response: sensitivity = 0.97, specificity = 0.33, PPV = 0.83, NPV = 0.75. Weighted scores did not significantly outperform the simple score.
Conclusion: A combined score of 4 innate immune biomarkers—CitH3-DNA, VCAM, IC, and NE-DNA—identifies patients who fail to achieve remission or response after RTX treatment. The simple additive score performed consistently across outcome definitions and was not improved by weighting. While promising for stratifying non-responders prior to B-cell–depleting therapy, this score requires external validation before clinical application.
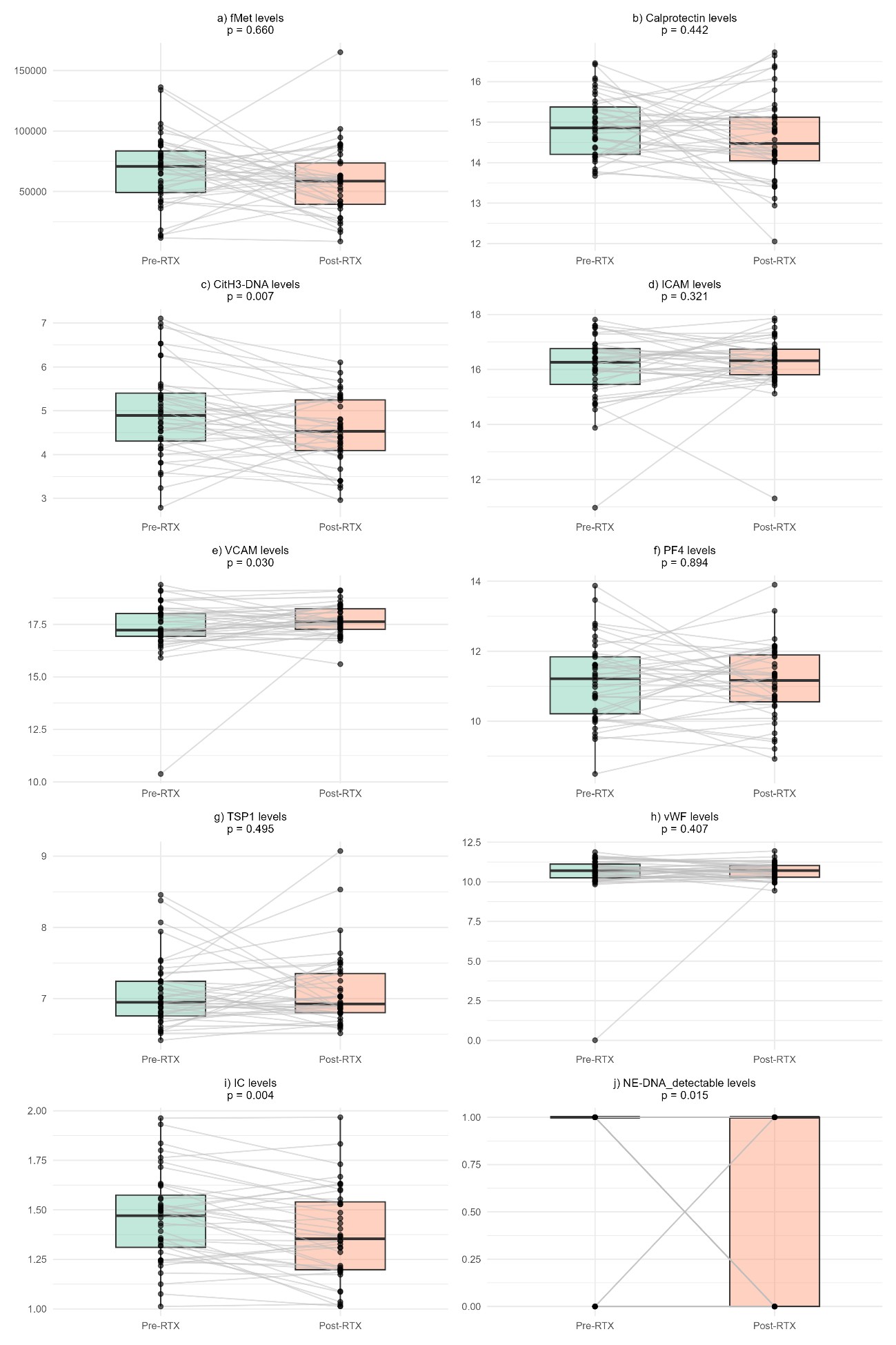 Figure 1: Comparison of the biomarker’s levels pre- and post-RTX. fMet: N-Formylmethionine; CitH3-DNA: Citrullinated histone H3-DNA complex; ICAM: Intercellular adhesion molecule 1; VCAM: Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1); PF4: Platelet factor 4 complement; TSP1: Thrombospondin 1, vWF: Von Willebrand factor; IC: Immune complexation; NE-DNA: Neutrophil Elastase-DNA Complexes.
Figure 1: Comparison of the biomarker’s levels pre- and post-RTX. fMet: N-Formylmethionine; CitH3-DNA: Citrullinated histone H3-DNA complex; ICAM: Intercellular adhesion molecule 1; VCAM: Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1); PF4: Platelet factor 4 complement; TSP1: Thrombospondin 1, vWF: Von Willebrand factor; IC: Immune complexation; NE-DNA: Neutrophil Elastase-DNA Complexes.
.jpg) Figure 2: Receiving operating characteristics (ROC) curves and areas under the curve (AUC) of no remission (a), no response (b). Scores 1 to 4 refers to the number of biomarkers that are positive according to the thresholds and their direction specified in the figure. Numbers next to the biomarkers inside the square indicate logarithmic value (raw value, percentile). CitH3-DNA: Citrullinated histone H3-DNA complex; VCAM: Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1); IC: Immune complexation; NE-DNA: Neutrophil Elastase-DNA Complexes.
Figure 2: Receiving operating characteristics (ROC) curves and areas under the curve (AUC) of no remission (a), no response (b). Scores 1 to 4 refers to the number of biomarkers that are positive according to the thresholds and their direction specified in the figure. Numbers next to the biomarkers inside the square indicate logarithmic value (raw value, percentile). CitH3-DNA: Citrullinated histone H3-DNA complex; VCAM: Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1); IC: Immune complexation; NE-DNA: Neutrophil Elastase-DNA Complexes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Carrión-Barberà I, Gonzalez-Chapa J, Cuthbertson D, Khalidi N, Koening C, Langford C, McAlear C, Monach P, Moreland L, Pagnoux C, Seo P, Specks U, Warrington K, Merkel P, Lood C. Biomarkers of Innate Immune Activation to Identify Non-Response to Rituximab in Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/biomarkers-of-innate-immune-activation-to-identify-non-response-to-rituximab-in-granulomatosis-with-polyangiitis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/biomarkers-of-innate-immune-activation-to-identify-non-response-to-rituximab-in-granulomatosis-with-polyangiitis/
