Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: RA – Treatments Poster II: PROs, Biomarkers, & Systemic Inflammation (1223–1256)
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: In patients with active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) refractory to biologic DMARDs (bDMARD-IR), a phase 3, double-blind and active-controlled study (SELECT-CHOICE) demonstrated that upadacitinib (UPA) 15 mg QD was superior to abatacept (ABA) IV in driving change from baseline in DAS28-CRP and achievement of clinical remission at week 12.1 The objective of this analysis was to compare the effects of UPA versus ABA on inflammatory biomarkers in bDMARD-IR RA patients, and to assess the dynamic relationship of such biomarkers with disease activity.
Methods: A subset of patients was randomly selected from the SELECT-CHOICE study cohort that consented sample collection for exploratory research (UPA: n = 99; ABA: n = 100). Plasma biomarker levels were assessed at baseline, week 2 and week 12 using the Olink Explore 384 Inflammation panel. Change from baseline was expressed as log2 fold change (log2FC). A Repeated Measure Mixed Linear Model identified biomarkers differentially modulated from baseline. Statistical tests were corrected for multiple comparison using the Benjamini – Hochberg False Discovery Rate (FDR) method. Downstream biological effects were predicted with Ingenuity Pathway Analysis. Responders in this analysis were defined by achieving DAS28-CRP Low Disease Activity (≤3.2) at week 12.
Results: Overall, 58 out of 368 biomarkers assessed were significantly modulated by UPA or ABA at week 12 (Table 1). Compared to ABA, treatment with UPA resulted in faster and broader modulation of inflammatory mediators implicated in RA pathogenesis in bDMARD-IR RA patients. Predictive analysis of downstream biological processes showed overlapped inhibitory effects by UPA and ABA on lymphocytes, myeloid cells, antigen presenting cells, and phagocyte activities, indicating a functional convergence of UPA and ABA mechanisms of action (MOA). IL-6, CCL7, CSF1 and HSD11B1 were identified as DAS28-CRP-related biomarkers in this analysis. The levels of IL-6, CCL7, CSF1, and HSD11B1 significantly correlated with DAS28-CRP at the baseline, and the changes in these biomarkers significantly correlated with changes in DAS28-CRP at week 12. UPA had significantly greater modulation effects on IL-6, CCL7, CSF1 and HSD11B1 compared to ABA; these were more profound in responders than in non-responders.
Conclusion: The results of inflammatory biomarker modulation by UPA and ABA treatment demonstrates their MOA in bDMARD-IR RA patients, consistent with previous findings.2,3 The more profound modulation of DAS28-CRP-related biomarkers by UPA may provide a mechanistic rationale for the superior efficacy of UPA compared to ABA, which warrants further investigation.
References
- Rubbert-Roth A, et al. N Engl J Med 2020;383:1511-21.
- Sornasse T, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2019;71(Suppl 10).
- Weisman MH, et al. J Rheumatol 2006; 33(11):2162-6.
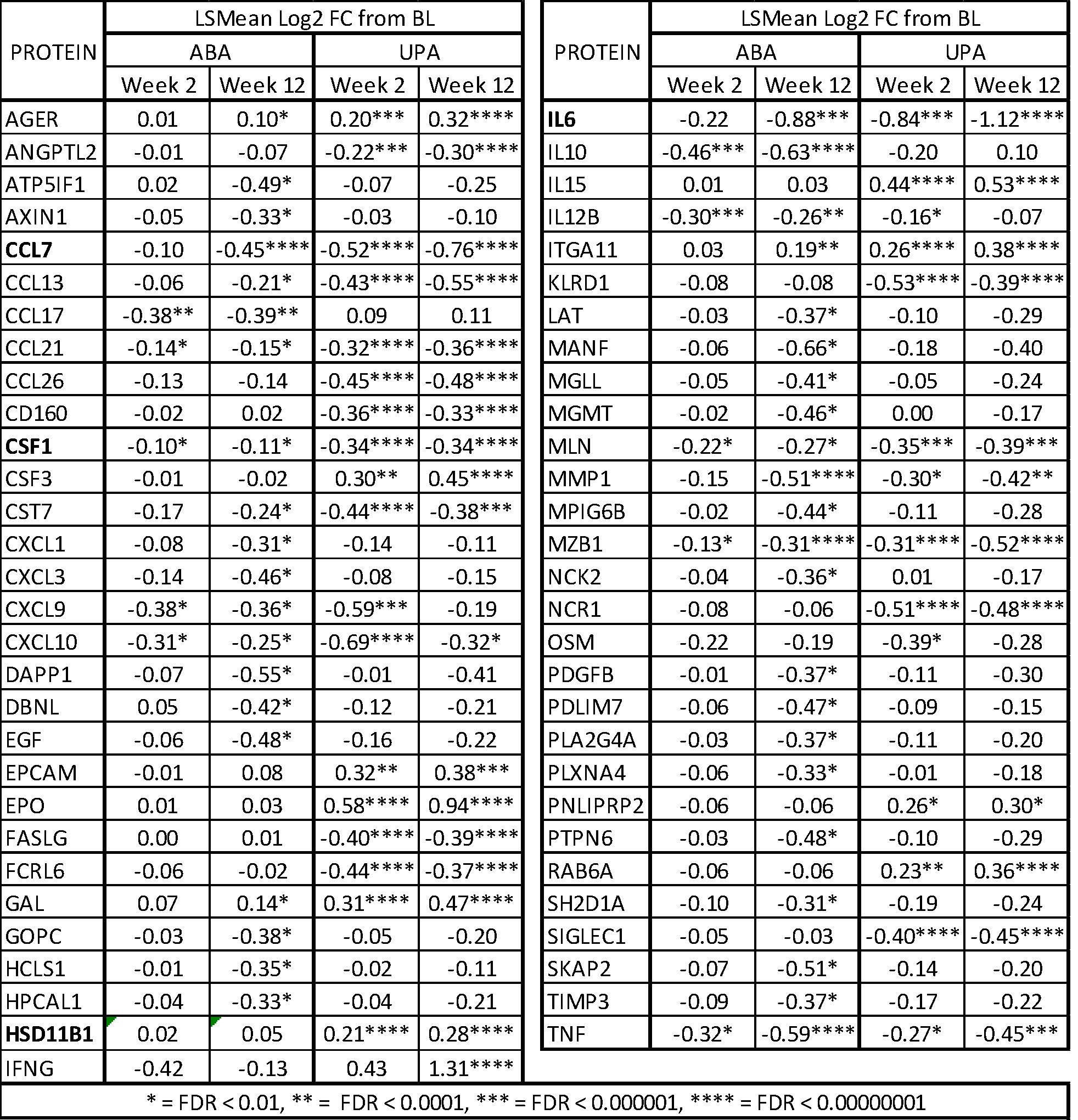 Table 1: Significantly modulated biomarkers by UPA or ABA in the bDMARD-IR RA patients
Table 1: Significantly modulated biomarkers by UPA or ABA in the bDMARD-IR RA patients
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cai F, Sornasse T, Hong F, Camp H, Kato K, McInnes I. Biomarker Driven Dissection of Inflammation Modulatory Effects of Upadacitinib versus Abatacept in Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis Refractory to Biologic DMARDs [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/biomarker-driven-dissection-of-inflammation-modulatory-effects-of-upadacitinib-versus-abatacept-in-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-refractory-to-biologic-dmards/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/biomarker-driven-dissection-of-inflammation-modulatory-effects-of-upadacitinib-versus-abatacept-in-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-refractory-to-biologic-dmards/
