Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Neurosarcoidosis (NS) is a severe complication of sarcoidosis. NS may be classified according to several subtypes. Data on therapy, including biological therapy (BT) is scarce. The purpose of the study is to assess efficacy and safety of BT in refractory NS subtypes.
Methods: Study of NS from a large cohort (n=234) of all consecutive patients diagnosed with sarcoidosis in a single university hospital from January 1, 1999 to December 31, 2019. Diagnosis of sarcoidosis was established according to ATS/ERS/WASOG criteria.
Efficacy was considered as complete or partial response and no-response according to the resolution of the neurological syndrome (signs and/or symptoms) after the BT onset.
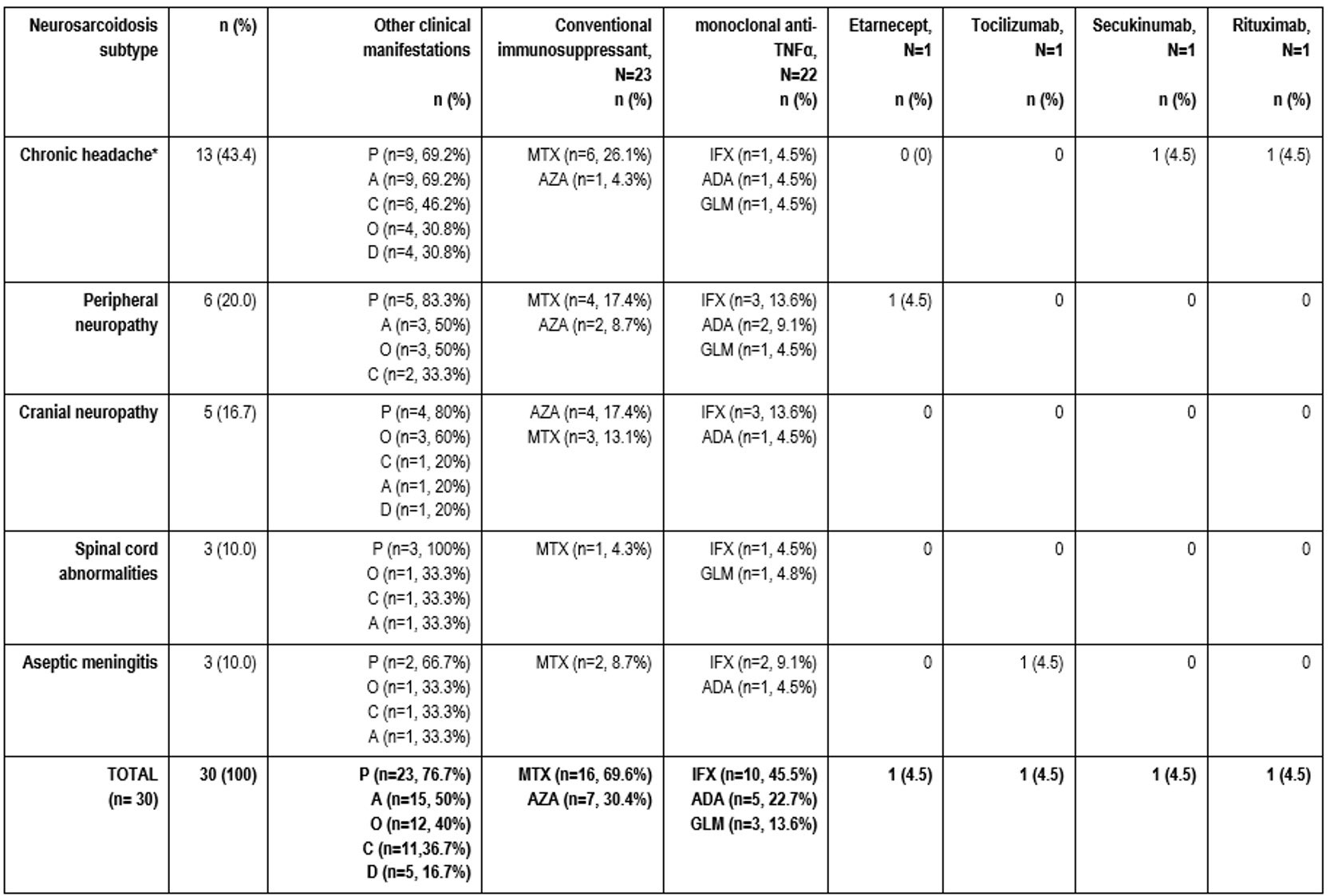
Results: NS was observed in 30 (19 women/11 men) of 234 (12.8%) patients; mean age, 55.0±15.8 years. NS subtypes were chronic headache (n=13, 43.4%), peripheral neuropathy (n=6, 20%), cranial neuropathy (n=5, 16.7%), spinal cord abnormalities (n=3, 10%) and aseptic meningitis (n=3, 10%). A total of 26 (86.7%) patients received oral corticosteroids (CT) (mean maximum dose: 50±19.2 mg/dL) and 7 (23.3%) IV CT. In addition, conventional immunosuppressants were administered to 18 (60%) patients and BT to 12 (40%) patients. No treatment was administered to 4 (13.3%) patients. TABLE shows treatment according to NS subtypes.
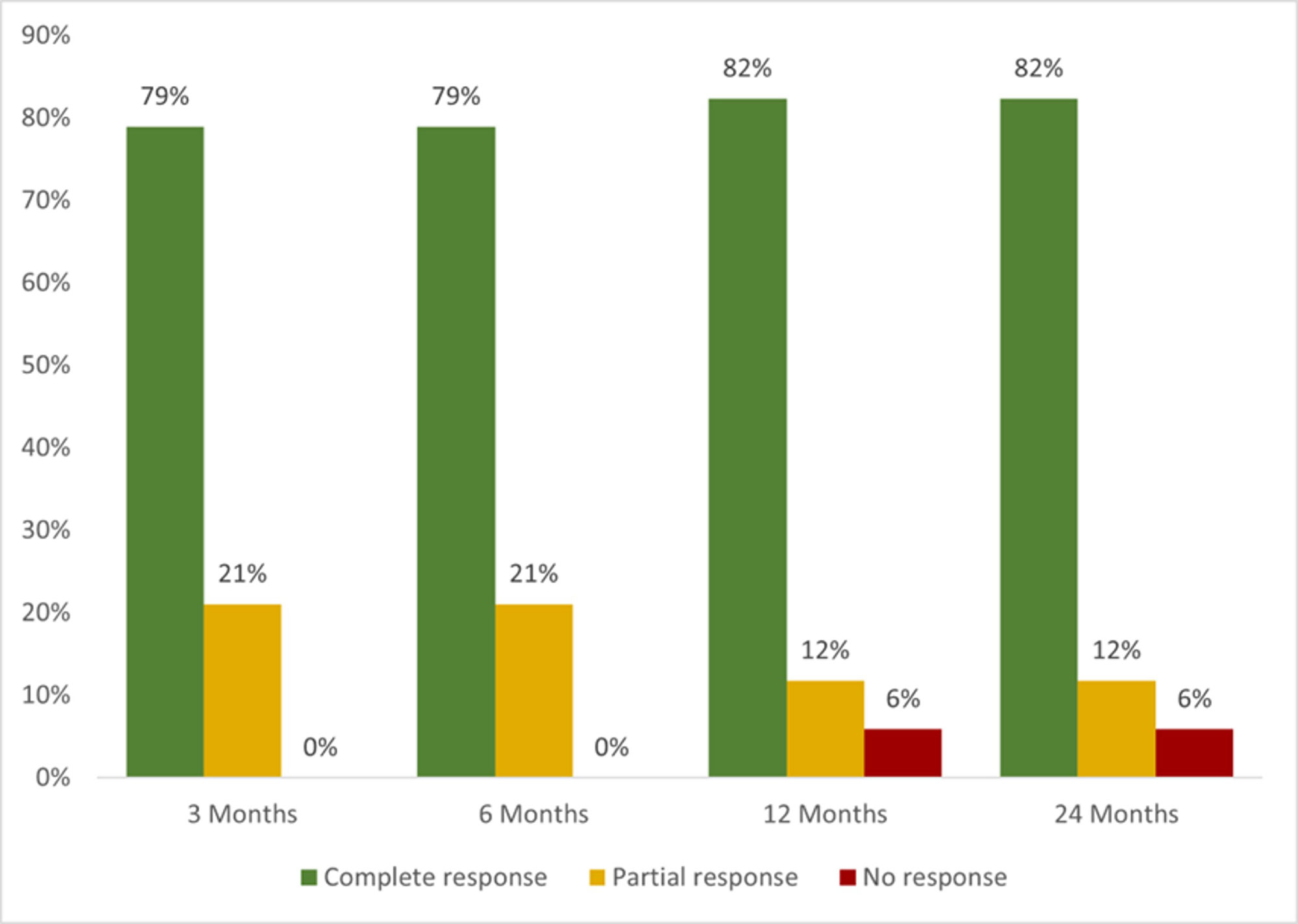
A total of 12 patients received treatment with 22 BT. Most used BT were monoclonal anti-TNFα (n=18, 81.8%), infliximab (IFX) (n= 10, 45.5%) and adalimumab (ADA) (n=5, 22.7%). After 12 months since the initiation of BT, complete, partial or no response was observed in 14 of 17 (82.4%), 2 (11.8%) and 1 patient (5.9%), respectively (FIGURE). Severe allergic reaction was observed in one patient on both IFX and ADA. No more severe adverse events were observed.
Conclusion: BT, especially monoclonal anti-TNFα, seems to be effective and safe in NS, regardless of subtype.
Abbreviations: A: Articular, ADA: Adalimumab, AZA: Azathioprine, C: Cutaneous, D: Digestive, GLM: Golimumab, IFX: Infliximab, MTX: Methotrexate, O: Ocular, P: Pulmonar
*With MRI, CSF, and/or EMG/NCS findings typical of granulomatous inflammation of the nervous system after rigorous exclusion of other causes and not meeting criteria for other neurosarcoidosis subtypes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Herrero-Morant A, Martínez-López D, Sánchez-Bilbao L, Gonzalez-Mazon i, Martín-Varillas J, fernández-ramón R, Alvarez Reguera C, González-Gay M, Blanco R. Biological Therapy in Neurosarcoidosis: Study of 30 Patients from a Series of 234 Systemic Sarcoidosis from a University Hospital [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/biological-therapy-in-neurosarcoidosis-study-of-30-patients-from-a-series-of-234-systemic-sarcoidosis-from-a-university-hospital/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/biological-therapy-in-neurosarcoidosis-study-of-30-patients-from-a-series-of-234-systemic-sarcoidosis-from-a-university-hospital/