Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0510–0542) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment: AxSpA Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In patients (pts) with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA), tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi) are the usual first line biologic treatment, yet many pts may experience loss of response over time, and some are intolerant to TNFis.1 Typically, response to second line biologics is limited in TNFi-inadequate responders (IR).
Bimekizumab (BKZ) is a monoclonal IgG1 antibody that selectively inhibits IL-17F in addition to IL‑17A. In the phase 3 BE MOBILE 1 and 2 studies, BKZ treatment resulted in rapid and sustained improvements in efficacy outcomes through 52 weeks (wks) in pts with active non‑radiographic (nr-)axSpA and radiographic (r‑)axSpA (i.e., AS).2,3 In studies of BKZ in psoriatic arthritis, similar efficacy between TNFi-naïve and TNFi-IR pts were observed.4 Here, we report the efficacy of BKZ in TNFi-naïve or -IR pts with active nr-axSpA and r‑axSpA through Wk 52 across multiple key endpoints.
Methods: In BE MOBILE 1 (nr-axSpA; NCT03928704) pts met Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society (ASAS) classification criteria and in BE MOBILE 2 (r-axSpA; NCT03928743) pts fulfilled modified New York and ASAS criteria. Pts were randomized to receive subcutaneous BKZ 160 mg every 4 wks (Q4W) or placebo (PBO) then BKZ 160 mg Q4W from Wk 16. This post hoc analysis reports pooled mean efficacy data, including disease activity, MRI inflammation, physical function, and quality of life (QoL), through Wk 52 of BE MOBILE 1 and 2, stratified by TNFi status (naïve/IR). TNFi-IR pts are defined as those who experienced loss of efficacy, contraindication or intolerance to prior TNFi treatment.
Results: This pooled analysis included 505 TNFi-naïve and 81 TNFi-IR pts. 302/505 (59.8%) TNFi-naïve and 47/81 (58.0%) TNFi-IR pts were randomized to BKZ.
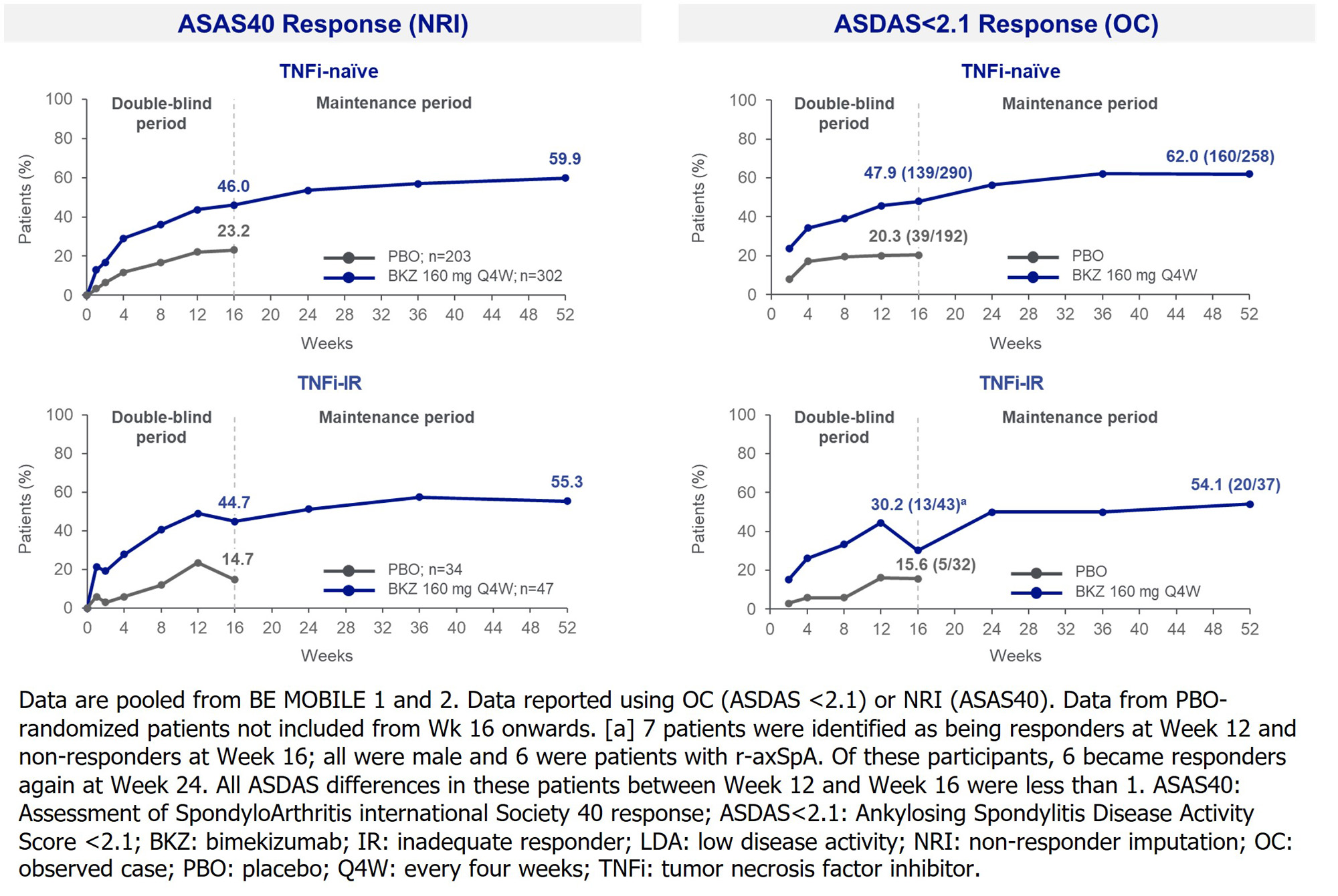
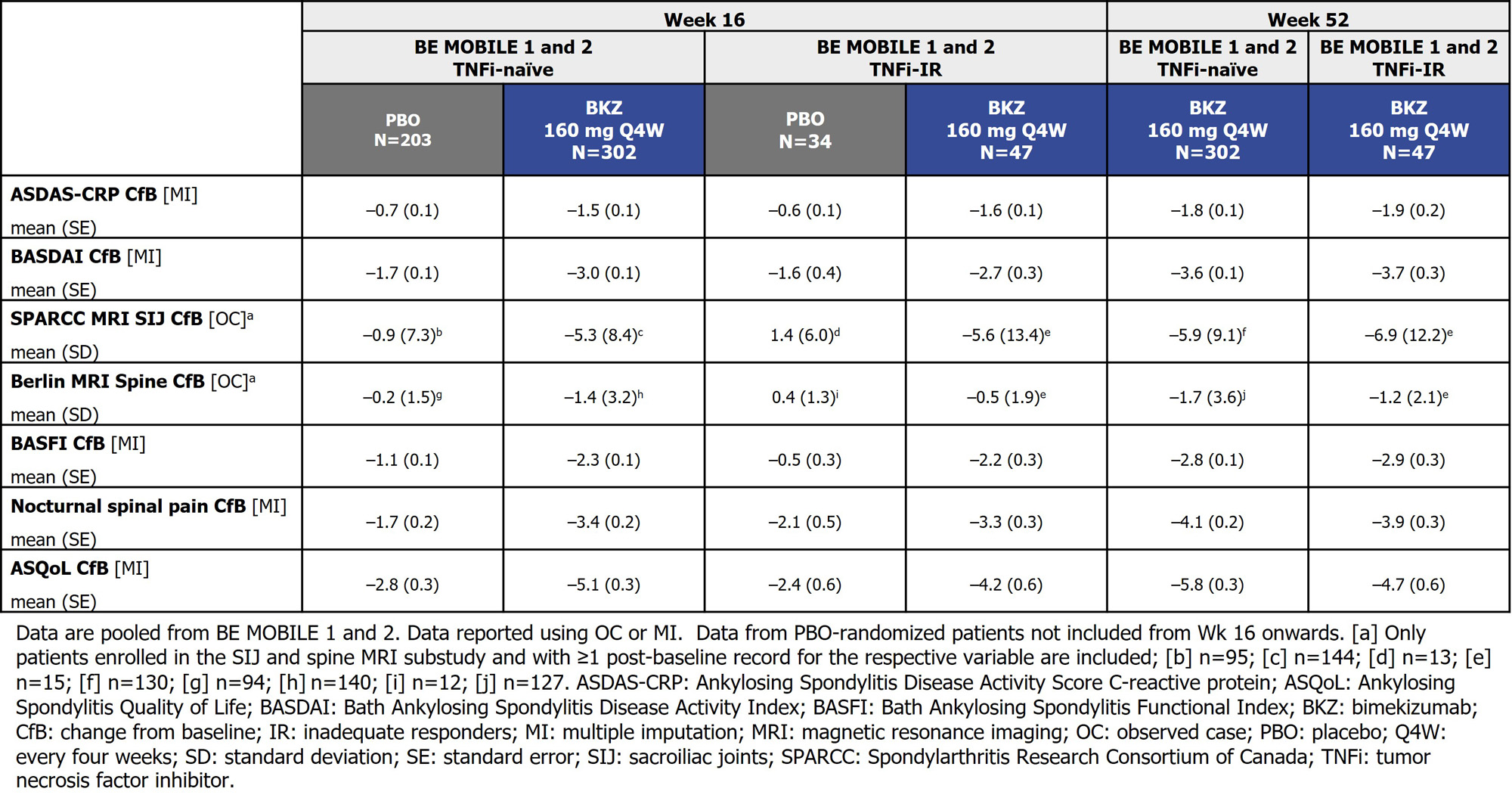
At Wk 16, the proportion of pts achieving ASAS40 and AS Disease Activity Score (ASDAS)< 2.1 (low disease activity) were higher in BKZ-randomized TNFi‑naïve/-IR pts vs PBO. In both TNFi-naïve/-IR continuous BKZ‑treated pts, responses were similar and increased to Wk 52 (Figure). Similar substantial reductions from baseline in ASDAS-CRP and MRI inflammation by Wk 16 were also achieved with BKZ vs PBO in both TNFi-naïve and IR pts; in continuous BKZ-treated pts this was sustained or further improved through 52 wks. Comparable improvements in physical function, nocturnal spinal pain and ASQoL were observed through 52 wks with BKZ in TNFi‑naïve/-IR pts(Table).
Conclusion: Across the full disease spectrum of axSpA, BKZ treatment resulted in clinically relevant improvements in key efficacy outcomes vs PBO, including suppression of inflammation and improvements in physical function and QoL, regardless of prior TNFi exposure. The improvements with BKZ at Wk 16 were sustained to Wk 52. References:1. Noureldin B. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2018;57(suppl 6); 2. Boel A. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78:1545–9; 3.Baraliakos X. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022;74 (suppl 9); 4. Mease P. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022;74 (suppl 9).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Magrey M, van de Sande M, Breban M, Van den Bosch F, Fleurinck C, Massow U, De Peyrecave N, Vaux T, Baraliakos X, Marzo-Ortega H. Bimekizumab Achieved Sustained Improvements in Efficacy Outcomes in Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis, Regardless of Prior TNF Inhibitor Treatment: Week 52 Pooled Results from Two Phase 3 Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bimekizumab-achieved-sustained-improvements-in-efficacy-outcomes-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-regardless-of-prior-tnf-inhibitor-treatment-week-52-pooled-results-from-two-phase-3-studies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bimekizumab-achieved-sustained-improvements-in-efficacy-outcomes-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-regardless-of-prior-tnf-inhibitor-treatment-week-52-pooled-results-from-two-phase-3-studies/