Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2022
Title: SLE – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: The results from the BEAT-lupus trial comparing belimumab vs placebo, both after rituximab in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) have recently been reported (1). We sought to identify biomarkers of response to belimumab after rituximab to aid a personalised approach to therapy.
Methods: Conventional and machine learning methodologies were adopted to analyse the immune profile (relevant serum autoantibodies and cytokines, peripheral blood RNA expression, B cell flow cytometry) of the 52 patients recruited to the BEAT-lupus trial to identify biomarkers of major clinical response (MCR, defined as reduction to BILAG C in all domains, steroid dose of ≤7.5mg/day & SLEDAI≤2, without anti-dsDNA antibody component) at 52 weeks and investigate the dynamics of B-cell repopulation.
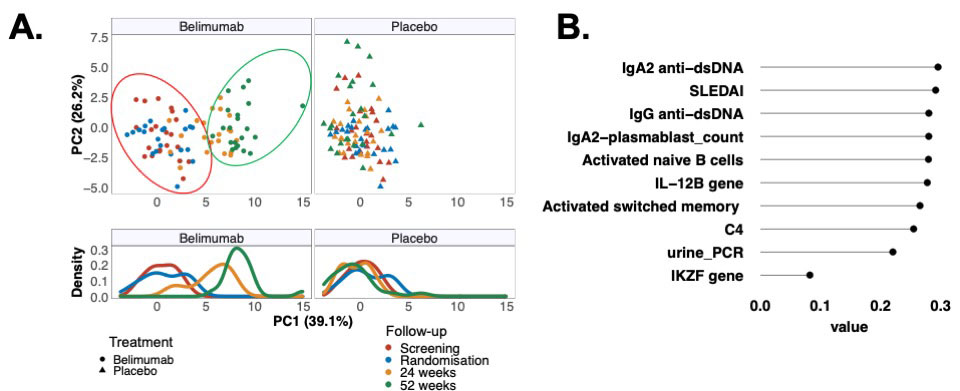
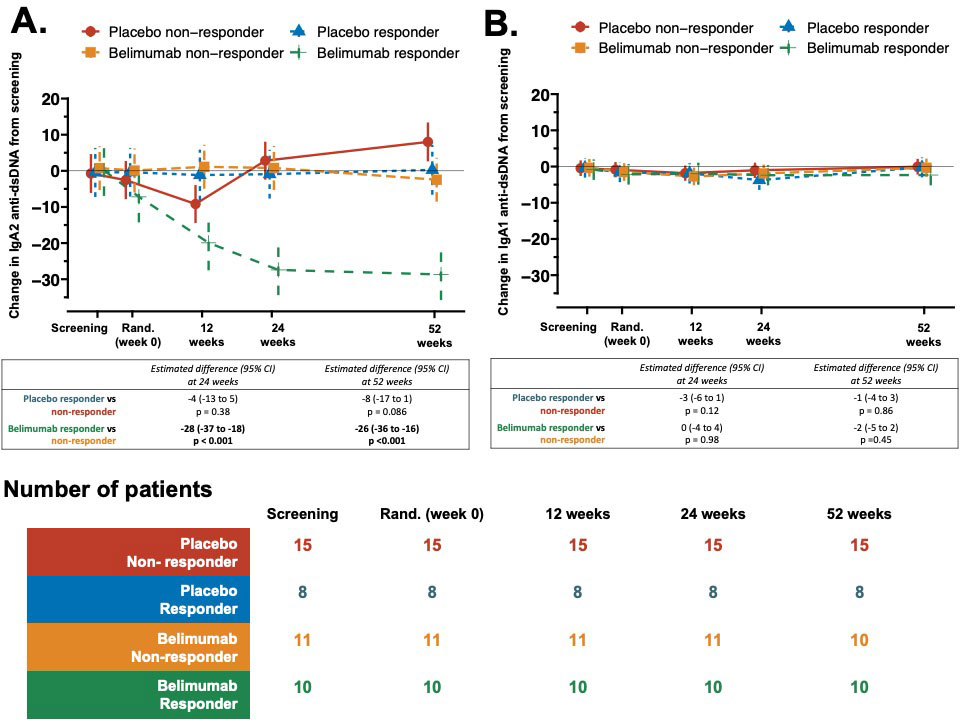
Results: Baseline serum IgA2 anti-dsDNA antibody levels emerged as the only positive predictor of attaining a MCR at 52 weeks in belimumab treated patients (AUROC 0.8, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.7-1.0), but negatively predicted a MCR in the placebo arm (AUROC 0.2, 95%CI 0.1-0.4). The difference in achieving a MCR between belimumab and placebo was 48% (95%CI 10% to 70% – in favor of belimumab) in patients with elevated serum IgA2 anti-dsDNA antibody levels compared to 13% (95%CI -15% to 38%) overall. Patients with a high baseline serum IL-6 were less likely to achieve an MCR irrespective of therapy (OR 0.4, CI 0.2-0.9, p=0.033).Principal component analysis identified serum IgA2 anti-dsDNA antibody levels as the top-ranked contributor to longitudinal variance in the immune profiles of patients treated with belimumab, whereas there was minimal longitudinal variance in the immune profiles of placebo treated patients (Figure 1A-B). Serum IgA2, but not IgA1, anti-dsDNA antibody levels decreased only in those patients treated with belimumab, but not placebo, who achieved an MCR, falling by 78% from baseline (Figure 2A-B) Although IgG anti-dsDNA antibody levels were reduced following belimumab therapy there was no association with MCR. The number of circulating IgA2 (but not IgA1 or IgG) plasmablasts were significantly reduced at 52 weeks following belimumab therapy compared to placebo (p=0.032). Activated naïve, activated switched memory and double-negative memory B cell numbers were lower (p< 0.001, 0.032, 0.021 respectively) at 52-weeks in belimumab treated patients compared to placebo. In contrast, belimumab increased the number of unswitched memory B cells (p=0.045) and anergic naïve B cells (p=0.046) compared to placebo at 52 weeks.
Conclusion: Belimumab after rituximab targets IgA2 anti-dsDNA antibody production and favours formation of anergic/resting B cells while reducing potentially pathogenic B-cell subsets. These results not only indicate how belimumab acts to restore healthy B-cell immunologic homeostasis after rituximab therapy in SLE but also targets a specific autoantibody subclass that could act as an easily assayed predictive biomarker of clinical response to belimumab after rituximab combination therapy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Shipa M, santos l, Nguyen D, Embleton-Thirsk A, parvaz M, Isenberg D, Gordon C, Ehrenstein M. Belimumab After Rituximab Targets IgA2 Anti-dsDNA Antibody Production and Shifts Repopulating B-cells Towards an Anergic, Non-pathogenic Phenotype in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/belimumab-after-rituximab-targets-iga2-anti-dsdna-antibody-production-and-shifts-repopulating-b-cells-towards-an-anergic-non-pathogenic-phenotype-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/belimumab-after-rituximab-targets-iga2-anti-dsdna-antibody-production-and-shifts-repopulating-b-cells-towards-an-anergic-non-pathogenic-phenotype-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/