Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Abatacept, a CTLA-4-Ig fusion protein, is widely used as a treatment for rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, data on predictive biomarkers associated with therapeutic response to abatacept is still limited. We conducted this study to identify novel biomarkers to predict the therapeutic efficacy of abatacept in patients with moderate to severe RA.
Methods: A total of 23 RA patients, who had an inadequate response to methotrexate and other conventional DMARDs, were enrolled in this study. Responders (n=10) to abatacept were defined as subjects who achieved ACR50 response at week 24. At baseline, week 6, week 14, and week 24, serum levels of soluble CD25, CD27, CD40L, CD80, CXCL10, CXCL13, IL-21, and PD-1 were measured with ProcartaPlex by Luminex, while serum levels of soluble CD83, CD163, and rheumatoid factor (RF) IgM were determined by ELISA. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated and analyzed for changes in different T cell and B cell subsets by flow cytometry at baseline, week 14, and week 24. Patients were also genotyped for human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DRB1 shared epitope (SE) alleles and classified as SE2 (≥ 2 SE allele, n=8), SE1 (≥ 1 SE allele, n=19) and SE0 (no SE alleles, n=4).
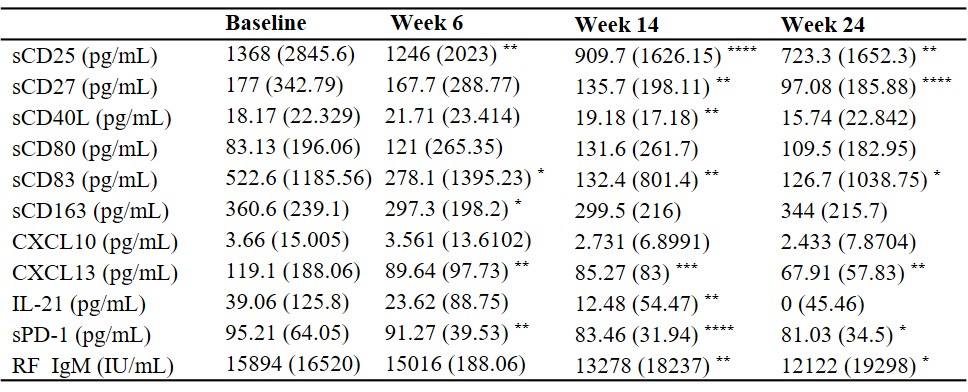
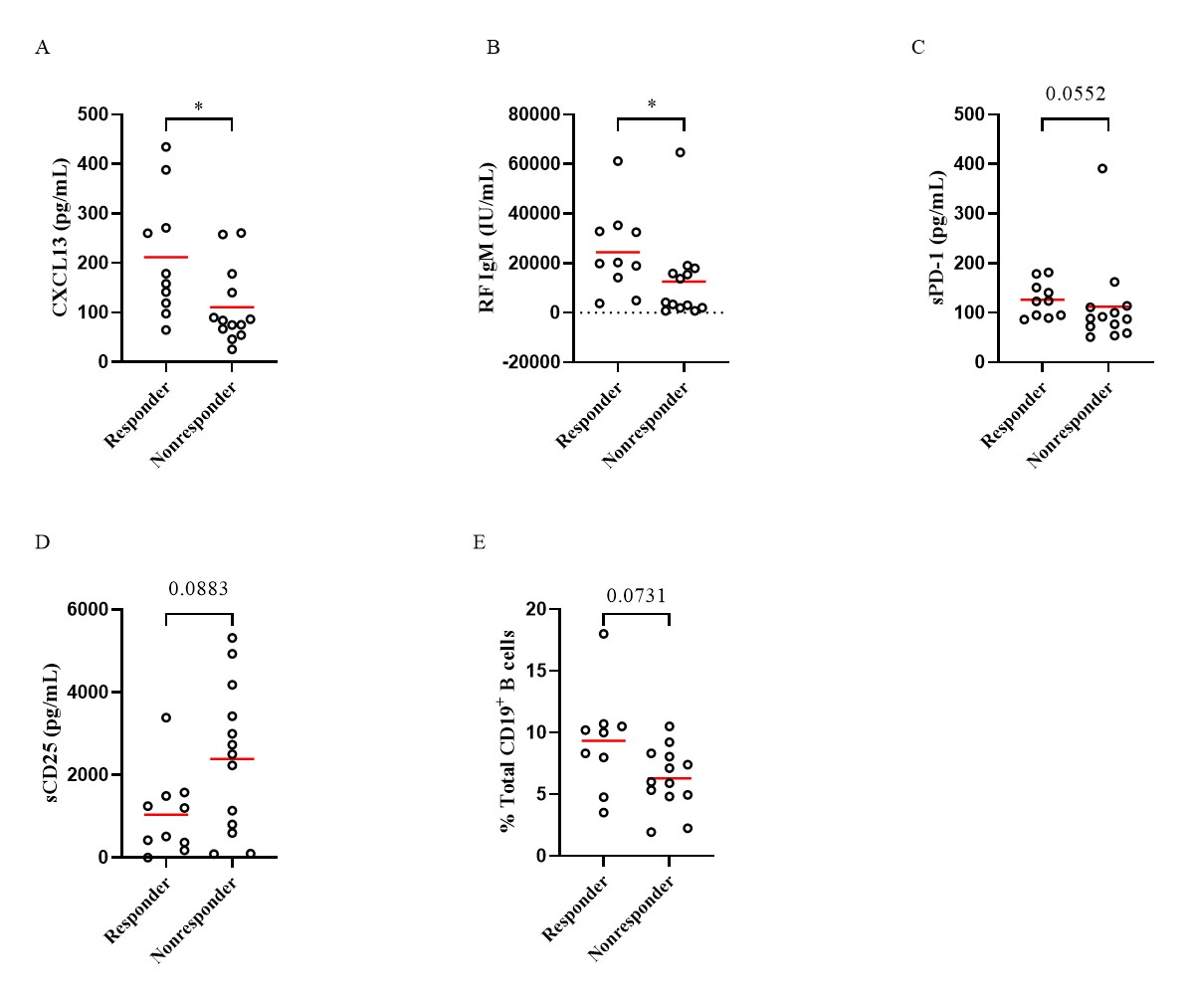
Results: Levels of sCD25, sCD27, sCD83, CXCL13, sPD-1 and RF IgM were significantly decreased at week 14 and week 24 with the treatment of abatacept when compared to baseline, while IL-21 levels were only decreased at week 14 (Table 1). Subjects treated with abatacept had a significant decline in the frequencies of circulating CD4+CXCR5+PD-1hi follicular helper T (Tfh) cells (p=0.0008 and p=0.0001 respectively) and CD4+CXCR5-PD-1hi peripheral helper T (Tph) cells (p=0.0004 and p< 0.0001 respectively) at week 14 and week 24. There was also a significant reduction in other T cell subsets, including CD4+CD25+CD127- regulatory T (Treg) cells, CD4+CD45RA-CCR7+ central memory T cells, and CD4+CD45RA-CCR7- effector memory T cells. Abatacept also reduced the frequencies of circulating CD19+IgD-CD27+ class-switched memory (SM) B cells (p=0.0239 and p=0.0237, respectively), CD19+CD27hiCD38hi plasmablasts/plasma (PL) B cells (p=0.0249 and p=0.0108, respectively) and CD19+CD11c+ B cells (p< 0.0001 and p=0.012, respectively) at week 14 and week 24. Compared to non-responders, baseline levels of CXCL13 (p=0.0178), RF IgM (p=0.0147), sPD-1 (p=0.0552), and the percentages of CD19+CD11c+ B cells (p=0.0731) were higher in the responders, while levels of sCD25 (p=0.0883) tended to be lower in the responders (Figure 1). Responders had a significantly higher percentage of patients with SE2 than non-responders (60% vs 15.38%, p=0.0393). Baseline serum CXCL13 levels were correlated with circulating Tph (r=0.5425, p=0.0075), Treg cells (r=0.4665, p=0.0248), CD19+CD11c+ B cells (r=0.4609, p=0.0309) and RF IgM levels (r=0.6108, p=0.0012).
Conclusion: These findings suggest that baseline CXCL13, RF IgM, sPD-1, CD19+CD11c+ B cell percentages, and HLA-DRB1 shared epitope alleles may be useful markers in predicting response to abatacept in moderate to severe RA patients.
Data are displayed as median (interquartile range). Differences between baseline and post-treatment (week 6, week 14, and week 24) were determined by the Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test. ****p<0.0001, ***p<0.001, **p<0.01 and *p<0.05.
Comparisons of serum levels of CXCL13 (A), RF IgM (B), sPD_1(C), sCD25 (D), and percentages of CD19+CD11c+ B cells (E) in circulation at baseline in patients treated with abatacept. Differences between groups were determined by the Mann-Whitney test. *p<0.05.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wang T, Giltiay N, Lood C, Han B. Baseline T Cell and B Cell-related Markers and HLA-DRB1 Shared Epitope Alleles Predict the Therapeutic Efficacy of Abatacept in Patients with Moderate to Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/baseline-t-cell-and-b-cell-related-markers-and-hla-drb1-shared-epitope-alleles-predict-the-therapeutic-efficacy-of-abatacept-in-patients-with-moderate-to-severe-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/baseline-t-cell-and-b-cell-related-markers-and-hla-drb1-shared-epitope-alleles-predict-the-therapeutic-efficacy-of-abatacept-in-patients-with-moderate-to-severe-rheumatoid-arthritis/