Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:45PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in combination with robotics into clinical diagnostics has the potential to increase precision and efficiency and relieve increasingly scarce staff. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), hand osteoarthritis (HOA), and psoriatic arthritis (PsoA) are common or relevant causes of hand complaints and impending functional limitations. The aim of the pilot phase is to introduce and test the safety, reliability, and acceptance of the hand examination using the ultrasound robot ARTHUR and the AI DIANA (both ROPCA Denmark) in an university outpatient clinic.
Methods: ARTHUR and DIANA offer automated scanning and evaluation of the wrists, all MCP, IP/PiP, and the DiP joints for synovial thickening, increased perfusion, and osteophytes based on the OMERACT guidelines. CANON aplio a ultrasound scanner with an 18L7 UHF ultra-wide linear probe was used. Procedures, reasons for discontinuation, and satisfaction were recorded in a standardized manner.
Results: Within the first 12 weeks of use, 10,000 joints in 500 patients were examined (200 patients with RA, 100 PsoA, 50 HOA, 150 with other conditions). 5 examinations were discontinued without data transfer. 16 examinations were transferred but not read; all other examinations were completed successfully. No discontinuations for safety reasons were necessary. The average time for examiation of both hands took 20 minutes. Patient satisfaction was high: 92% reported being “very satisfied,” 8% described themselves as “satisfied,” and one patient rated the experience as “undecided.” No one expressed dissatisfaction. The willingness to participate in a follow-up examination was 99.7%. Five patients reported mild pain during the examination but would still undergo the procedure again.The figure shows the ARTHUR diagnostic unit on the left, a DIANA report on the top, and the corresponding image documentation below (red bone, blue synovium, green tendon in the example of an MCP joint, and Doppler of an IP joint).In 91% of joints examined by ARTHUR documentation and recognizability of the joint structures was good or very. Difficulties were encountered with pronounced deformities or extension deficits. In the AI-supported interpretation of the stored images, DIANA shows a fair detection and differentiation of synovitis, with a relevant error rate of < 5%, but the detection of osteophytes is still unsatisfactory.
Conclusion: The implementation of a new AI-supported technology is associated with administrative hurdles and requirements. Technically, the robot demonstrates good performance, including robust image acquisition for synovitis and effusion. The joint-related correction rate for gross deviations exceeding at least 2 score points for synovitis by the experienced rheumatologist was below 5%. Currently, parallel evaluation and approval by experienced examiners is still necessary. Further training of the evaluation AI promises to further increase reliability and thus significantly improve the patient experience. Patient acceptance of the examination was very high.
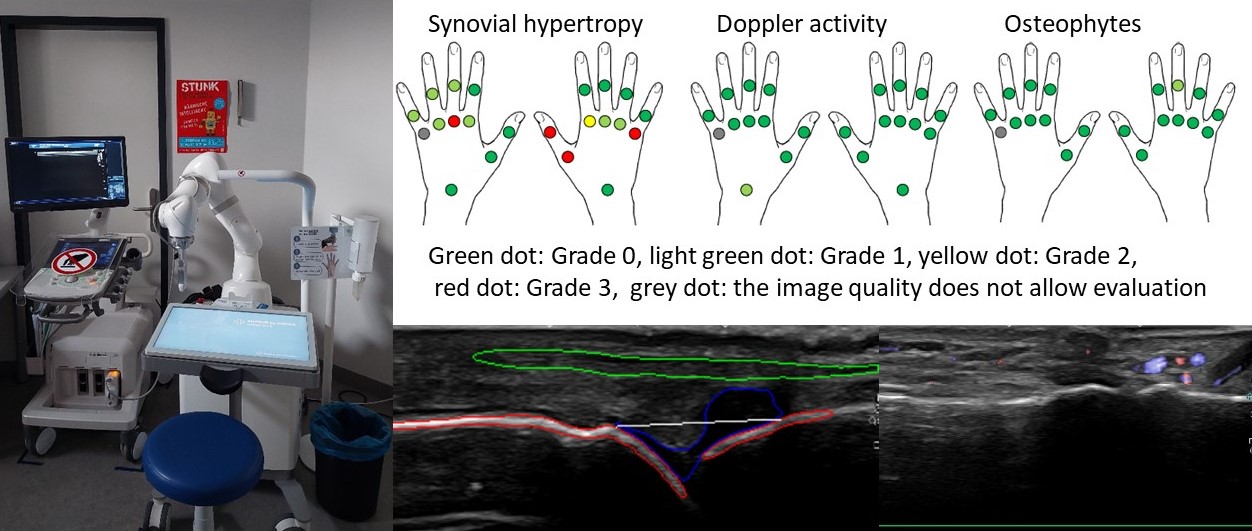 ARTHUR diagnostic unit and DIANA report
ARTHUR diagnostic unit and DIANA report
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sander O, Ormeloh L, Grünkewitz L, Gallmann M, Blümel B, Adhikari R, Acar H, Chehab G, Distler J, Richter J. Automated, Artificial Intelligence-supported Sonographic Examination of the Hands for the Detection and Quantification of Arthritis and Osteoarthritis in the Hand and Finger Joints in Outpatient Rheumatology Care [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/automated-artificial-intelligence-supported-sonographic-examination-of-the-hands-for-the-detection-and-quantification-of-arthritis-and-osteoarthritis-in-the-hand-and-finger-joints-in-outpatient/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/automated-artificial-intelligence-supported-sonographic-examination-of-the-hands-for-the-detection-and-quantification-of-arthritis-and-osteoarthritis-in-the-hand-and-finger-joints-in-outpatient/
