Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: B Cell Biology & Targets in Autoimmune & Inflammatory Disease Poster
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Myositis autoantibodies are important clinical biomarkers however, around 40% of patients with juvenile myositis (JM) are classified as ‘autoantibody negative’ (1) and therefore cannot benefit from autoantibody associated prognostic information and a more personalised treatment approach. This study aims to address the seronegative gap and help those currently classified as antibody negative by identifying unknown JM autoantibodies.
Methods: 53 JM patients recruited to NIH myositis natural history studies previously classified as myositis-specific autoantibody negative by immunoprecipitation (IP)-Blot were analysed by radio-IP. Samples with clear unknown bands on radio-IP were selected for autoantigen identification by liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS). MS results were confirmed using immunoblotting. HEp-2 IIF performed as per manufacturer’s instruction (Werfen, 708100).
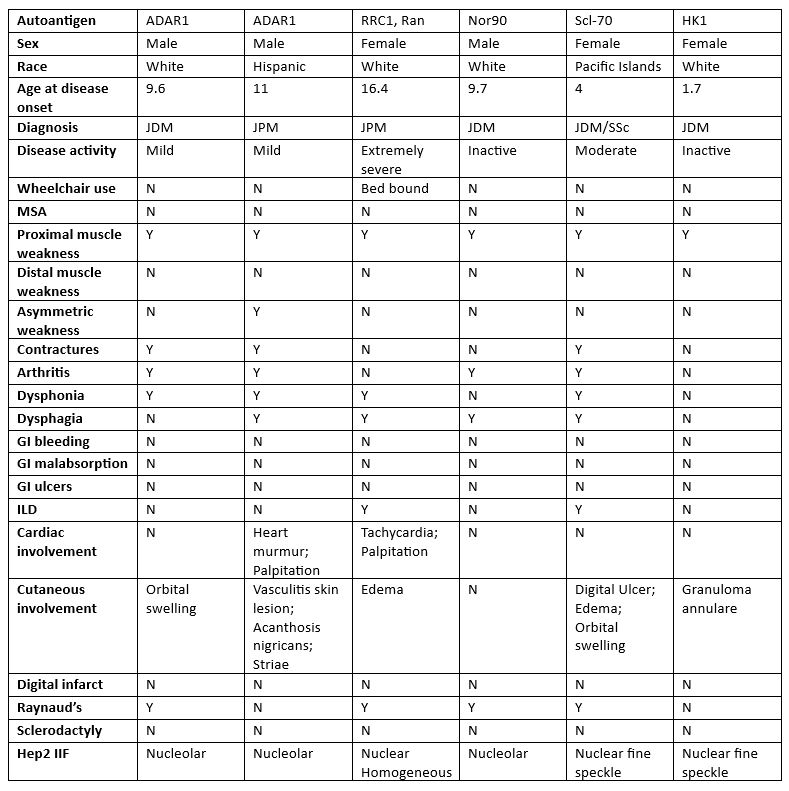
Results: 35/53 samples had unknown bands on IP. Two patients had unknown bands at 110 and 150 kDa, LC-MS identified this protein as adenosine deaminase acting on RNA-1 (ADAR1). 25 and 50 kDa unknown bands identified in one patient were characterised as two interacting antigens GTP-binding nuclear protein Ran (RAN) and regulator of chromosome condensation 1 (RCC1). Unknown bands in three additional patients were identified as Nor90, Scl-70 and Hexokinase 1 (HK1) by LC-MS, the anti-Scl-70 positive patient had JDM overlap with systemic sclerosis (SSc). Clinical features are described in Table 1.
Results were confirmed by commercial line blot (Nor90, Scl-70) and western blot (ADAR1, RCC1, HK1). ANA patterns correlated with previously described pattern or antigen subcellular localisation.
Conclusion: We have identified autoantibodies targeting RNA editing enzyme ADAR1 and RCC1 for the first time in JM . Anti-ADAR1 has previously been identified in two adults with DM and SLE (2), Anti-RCC1 had been identified in one adult with SSc (3), and anti-HK1 has been implicated in primary biliary cholangitis. Both Scl-70 and Nor90 are SSc associated autoantibodies detectable in routine practice but not included in myositis panels. Further testing of seronegative JM patients can identify rare autoantibodies and those associated with overlapping connective tissue diseases. Understanding the prevalence and clinical associations of these autoantibodies will improve our understanding of JM as a disease and facilitate a personalised treatment approach.
1. Tansley SL, Simou S, Shaddick G, Betteridge ZE, Almeida B, Gunawardena H, et al. Autoantibodies in juvenile-onset myositis: Their diagnostic value and associated clinical phenotype in a large UK cohort. J Autoimmun. 2017;84:55-64.
2. Muro Y, Ogawa-Momohara M, Takeichi T, Fukaya S, Yasuoka H, Kono M, et al. Clinical and serological features of dermatomyositis and systemic lupus erythematosus patients with autoantibodies to ADAR1. Journal of Dermatological Science. 2020;100(1):82-4.
3. Vulsteke J-B, Smith V, Bonroy C, Derua R, Blockmans D, De Haes P, et al. Identification of new telomere- and telomerase-associated autoantigens in systemic sclerosis. Journal of Autoimmunity. 2023;135:102988.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
MCMORROW F, Rider L, McHugh N, Tansley S. Autoantibodies Identified in Myositis-Specific Autoantibody Negative Juvenile Myositis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/autoantibodies-identified-in-myositis-specific-autoantibody-negative-juvenile-myositis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/autoantibodies-identified-in-myositis-specific-autoantibody-negative-juvenile-myositis-patients/