Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Genetic studies in various systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases (SARDs) support that human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class II alleles are associated with specific autoimmune disorders and clinical phenotypes. The purpose of this study was to investigate the associations of HLA class II with interstitial lung disease (ILD) across different SARDs.
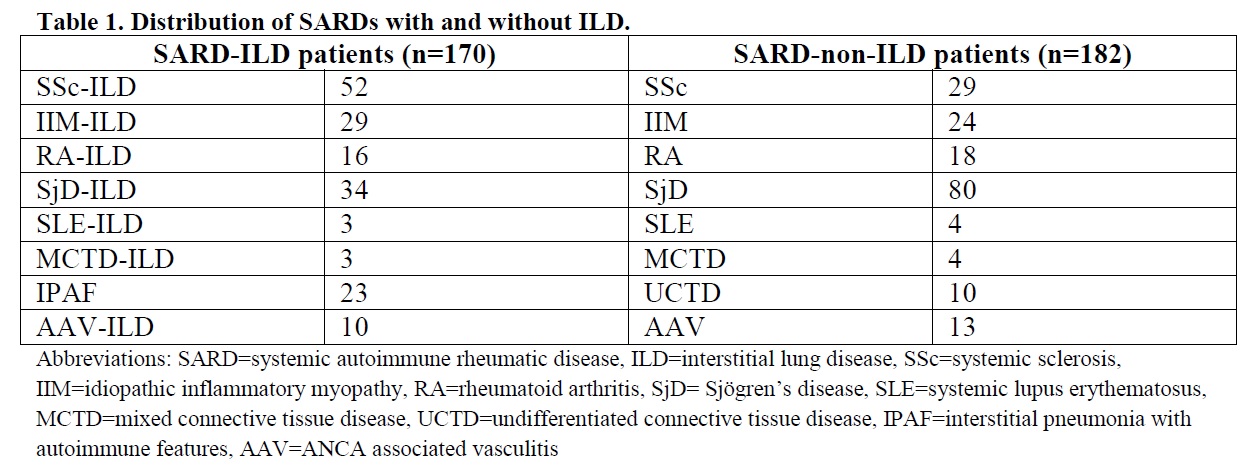
Methods: In the current study, HLA-class II genotypic and clinical data were collected from 3 groups: a) 170 SARD-ILD patients, followed up from June 2020 to January 2024 in the Department of Pathophysiology (Table 1). The presence of ILD was determined by high resolution computed tomography, evaluated blindly by a specialized radiologist, b) 182 SARD-non-ILD, defined by the absence of respiratory symptoms (dyspnea, cough) and the presence of either normal HRCT or pulmonary function tests (spirometry, measurement of diffusion capacity) and c) 105 healthy controls (HC) of the same ethnicity whose genotypic data served as the genetic background of the general population. Genotyping was performed with the sequence-based typing method. Statistical analyses were performed to identify alleles associated with ILD independently of the background disease as well as per disease and per selected autoantibodies.
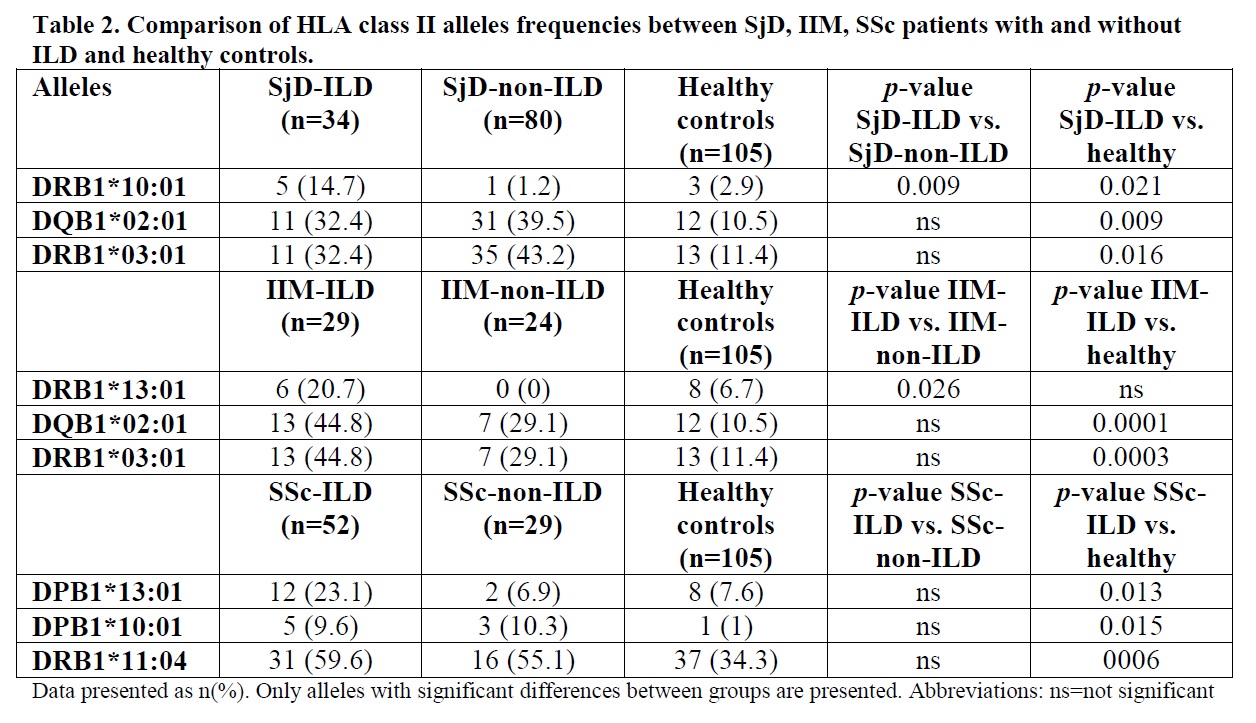
Results: The distribution of patients who participated in the study is presented in Table 1. Analyses per disease were focused to Sjogren’s Disease (SjD), idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) and scleroderma (SSc) patients. Overall, 74 HLA class II alleles were identified among the total cohort of SARDs patients (Table 2). HLA-DPB1*13:01 and HLA-DRB1*13:02 were more commonly observed in SARD-ILD compared to SARD-non-ILD patients (10% vs. 3.8%, p=0.038 and 8.2% vs. 1.6%, p=0.005 respectively), displaying also higher frequencies compared to HC (10% vs. 7.6%, p=0.652 and 8.2% vs. 5.7%, p=0.078 respectively). DQB1*06:02 and DRB1*15:01 were less frequent in anti-Ro52(+) SARD-ILD compared to anti-Ro52(+) SARD-non-ILD patients (0% vs. 13.2%, p=0.014 and 6.4% vs. 20.8%, p=0.046 respectively). In addition, DQB1*06:02 and DRB1*15:01 were less prevalent in anti-Ro60(+) SARD-ILD compared to anti-Ro60(+) SARD-non-ILD patients (0% vs. 18%, p=0.023 and 3.3% vs. 26%, p=0.013 respectively). DRB1*10:01 was highly encountered in SjD-ILD patients (n=34) compared to other SARD-ILD (14.7% vs. 2.2%, p=0.009), SjD-non-ILD (n=80) (14.7% vs. 1.2%, p=0.009) and HC (14.7% vs. 2.9%, p=0.021). Furthermore, DRB1*13:01 was more prevalent in IIM-ILD (n=29) patients as compared to other SARD-ILD (n=141) (20.7% vs. 3.5%, p=0.004), IIM-non-ILD (n=24) (20.7% vs. 0%, p=0.026) and HC (20.7% vs. 6.7%, p=0.097). Finally, DPB1*13:01 exhibited higher frequency in SSc-ILD (n=52) patients as opposed to other SARD-ILD (n=118) (23.1% vs. 4.2%, p=0.004), SSc-non-ILD (n=29) (23.1% vs. 6.9%, p=0.074) and HC (23.1% vs. 7.6%, p=0.013).
Conclusion: Certain HLA-class II associations seem to define ILD of autoimmune origin. The HLA-DPB1*13:01 and HLA-DRB1*13:02 alleles are associated with ILD independently of the underlying autoimmune disease and DRB1*10:01, DRB1*13:01 and DPB1*13:01 with ILD related to SjD, IIM and SSc respectively.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Panagopoulos P, chatzis L, Kitsiou V, Tarassi K, Chatzinikita E, Malagari K, Vassilakopoulos T, Tsirogianni A, Goules A, Tzioufas A. Associations of Human Leukocyte Antigens (HLA) Class II with Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD) in Patients with Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases (SARDs). A Prospective Study in Sequential Patients with SARD-ILD [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/associations-of-human-leukocyte-antigens-hla-class-ii-with-interstitial-lung-disease-ild-in-patients-with-systemic-autoimmune-rheumatic-diseases-sards-a-prospective-study-in-sequential-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/associations-of-human-leukocyte-antigens-hla-class-ii-with-interstitial-lung-disease-ild-in-patients-with-systemic-autoimmune-rheumatic-diseases-sards-a-prospective-study-in-sequential-patients/